Life Histories Of Some Stars
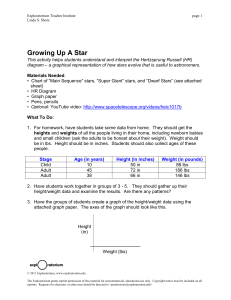
... all? Describe the shape of the graph? Is it a straight line? A curve? 5. Give each group the list of stars attached and the HR diagram attached. Instead of height and weight, the information is in Luminosity (compared to sun) and Surface Temperature (in K). The chart also gives the star’s current st ...
... all? Describe the shape of the graph? Is it a straight line? A curve? 5. Give each group the list of stars attached and the HR diagram attached. Instead of height and weight, the information is in Luminosity (compared to sun) and Surface Temperature (in K). The chart also gives the star’s current st ...
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision
... • Necessary to determine the complete 3D velocity of an object • “Easy” to measure for stars close to the Sun • Very small and difficult to measure for distant objects • Never measured for Andromeda (tried since 1898) • Now finally measured with Hubble Space Telescope ...
... • Necessary to determine the complete 3D velocity of an object • “Easy” to measure for stars close to the Sun • Very small and difficult to measure for distant objects • Never measured for Andromeda (tried since 1898) • Now finally measured with Hubble Space Telescope ...
Physics of Star Formation: Milky Way and Beyond
... winds, super novae, and multi-band radiation transport and pressure. As our understanding of stellar feedback is tied to interpreting observations, we also present OPIATE, an Optimal Post-processing Iterative Approach to Emissivities, a general purpose, publicly available code and data base for live ...
... winds, super novae, and multi-band radiation transport and pressure. As our understanding of stellar feedback is tied to interpreting observations, we also present OPIATE, an Optimal Post-processing Iterative Approach to Emissivities, a general purpose, publicly available code and data base for live ...
March 15 Newsletter
... accumulate a lethal dose within seconds. It produces a noticeable heating effect. Light years away, the pulsar at the nebula’s core is a stroboscope. Its light comes in bursts, a brilliant flash and then a fainter one: Sixty pulses a second in a steady rhythm. From the outskirts of the nebula the ob ...
... accumulate a lethal dose within seconds. It produces a noticeable heating effect. Light years away, the pulsar at the nebula’s core is a stroboscope. Its light comes in bursts, a brilliant flash and then a fainter one: Sixty pulses a second in a steady rhythm. From the outskirts of the nebula the ob ...
Characterization of the four new transiting planets KOI
... Even if the precision is lower than the HARPS-N measurements for such faint targets, SOPHIE measurements can reveal large radial velocity variations corresponding to transiting stars, brown dwarfs, or massive planets, which would not require HARPS-N to be characterized (see, e.g., Ehrenreich et al. ...
... Even if the precision is lower than the HARPS-N measurements for such faint targets, SOPHIE measurements can reveal large radial velocity variations corresponding to transiting stars, brown dwarfs, or massive planets, which would not require HARPS-N to be characterized (see, e.g., Ehrenreich et al. ...
key - Scioly.org
... - You have 50 minutes to complete the exam. Note that the test is quite long, so teams are not expected to finish. Kudos to any team who gets through more than half the test. - You are allowed up to two reference sources (e.g. laptops, binders) and any number of calculators. Using outside sources (e ...
... - You have 50 minutes to complete the exam. Note that the test is quite long, so teams are not expected to finish. Kudos to any team who gets through more than half the test. - You are allowed up to two reference sources (e.g. laptops, binders) and any number of calculators. Using outside sources (e ...
Topic 2 Chemical Composition of Stars
... different factors which include: • Point in the star’s evolution − for example, some advanced stars can lose the “envelope” of gas around them (we will look more closely at this later in the course) • Mixing of surface layers • Certain stars are Chemically Peculiar (CP) and exhibit dramatic over/ ...
... different factors which include: • Point in the star’s evolution − for example, some advanced stars can lose the “envelope” of gas around them (we will look more closely at this later in the course) • Mixing of surface layers • Certain stars are Chemically Peculiar (CP) and exhibit dramatic over/ ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 15 Notes: Stars Before
... many more that we can use, involving both different transitions of CO and of other molecules – thousands have been detected. These clouds are extremely cold, typically around 10 K, mainly because the CO molecules are very efficient at radiating away energy. The clouds are also very dusty, and the du ...
... many more that we can use, involving both different transitions of CO and of other molecules – thousands have been detected. These clouds are extremely cold, typically around 10 K, mainly because the CO molecules are very efficient at radiating away energy. The clouds are also very dusty, and the du ...
