Measuring stars Part I
... Deneb has an Absolute visual magnitude of -8.73 (this is about the same brightness as the quarter moon---but at 32.6 light years away!) Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolu ...
... Deneb has an Absolute visual magnitude of -8.73 (this is about the same brightness as the quarter moon---but at 32.6 light years away!) Using the weird equation, the distance to deneb can be calculated: 2500 light years (M – m = 5 – 5log(d)) One last obvious question: How did we ever know the Absolu ...
Earth and Stars
... •Then, a difference expressed in degrees would be found. If the distance between the two cities was known, from estimates by caravaneers for instance, it would then be possible to find the value of a degree of meridian and hence derive the value of the terrestrial ...
... •Then, a difference expressed in degrees would be found. If the distance between the two cities was known, from estimates by caravaneers for instance, it would then be possible to find the value of a degree of meridian and hence derive the value of the terrestrial ...
... recent observations for the majority of the systems. For each of the 44 original “well-observed trapezia” , we plotted the new observations, along with the old ones, as a function of time. We thus obtained a number of graphs like that shown in Figure 1. In order to combine modern observations of pos ...
Unit 1
... • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set off a massive fusion reaction. The star then ...
... • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set off a massive fusion reaction. The star then ...
main sequence star
... sequence star. • Stars remain main sequence stars for 90% of their life. It is the longest stage in stellar evolution. • In the core, nuclear fusion is taking place. The first fusion to take place is hydrogen atoms fusing to become helium atoms. • The star stays about the same size because the gravi ...
... sequence star. • Stars remain main sequence stars for 90% of their life. It is the longest stage in stellar evolution. • In the core, nuclear fusion is taking place. The first fusion to take place is hydrogen atoms fusing to become helium atoms. • The star stays about the same size because the gravi ...
The Sun's Crowded Delivery Room
... observations suggest that stars, even isolated ones like the Sun, form in clusters • Meteorite studies can test this idea and give additional information about events leading to formation of the Solar System ...
... observations suggest that stars, even isolated ones like the Sun, form in clusters • Meteorite studies can test this idea and give additional information about events leading to formation of the Solar System ...
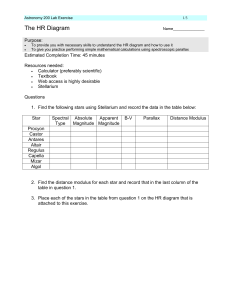
The HR Diagram - Faculty Web Pages
... A star is a delicately balanced ball of gas, fighting between two impulses: gravity, which wants to squeeze the gas all down to a single point, and radiation pressure, which wants to blast all the gas out to infinity. These two opposite forces balance out in a process called Hydrostatic Equilibrium, ...
... A star is a delicately balanced ball of gas, fighting between two impulses: gravity, which wants to squeeze the gas all down to a single point, and radiation pressure, which wants to blast all the gas out to infinity. These two opposite forces balance out in a process called Hydrostatic Equilibrium, ...
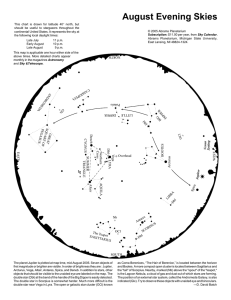
August Evening Skies
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... waiting ½ year, not ½ day Baseline: 300 million km Parallax can be used out to about 100 light years The bigger the parallactic angle, the closer the star! ...
... waiting ½ year, not ½ day Baseline: 300 million km Parallax can be used out to about 100 light years The bigger the parallactic angle, the closer the star! ...
File
... • To measure to greater distances, we use more indirect methods which are calibrated by stellar parallax. • All other methods, except cosmological redshift, use the 1/r2 dimming of light. – We measure apparent brightness or magnitude and compare it with absolute brightness or magnitude. ...
... • To measure to greater distances, we use more indirect methods which are calibrated by stellar parallax. • All other methods, except cosmological redshift, use the 1/r2 dimming of light. – We measure apparent brightness or magnitude and compare it with absolute brightness or magnitude. ...
Space Key Word Search
... CELESTIAL SPHERE - system of mapping the space around the Earth; an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth. CIRCUMPOLAR - circling the pole star (Polaris). COMET - chunk of dirty, dark ice mixed with dust, rocks, and gases which revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit; emits volatiles (gases) in ...
... CELESTIAL SPHERE - system of mapping the space around the Earth; an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth. CIRCUMPOLAR - circling the pole star (Polaris). COMET - chunk of dirty, dark ice mixed with dust, rocks, and gases which revolves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit; emits volatiles (gases) in ...
Document
... • Since the parallax of stars is very small, it is measured in parsec (parallax second) distance d= 1/p OR p = 1/d • 1 parsec = 3.26 LY = 206,265 AU ...
... • Since the parallax of stars is very small, it is measured in parsec (parallax second) distance d= 1/p OR p = 1/d • 1 parsec = 3.26 LY = 206,265 AU ...
