here
... When most stars get old they bloat and become ‘red giants’. Our sun will eventually run out of fuel and become a red giant. As it gets larger it will engulf the inner planets, possibly the earth as well. It may explode or go ‘Super Nova’. Some times a red giant just runs out of fuel, dims and grows ...
... When most stars get old they bloat and become ‘red giants’. Our sun will eventually run out of fuel and become a red giant. As it gets larger it will engulf the inner planets, possibly the earth as well. It may explode or go ‘Super Nova’. Some times a red giant just runs out of fuel, dims and grows ...
HOW TO HOLD A DEAD STAR IN YOUR HAND - Chandra X
... place in an expanding shock wave generated by the explosion. The red and green regions show material from the destroyed star that has been heated to millions of degrees by the explosion. NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has observed Cas A many times over the 17 years it has been in operation. The ag ...
... place in an expanding shock wave generated by the explosion. The red and green regions show material from the destroyed star that has been heated to millions of degrees by the explosion. NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has observed Cas A many times over the 17 years it has been in operation. The ag ...
No Slide Title
... Borealis or Northern Lights (and the Aurora Australis or Southern Lights). As the solar wind approaches the earth, it gets caught in the earth’s magnet field, the magnetosphere, some of the particles, especially after a massive solar storm, get funneled along the lines of the earth’s magnet field do ...
... Borealis or Northern Lights (and the Aurora Australis or Southern Lights). As the solar wind approaches the earth, it gets caught in the earth’s magnet field, the magnetosphere, some of the particles, especially after a massive solar storm, get funneled along the lines of the earth’s magnet field do ...
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
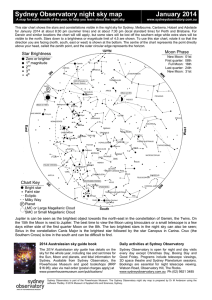
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
Sydney Observatory night sky map January 2014
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... 7. Most of the constellations visible from the northern hemisphere which are "officially" recognized are of ancient _________derivation. But other civilizations created _______________________________ ______________________________________________________. 8. It is important to recognize the _______ ...
... 7. Most of the constellations visible from the northern hemisphere which are "officially" recognized are of ancient _________derivation. But other civilizations created _______________________________ ______________________________________________________. 8. It is important to recognize the _______ ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Astronomical Unit (AU) = 93 million miles or 1.5 x 108 km Distance between Earth and Sun ...
... Astronomical Unit (AU) = 93 million miles or 1.5 x 108 km Distance between Earth and Sun ...
MilkyWay
... Astronomical Unit (AU) = 93 million miles or 1.5 x 108 km Distance between Earth and Sun ...
... Astronomical Unit (AU) = 93 million miles or 1.5 x 108 km Distance between Earth and Sun ...
The Naked Eye Stars as Data Supporting Galileo`s
... Galileo's interpretation of the Copernican theory included something not original to Copernicus -- that the fixed stars were “so many suns”4 distributed through space so that “some are two or three times as remote as others”5. ...
... Galileo's interpretation of the Copernican theory included something not original to Copernicus -- that the fixed stars were “so many suns”4 distributed through space so that “some are two or three times as remote as others”5. ...
Lecture 24, PPT version
... • Emission, absorption and continuous spectra • Spectra as the “fingerprints” of atoms (due to changes in energy levels) ...
... • Emission, absorption and continuous spectra • Spectra as the “fingerprints” of atoms (due to changes in energy levels) ...
Astronomy (stars, galaxies and the Universe)
... stars and to understand how stars change over time As the absolute magnitude of main sequence stars increases, the temperature increase as well ...
... stars and to understand how stars change over time As the absolute magnitude of main sequence stars increases, the temperature increase as well ...
November 2005 - Otterbein University
... • Careful study of the Sun ~ 370 years • We have studied the Sun for only 1/27 millionth of its lifetime! ...
... • Careful study of the Sun ~ 370 years • We have studied the Sun for only 1/27 millionth of its lifetime! ...
Olivewood Gardens
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Permission is hereby granted to ...
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Permission is hereby granted to ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
answer key
... The Universe: Life & Death of a Star Key Forces of Gravity 1. How many stars are in our galaxy? ...
... The Universe: Life & Death of a Star Key Forces of Gravity 1. How many stars are in our galaxy? ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.