lec03_30sep2011
... -~7% of solar-type stars have >Mj planets in the “terrestrial planet” region. Extrapolation of current incompeteness suggests >12% w/planets @ <20 AU. - multiple planetary systems are ~common - planetary resonances are ~common What can explain these properties? ...
... -~7% of solar-type stars have >Mj planets in the “terrestrial planet” region. Extrapolation of current incompeteness suggests >12% w/planets @ <20 AU. - multiple planetary systems are ~common - planetary resonances are ~common What can explain these properties? ...
Spring 2014 Astronomy Exam Study Guide (Co-Taught)
... Location of stars based on their temperature, luminosity and size. Location and color of hottest and brightest stars Location and color of coolest and dimmest stars Life cycle of various stars Location of most stars Temperature and luminosity of specific stars The Lives of Stars Stars ...
... Location of stars based on their temperature, luminosity and size. Location and color of hottest and brightest stars Location and color of coolest and dimmest stars Life cycle of various stars Location of most stars Temperature and luminosity of specific stars The Lives of Stars Stars ...
Why Aren`t All Galaxies Barred?
... but after a while remains fairly constant over a wide range of distances from the centre. This means that the galaxy is rotating differentially, since the stars near the centre take less time to complete one orbit about the centre than those further out. The typical average in the outer parts is 250 ...
... but after a while remains fairly constant over a wide range of distances from the centre. This means that the galaxy is rotating differentially, since the stars near the centre take less time to complete one orbit about the centre than those further out. The typical average in the outer parts is 250 ...
docx - STAO
... colour) and the distance from the observer. Sometimes the brightest-looking stars are not actually the brightest, and sometimes the closest-looking stars are not the closest. Light energy dissipates (spreads out) as it travels from its source. You could briefly discuss the idea of the inverse square ...
... colour) and the distance from the observer. Sometimes the brightest-looking stars are not actually the brightest, and sometimes the closest-looking stars are not the closest. Light energy dissipates (spreads out) as it travels from its source. You could briefly discuss the idea of the inverse square ...
Stages of stars - University of Dayton
... gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a Planetary Nebula. ...
... gaseous shell, this gas that surrounds the core is called a Planetary Nebula. ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
... small, portable star wheel locator, the celestial globe with stellar objects distributed across the surface of a sphere, and the flat star map that is often published in astronomy magazines or mounted on the walls of classrooms. But there is also available astronomy software for the computer that ca ...
... small, portable star wheel locator, the celestial globe with stellar objects distributed across the surface of a sphere, and the flat star map that is often published in astronomy magazines or mounted on the walls of classrooms. But there is also available astronomy software for the computer that ca ...
Luminosity
... It would be only 1/3 as bright. It would be only 1/6 as bright. It would be only 1/9 as bright. It would be three times as bright. ...
... It would be only 1/3 as bright. It would be only 1/6 as bright. It would be only 1/9 as bright. It would be three times as bright. ...
PS #1 Solutions - Stars and Stellar Explosions 1. Opacity sources
... gas law is a reasonable assumption. Note that you do not need any quantum mechanics for this problem. It’s purely classical. a) Provide a quantitative relation between the temperature and density of a star which indicates when we can treat it as a gas (rather than a liquid) throughout its interior, ...
... gas law is a reasonable assumption. Note that you do not need any quantum mechanics for this problem. It’s purely classical. a) Provide a quantitative relation between the temperature and density of a star which indicates when we can treat it as a gas (rather than a liquid) throughout its interior, ...
Inverse Square Law
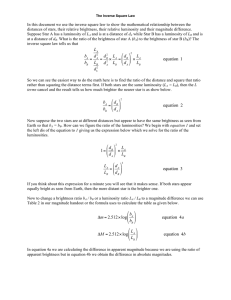
... If you think about this expression for a minute you will see that it makes sense. If both stars appear equally bright as seen from Earth, then the more distant star is the brighter one. Now to change a brightness ratio bA / bB or a luminosity ratio LA / LB to a magnitude difference we can use Table ...
... If you think about this expression for a minute you will see that it makes sense. If both stars appear equally bright as seen from Earth, then the more distant star is the brighter one. Now to change a brightness ratio bA / bB or a luminosity ratio LA / LB to a magnitude difference we can use Table ...
Here
... the x-axis of the plot, and some measure of the intrinsic luminosity is plotted on the y-axis. ...
... the x-axis of the plot, and some measure of the intrinsic luminosity is plotted on the y-axis. ...
AST4930 Star and Planet Formation
... Spectroscopic analysis can identify if an early type star is in main-sequence or already leaving the main sequence. In the first case, it follows a given temperature-luminosity relation, which can be exploited to determine their distance (but reddening must be corrected for). ...
... Spectroscopic analysis can identify if an early type star is in main-sequence or already leaving the main sequence. In the first case, it follows a given temperature-luminosity relation, which can be exploited to determine their distance (but reddening must be corrected for). ...
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife
... while stars are forming within it. The cloud typically begins (Fig. 2A) enveloped by a surrounding layer of atomic hydrogen – this atomic hydrogen provides shielding from the destructive power of the interstellar radiation field. The GMC itself is made up of dust and molecules, with H2 being the dom ...
... while stars are forming within it. The cloud typically begins (Fig. 2A) enveloped by a surrounding layer of atomic hydrogen – this atomic hydrogen provides shielding from the destructive power of the interstellar radiation field. The GMC itself is made up of dust and molecules, with H2 being the dom ...
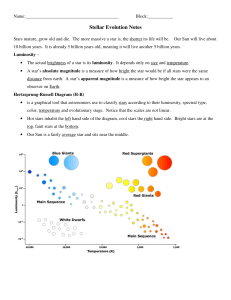
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
... 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old, meaning it will live another 5 billion years. Luminosity – ...
AS2001 - University of St Andrews
... (Temperature, surface gravity, and metal abundances in the stellar atmosphere models are adjusted until they fit the observed equivalent widths of lines in the observed spectrum. Full details of this are part of ...
... (Temperature, surface gravity, and metal abundances in the stellar atmosphere models are adjusted until they fit the observed equivalent widths of lines in the observed spectrum. Full details of this are part of ...
Document
... Note: Numerical modeling is often used in the study of stellar structure and evolution - the timescale over which a star is evolves is too long for us to follow the evolution of any one star. Also, numerical modeling allows us to build up a picture of things that we cannot see (such as the core of a ...
... Note: Numerical modeling is often used in the study of stellar structure and evolution - the timescale over which a star is evolves is too long for us to follow the evolution of any one star. Also, numerical modeling allows us to build up a picture of things that we cannot see (such as the core of a ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
the curious incident of the dog in the night-time
... black hole is what is called a singularity, which means it is impossible to find out what is on the other side because the gravity of a black hole is so big that even electromagnetic waves like light can’t get out of it, and electromagnetic waves are how we get information about things which are far ...
... black hole is what is called a singularity, which means it is impossible to find out what is on the other side because the gravity of a black hole is so big that even electromagnetic waves like light can’t get out of it, and electromagnetic waves are how we get information about things which are far ...
The Solar Neighborhood
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
... The globular star clusters are bright, and can be seen for a long distance. Their distances can be estimated accurately from their main sequence turnoffs, as well as by measuring the periods of variable stars that belong to each cluster. In the table below are listed several dozen Galactic globular ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.