
Planets orbiting stars more massive than the Sun
... In order to prove that this star has a substellar companion, we have shown that it is not an FP, and that the companion is not a low-mass star. As shown by Almenara et al. (2009) most of the binaries and FPs can already be identified with a very detailed analysis of the light-curve. After this had b ...
... In order to prove that this star has a substellar companion, we have shown that it is not an FP, and that the companion is not a low-mass star. As shown by Almenara et al. (2009) most of the binaries and FPs can already be identified with a very detailed analysis of the light-curve. After this had b ...
ppt
... bias subtraction. The flat field is an observation of a white lamp. For imaging one must take either sky flats, or dome flats (an illuminated white screen or dome observed with the telescope). For spectral observations „internal“ lamps (i.e. ones that illuminate the spectrograph, but not observed th ...
... bias subtraction. The flat field is an observation of a white lamp. For imaging one must take either sky flats, or dome flats (an illuminated white screen or dome observed with the telescope). For spectral observations „internal“ lamps (i.e. ones that illuminate the spectrograph, but not observed th ...
Chapter 16--Properties of Stars
... to stars is with stellar parallax, the small annual shifts in a star’s apparent position caused by Earth’s motion around the Sun [Section 2.6]. Recall that you can observe parallax of your finger by holding it at arm’s length and looking at it alternately with first one eye closed and then the other ...
... to stars is with stellar parallax, the small annual shifts in a star’s apparent position caused by Earth’s motion around the Sun [Section 2.6]. Recall that you can observe parallax of your finger by holding it at arm’s length and looking at it alternately with first one eye closed and then the other ...
15-3 Notes: Galaxies
... of sizes and shapes. The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Astronomers classify a galaxy as a spiral, elliptical, or irregular galaxy according to its shape. Spiral galaxies, such as the Andromeda galaxy, have a bulge at the center and spiral arms. The spiral arms are made up of g ...
... of sizes and shapes. The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Astronomers classify a galaxy as a spiral, elliptical, or irregular galaxy according to its shape. Spiral galaxies, such as the Andromeda galaxy, have a bulge at the center and spiral arms. The spiral arms are made up of g ...
Deep SDSS optical spectroscopy of distant halo stars I. Atmospheric
... site2 ), enhanced with damping constants from Barklem (2007 and references therein) when available. We calculated a grid of model spectra covering −5 <[Fe/H]< +0.5 and 0.5 < log g < 4.5 in steps of 0.5 dex, and 4750 < T eff < 6500 K, in steps of 250 K. The α/Fe ratio adopted was solar at [Fe/H]= 0, ...
... site2 ), enhanced with damping constants from Barklem (2007 and references therein) when available. We calculated a grid of model spectra covering −5 <[Fe/H]< +0.5 and 0.5 < log g < 4.5 in steps of 0.5 dex, and 4750 < T eff < 6500 K, in steps of 250 K. The α/Fe ratio adopted was solar at [Fe/H]= 0, ...
Calculate the Mass of the Milky Way Galaxy
... Few of the points fall exactly on the line. This is because all galaxies have some additional residual motion in addition to the pure expansion. This is referred to as the "cosmic velocity dispersion" or "cosmic scatter" and is probably due to the fact that the gas clouds that formed the galaxies al ...
... Few of the points fall exactly on the line. This is because all galaxies have some additional residual motion in addition to the pure expansion. This is referred to as the "cosmic velocity dispersion" or "cosmic scatter" and is probably due to the fact that the gas clouds that formed the galaxies al ...
Distance to VY Canis Majoris with VERA
... in the literature. These new effective temperature values seem to be consistent with the theoretical stellar evolutionary tracks. However, the luminosities of the red supergiants still had large uncertainty due to possible errors in the estimated distances. Since most red supergiants are very far, i ...
... in the literature. These new effective temperature values seem to be consistent with the theoretical stellar evolutionary tracks. However, the luminosities of the red supergiants still had large uncertainty due to possible errors in the estimated distances. Since most red supergiants are very far, i ...
The Evolution of Stars - a More Detailed Picture (Chapter 8
... massive stars form first and explode into supernova. This makes shock waves into the molecular cloud, causing nearby gas to compress and form more stars. This allows a type of stellar coherence (young stars are found near other young stars) to build up, and is responsible for the pinwheel patterns w ...
... massive stars form first and explode into supernova. This makes shock waves into the molecular cloud, causing nearby gas to compress and form more stars. This allows a type of stellar coherence (young stars are found near other young stars) to build up, and is responsible for the pinwheel patterns w ...
