Supernovae: Heavy Elements
... Once the core contracts to a density of ~1 million g/cm3 , approximately 1 million years after the hydrogen was spent, the temperature has risen to over 100 million K, fusion begins again converting helium into ...
... Once the core contracts to a density of ~1 million g/cm3 , approximately 1 million years after the hydrogen was spent, the temperature has risen to over 100 million K, fusion begins again converting helium into ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... along the main sequence! Once they reach it, they are in equilibrium and do not move until their fuel begins to run out. ...
... along the main sequence! Once they reach it, they are in equilibrium and do not move until their fuel begins to run out. ...
ASTR3007/4007/6007, Class 1: Observing the Stars 23 February
... two energy levels in some atom or molecule in the stellar atmosphere. Those photons are strongly absorbed by those atoms or molecules, leading to a drop in the light we see coming out of the star at those wavelengths. Although this is not the case for the Sun, in some stars there are strong emissio ...
... two energy levels in some atom or molecule in the stellar atmosphere. Those photons are strongly absorbed by those atoms or molecules, leading to a drop in the light we see coming out of the star at those wavelengths. Although this is not the case for the Sun, in some stars there are strong emissio ...
Stellar Evolution (Powerpoint) 17
... • Added luminosity is so strong, it lifts the red giant’s low density outer envelope completely off the star. • As it expands, its opacity drops and we see to a deeper and deeper and hotter and hotter depth, so the star moves left on the HR diagram • Until… we see the electron degenerate core; the n ...
... • Added luminosity is so strong, it lifts the red giant’s low density outer envelope completely off the star. • As it expands, its opacity drops and we see to a deeper and deeper and hotter and hotter depth, so the star moves left on the HR diagram • Until… we see the electron degenerate core; the n ...
1201 Discussion Notes
... right? (I’m really looking forward to hearing feedback from you!) Remember, those need to be completed by December 10. Well, while you’re online, you might as well complete the extra credit assignment on the astronomy place web site – the "Detecting Dark Matter in Spiral ...
... right? (I’m really looking forward to hearing feedback from you!) Remember, those need to be completed by December 10. Well, while you’re online, you might as well complete the extra credit assignment on the astronomy place web site – the "Detecting Dark Matter in Spiral ...
Powers of ten notation
... Solar and sidereal days Mean solar day – 24 hours Sidereal day – 23 hours 56 minutes is the actual rotation period of the Earth ...
... Solar and sidereal days Mean solar day – 24 hours Sidereal day – 23 hours 56 minutes is the actual rotation period of the Earth ...
Star Life Cycle – Web Activity
... 3. How long ago was our sun born in a nebula? Protostar 4. Click on the animation that shows how a star forms from a nebula. Describe why the core of a forming star is hot. ...
... 3. How long ago was our sun born in a nebula? Protostar 4. Click on the animation that shows how a star forms from a nebula. Describe why the core of a forming star is hot. ...
solar system formation and gal
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
17_LectureOutline
... In 1604, stars within a constellation were ranked in order of brightness and labeled with Greek letters (Alpha Centauri) In the early 18th century, stars were numbered from west to east in a constellation (61 Cygni) ...
... In 1604, stars within a constellation were ranked in order of brightness and labeled with Greek letters (Alpha Centauri) In the early 18th century, stars were numbered from west to east in a constellation (61 Cygni) ...
Slide 1
... In 1604, stars within a constellation were ranked in order of brightness and labeled with Greek letters (Alpha Centauri) In the early 18th century, stars were numbered from west to east in a constellation (61 Cygni) ...
... In 1604, stars within a constellation were ranked in order of brightness and labeled with Greek letters (Alpha Centauri) In the early 18th century, stars were numbered from west to east in a constellation (61 Cygni) ...
Parallax - The Universe Adventure
... the moon using the parallax shift viewed between two cities on Earth. The distance he calculated is surprisingly close to the accurate distance we can measure today! Later astronomers were able to estimate the distance to planets and nearby stars using parallax with the diameter of the Earth’s orbit ...
... the moon using the parallax shift viewed between two cities on Earth. The distance he calculated is surprisingly close to the accurate distance we can measure today! Later astronomers were able to estimate the distance to planets and nearby stars using parallax with the diameter of the Earth’s orbit ...
$doc.title
... subtends 1 arcsec, so, using the small angle approximation, 1 pc = 1 AU/1 arcsec (in radians) = 1.5 × 1013 × (57.2 × 3600) = 3.08 × 1018 cm. Movie illustrating parallax: www.astronomy.ohio-state.edu/ pogge/Ast162/Movies/parallax.html (from Richard Pogge) We now introduce the concept of proper motion ...