A search for kilogauss magnetic fields in white dwarfs and hot
... Feige 34 or WD1036+433 (McCook & Sion 1999) is one of the brightest (V = 11.22) weak-lined subdwarf stars spectroscopically classified as sdO (Greenstein & Sargent 1974; McCook & Sion 1999, and references therein). Thejll et al. (1991, 1995) suggested this star to be a close binary system having a c ...
... Feige 34 or WD1036+433 (McCook & Sion 1999) is one of the brightest (V = 11.22) weak-lined subdwarf stars spectroscopically classified as sdO (Greenstein & Sargent 1974; McCook & Sion 1999, and references therein). Thejll et al. (1991, 1995) suggested this star to be a close binary system having a c ...
Goal: To understand clusters of stars
... Distance to cluster A key step in finding distances to other galaxies. How stars evolve How clusters evolve How our galaxy evolves How the composition of our galaxy changes with ...
... Distance to cluster A key step in finding distances to other galaxies. How stars evolve How clusters evolve How our galaxy evolves How the composition of our galaxy changes with ...
Goal: To understand clusters of stars
... Distance to cluster A key step in finding distances to other galaxies. How stars evolve How clusters evolve How our galaxy evolves How the composition of our galaxy changes with ...
... Distance to cluster A key step in finding distances to other galaxies. How stars evolve How clusters evolve How our galaxy evolves How the composition of our galaxy changes with ...
pilot_projSOW_long - New Mexico Institute of Mining and
... 4) Modify current observing strategy of faster rotators to include longer coverage in an attempt to identify any additional binary systems. 5) Perform an extended study of 3782 Celle during its 2004 apparition. 6) Scan all images for new asteroids and perform follow-up astrometry if observing time p ...
... 4) Modify current observing strategy of faster rotators to include longer coverage in an attempt to identify any additional binary systems. 5) Perform an extended study of 3782 Celle during its 2004 apparition. 6) Scan all images for new asteroids and perform follow-up astrometry if observing time p ...
Introduction
... Planets orbiting around other stars can also be detected with the gravitational microlensing effect (Mao & Paczyński 1991; Gould & Loeb 1992). When a star (the lens) passes in front of a background source, this effect causes a magnification with a well known symmetrical light curve profile. If the ...
... Planets orbiting around other stars can also be detected with the gravitational microlensing effect (Mao & Paczyński 1991; Gould & Loeb 1992). When a star (the lens) passes in front of a background source, this effect causes a magnification with a well known symmetrical light curve profile. If the ...
L The James Webb Space Telescope
... ambition: it will be the largest telescope of any kind in the world. Today’s biggest singleaperture radio telescope, the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, has just 73,000 square metres of collecting area. SKA is aiming for a million. This collecting area will be distributed between thousands of sm ...
... ambition: it will be the largest telescope of any kind in the world. Today’s biggest singleaperture radio telescope, the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, has just 73,000 square metres of collecting area. SKA is aiming for a million. This collecting area will be distributed between thousands of sm ...
Crowdclass Supplemental Materials - Doris Jung
... • (*) When galaxies merge, the turbluent gas inflowing into the interaction region injects extra energy goes into triggering new stars to form. • I don’t know 4) Which of the following statement about tidal debris is true? • Tidal debris is due to the highly active active-galactic centers that eject ...
... • (*) When galaxies merge, the turbluent gas inflowing into the interaction region injects extra energy goes into triggering new stars to form. • I don’t know 4) Which of the following statement about tidal debris is true? • Tidal debris is due to the highly active active-galactic centers that eject ...
Chapter 30: Stars
... However, astronomers can use special filters to observe the chromosphere when the Sun is not eclipsed. The chromosphere appears red, as shown in Figure 30-1B, because it emits most strongly in a narrow band of red wavelengths. The top layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, called the corona, extends several ...
... However, astronomers can use special filters to observe the chromosphere when the Sun is not eclipsed. The chromosphere appears red, as shown in Figure 30-1B, because it emits most strongly in a narrow band of red wavelengths. The top layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, called the corona, extends several ...
HWWS 2010 - Monash University
... • The spectrum also is distorted slightly so we must correct based on assumptions about the photosphere • Blackbody normalisation Rbb measured throughout tail… not always constant, or consistent… Galloway, “Accreting Neutron Stars – tiny Galactic Powerhouses” ...
... • The spectrum also is distorted slightly so we must correct based on assumptions about the photosphere • Blackbody normalisation Rbb measured throughout tail… not always constant, or consistent… Galloway, “Accreting Neutron Stars – tiny Galactic Powerhouses” ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.