23.1 Telescopes - Ms. Billings Website
... is located in a naturally occurring sinkhole that formed when water flowing underground dissolved the limestone rock. If this telescope were not supported by the ground, it would collapse under its own weight. Since the telescope is set into the ground it cannot be aimed to different parts of the sk ...
... is located in a naturally occurring sinkhole that formed when water flowing underground dissolved the limestone rock. If this telescope were not supported by the ground, it would collapse under its own weight. Since the telescope is set into the ground it cannot be aimed to different parts of the sk ...
2. The Anatomy of Stellar Life and Death
... Over the last 4.5 billion years the Sun has grown hotter and slightly larger, and is now more luminous in response to this effect; the same is true for more massive stars. As the fuel is consumed the luminosity slowly increases. The effect is quite subtle in comparison to later changes, but over the ...
... Over the last 4.5 billion years the Sun has grown hotter and slightly larger, and is now more luminous in response to this effect; the same is true for more massive stars. As the fuel is consumed the luminosity slowly increases. The effect is quite subtle in comparison to later changes, but over the ...
103-122
... the abundance derived from ESO's CASPEC and even omit the 'CASPEC’ abundances from several plots. The lines of Mg I, Si I, and Ca I are extremely weak and the available spectra are too noisy to permit reliable measurements. The problems are not inherent to the CCD-equipped CASPEC because several inv ...
... the abundance derived from ESO's CASPEC and even omit the 'CASPEC’ abundances from several plots. The lines of Mg I, Si I, and Ca I are extremely weak and the available spectra are too noisy to permit reliable measurements. The problems are not inherent to the CCD-equipped CASPEC because several inv ...
Powerpoint - Physics and Astronomy
... As stars evolve during their main-sequence lifetime a) they gradually become cooler and dimmer (spectral type O to type M). b) they gradually become hotter and brighter (spectral type M to type O). c) they don’t change their spectral type. Explanation: A star’s main-sequence characteristics of surfa ...
... As stars evolve during their main-sequence lifetime a) they gradually become cooler and dimmer (spectral type O to type M). b) they gradually become hotter and brighter (spectral type M to type O). c) they don’t change their spectral type. Explanation: A star’s main-sequence characteristics of surfa ...
Observing Galaxies - Denver Astronomical Society
... thousandth of a magnitude to as much as 20 magnitudes. It’s interesting that certain galaxies, too, can change in brightness. But unlike variable stars, which are observed from relatively close distances, galaxies are observed as far out as our instrumentation will allow, over 15 billion light years ...
... thousandth of a magnitude to as much as 20 magnitudes. It’s interesting that certain galaxies, too, can change in brightness. But unlike variable stars, which are observed from relatively close distances, galaxies are observed as far out as our instrumentation will allow, over 15 billion light years ...
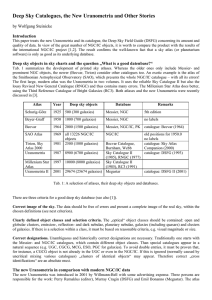
Deep Sky Catalogues, the New Uranometria and Other Stories
... Prior to the publication of the new Uranometria, Murray Cragin reported on the U.S. mailing list „amastro“ about the quality of the database (DSFG) and the involved experts. As some of my project colleagues are mentioned, I was first convinced that our work hab been taken into account. However, I wa ...
... Prior to the publication of the new Uranometria, Murray Cragin reported on the U.S. mailing list „amastro“ about the quality of the database (DSFG) and the involved experts. As some of my project colleagues are mentioned, I was first convinced that our work hab been taken into account. However, I wa ...
Some Examples of Virtual Observatory Enabled Science What Are the Some Distinguishing
... • In order to study QSOs (and other AGN), we first have to find them, in large numbers, and hopefully in a systematic fashion – This is especially important for studies of their evolution ...
... • In order to study QSOs (and other AGN), we first have to find them, in large numbers, and hopefully in a systematic fashion – This is especially important for studies of their evolution ...
X-ray binaries
... Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classifiction is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a source is unidentified in optics, but exhibits T ...
... Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an accretion disc around a compact object. Clear classifiction is based on optical data or on mass function derived from X-ray observations. If a source is unidentified in optics, but exhibits T ...
Stellar Structure and Evolution II
... stars of different mass that were born about the same time ...
... stars of different mass that were born about the same time ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.





















![Module 4.1 - The Scale of the Universe [slide 1] We now turn to](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002846843_1-9e0ec9d1a2abbbab3c0d406694bfc4e2-300x300.png)