... subtends 1 arcsec, so, using the small angle approximation, 1 pc = 1 AU/1 arcsec (in radians) = 1.5 × 1013 × (57.2 × 3600) = 3.08 × 1018 cm. Movie illustrating parallax: www.astronomy.ohio-state.edu/ pogge/Ast162/Movies/parallax.html (from Richard Pogge) We now introduce the concept of proper motion ...
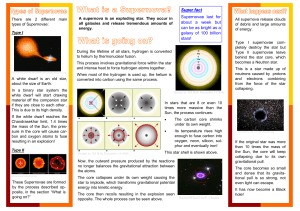
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... If the white dwarf reaches the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, the pressure in the core will cause carbon and oxygen atoms to fuse resulting in an explosion! ...
... If the white dwarf reaches the Chandrasekhar limit, 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, the pressure in the core will cause carbon and oxygen atoms to fuse resulting in an explosion! ...
Parallax, Apparent Magnitude and Absolute Magnitude
... We can see this parallax shift when we compare the positions on the sky of a nearby star observed six months apart. As the Earth orbits the Sun, its line of sight towards the star changes, which makes the star’s position shift against the (more distant) background stars (see Figure 2). Because the s ...
... We can see this parallax shift when we compare the positions on the sky of a nearby star observed six months apart. As the Earth orbits the Sun, its line of sight towards the star changes, which makes the star’s position shift against the (more distant) background stars (see Figure 2). Because the s ...
Document
... the temperature of this reball decreased from unbelievably high values of more than 1032 K to a few thousand K, and hydrogen and helium gas formed. No other constituents, except for traces of some very light chemical elements, were present at that time. However, after about 100 million years, due t ...
... the temperature of this reball decreased from unbelievably high values of more than 1032 K to a few thousand K, and hydrogen and helium gas formed. No other constituents, except for traces of some very light chemical elements, were present at that time. However, after about 100 million years, due t ...
Chapter20
... Black holes are gravity wells that can not only draw mater in but can spin it as well. This effect, called framedragging, is most prominent near massive, fast spinning objects. Matter in this system gets caught up and spun around the black hole. Such discoveries help scientists better understand gra ...
... Black holes are gravity wells that can not only draw mater in but can spin it as well. This effect, called framedragging, is most prominent near massive, fast spinning objects. Matter in this system gets caught up and spun around the black hole. Such discoveries help scientists better understand gra ...
Our Universe
... Asteroids and other objects come close to our planet EVERY DAY! Most of the time we never notice them, but with improving technologies we are detecting more of them, and detecting them earlier. ...
... Asteroids and other objects come close to our planet EVERY DAY! Most of the time we never notice them, but with improving technologies we are detecting more of them, and detecting them earlier. ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 3
... Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In these systems supernovas occur also. Stars up to eight times the mass of our sun usually evolve into white dwarfs. A star that is condensed to this size has a very strong gravitational pull. With that gravity, ...
... Binary stars are when there are two stars and they revolve around each other. In these systems supernovas occur also. Stars up to eight times the mass of our sun usually evolve into white dwarfs. A star that is condensed to this size has a very strong gravitational pull. With that gravity, ...
Chapter 4
... 2. Studies have shown that there is no cause-andeffect relationship between vaccines and autism 3. Studies into the proposed links between autism and vaccines have not yet been conducted ...
... 2. Studies have shown that there is no cause-andeffect relationship between vaccines and autism 3. Studies into the proposed links between autism and vaccines have not yet been conducted ...
Deducing Temperatures and Luminosities of Stars
... • EM radiation is the combination of time- and space- varying electric + magnetic fields that convey energy. • Physicists often speak of the “particle-wave duality” of EM ...
... • EM radiation is the combination of time- and space- varying electric + magnetic fields that convey energy. • Physicists often speak of the “particle-wave duality” of EM ...
DP11 Foundations of Astronomy
... understanding of cosmic distances on what we find out from the closest stars with directly measured distances. The HIPPARCOS satellite measured stellar positions to an accuracy of 0.001 arcseconds, so the current limit of parallax measurements is about 1000 parsecs. ...
... understanding of cosmic distances on what we find out from the closest stars with directly measured distances. The HIPPARCOS satellite measured stellar positions to an accuracy of 0.001 arcseconds, so the current limit of parallax measurements is about 1000 parsecs. ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.