Part 1- The Basics
... • The apparent position shift of a star as the Earth moves from one side of its orbit to the other (the largest separation of two viewpoints possibly from the Earth) ...
... • The apparent position shift of a star as the Earth moves from one side of its orbit to the other (the largest separation of two viewpoints possibly from the Earth) ...
December 1, 2011 - Perry Local Schools
... 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and compare the apparent brightness of the two flashlights. 7. Move the two flashlights back and forth until they both appear to have the same brightness. ...
... 3. Gather at the front of the room so they can all see both flashlights easily. 4. Turn on both flashlights. 5. Darken the room. 6. Observe and compare the apparent brightness of the two flashlights. 7. Move the two flashlights back and forth until they both appear to have the same brightness. ...
PHYS299B_Final_HudsonJustin
... a solar eclipse. The smaller dips in brightness is when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From these curves, we can tell if stars follow the characteristics of an eclipsing binary or other types of variable stars. ...
... a solar eclipse. The smaller dips in brightness is when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From these curves, we can tell if stars follow the characteristics of an eclipsing binary or other types of variable stars. ...
6. Star Colors and the Hertzsprung
... is M = -19.5, how far away can we use them as standard candles for getting distance? ...
... is M = -19.5, how far away can we use them as standard candles for getting distance? ...
A billion pixels, a billion stars
... indicate the positions of the stars at different seasons of observation. (a) shows these parallax ellipses in a single small area of the sky, which means that the ellipses are all aligned. In (b), parallax ellipses from different parts of the sky (field of view 1 and field of view 2) have been proje ...
... indicate the positions of the stars at different seasons of observation. (a) shows these parallax ellipses in a single small area of the sky, which means that the ellipses are all aligned. In (b), parallax ellipses from different parts of the sky (field of view 1 and field of view 2) have been proje ...
Stellar Evolution Slideshow
... only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
... only neutrons are left (Guess where the name “Neutron Stars” came from?) Also called Pulsars because they emit radio waves with incredible regularity. Appear to be rapidly rotating neutron star ...
stars_2nd_edit
... Red Dwarf stars can range in size from a hundred times smaller than the sun, to only a couple of times smaller. Because of their small size these stars burn their fuel very slowly, which allows them to live a very long time. Some red dwarf stars will live trillions of years before they run out of fu ...
... Red Dwarf stars can range in size from a hundred times smaller than the sun, to only a couple of times smaller. Because of their small size these stars burn their fuel very slowly, which allows them to live a very long time. Some red dwarf stars will live trillions of years before they run out of fu ...
File
... A. Identify the area where stars can be seen all year in the northern hemisphere. B. Identify the area where stars can never be seen in the northern hemisphere. C. Identify the area showing where stars rise and set in the northern hemisphere. D. Identify the Celestial Horizon. E. Identify stars abov ...
... A. Identify the area where stars can be seen all year in the northern hemisphere. B. Identify the area where stars can never be seen in the northern hemisphere. C. Identify the area showing where stars rise and set in the northern hemisphere. D. Identify the Celestial Horizon. E. Identify stars abov ...
Unit Test Review Questions
... 45. What is the function of the objective lens? 46. Why can radio telescopes be so large? 47. What is the main problem with the atmosphere and ground based telescopes? 48. Who came up with the idea that planets move in an elliptical orbit? 49. Which type of electromagnetic radiation could cause canc ...
... 45. What is the function of the objective lens? 46. Why can radio telescopes be so large? 47. What is the main problem with the atmosphere and ground based telescopes? 48. Who came up with the idea that planets move in an elliptical orbit? 49. Which type of electromagnetic radiation could cause canc ...
Two Summers in the UCSC Science Internship Program
... clusters. In conducting background research, I learned that field stars are unusual: Stars are known to form in clusters, so it is rare to find a young, recently formed star in isolation. This anomalous behavior makes field stars an exciting and hotly debated subject. One theory proposes that field ...
... clusters. In conducting background research, I learned that field stars are unusual: Stars are known to form in clusters, so it is rare to find a young, recently formed star in isolation. This anomalous behavior makes field stars an exciting and hotly debated subject. One theory proposes that field ...
Chapter 19 Notes Stars Stars are bright balls of gas that are trillions
... a. Stars are bright balls of gas that are trillions of kilometers away from Earth b. The color of stars indicate their temperature i. Red and yellow are cool stars, like our sun ii. Blue and white are hot stars. c. Astronomers use an instrument called a spectrograph to break a star’s light into a sp ...
... a. Stars are bright balls of gas that are trillions of kilometers away from Earth b. The color of stars indicate their temperature i. Red and yellow are cool stars, like our sun ii. Blue and white are hot stars. c. Astronomers use an instrument called a spectrograph to break a star’s light into a sp ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.