A Unique Environmental Studies Program
... you look at Alpha Centauri through a telescope you will find that is actually is two stars (a binary star), and they revolve around each other once every 80,000 years. Alpha Centauri is particularly interesting to astronomers because it is the nearest star visible to the naked eye, being 'only' 4.3 ...
... you look at Alpha Centauri through a telescope you will find that is actually is two stars (a binary star), and they revolve around each other once every 80,000 years. Alpha Centauri is particularly interesting to astronomers because it is the nearest star visible to the naked eye, being 'only' 4.3 ...
btg_2016_astromony
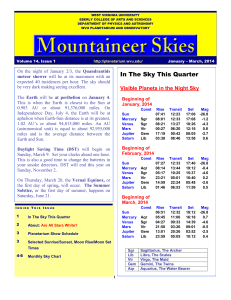
... 149,600,000km (sun to earh) / 300,000 (speed of light) = 498.7sec or 8.3min Example 1: Take a head torch and flash it up at the tarp or over to a tent. Q?: If light could curve around the earth and land back at this headtorch/tarp/tent (if in a vacuum and unhindered) – how long do you think it would ...
... 149,600,000km (sun to earh) / 300,000 (speed of light) = 498.7sec or 8.3min Example 1: Take a head torch and flash it up at the tarp or over to a tent. Q?: If light could curve around the earth and land back at this headtorch/tarp/tent (if in a vacuum and unhindered) – how long do you think it would ...
The Parallax Activity: Measuring the Distances to
... longer be used to find the distance to a star with an error of less than 10% using ground-based measurements. Other techniques must be used (see Extension Activity D) beyond 200 light years. 4. The Hipparcos satellite (1989-93) measured the positions of ...
... longer be used to find the distance to a star with an error of less than 10% using ground-based measurements. Other techniques must be used (see Extension Activity D) beyond 200 light years. 4. The Hipparcos satellite (1989-93) measured the positions of ...
Final Exam Space Unit Review
... Azimuth: angle clockwise from North, the direction we must face to see the star (i.e. 180oS or “at an azimuth of 180oS). Azimuth coordinates MUST have degrees PLUS direction. Do the 3 practice problems on pg. 359 and the Alt-Azimuth Coordinates Practice Sheet (BLM 5Draw and label “altitude” and “a ...
... Azimuth: angle clockwise from North, the direction we must face to see the star (i.e. 180oS or “at an azimuth of 180oS). Azimuth coordinates MUST have degrees PLUS direction. Do the 3 practice problems on pg. 359 and the Alt-Azimuth Coordinates Practice Sheet (BLM 5Draw and label “altitude” and “a ...
January 2007 - Western Nevada Astronomical Society
... day uses a star. A solar day is 24 hours long, the length of time required for two successive meridian transits by the Sun. A sidereal day is 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds long, the length it takes a star to cross your meridian two times successively. A solar day is about 4 minutes longer than a s ...
... day uses a star. A solar day is 24 hours long, the length of time required for two successive meridian transits by the Sun. A sidereal day is 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds long, the length it takes a star to cross your meridian two times successively. A solar day is about 4 minutes longer than a s ...
Magnetic Activity Cycles and the Solar
... • Measure ratio of total emission in line cores to flux in the wings Frohlich & Lean (2004) ...
... • Measure ratio of total emission in line cores to flux in the wings Frohlich & Lean (2004) ...
Stellar Distances - Red Hook Central School District
... To find brightness b using apparent magnitude; raise 2.51 to power Dm (mag). Ex 3: A 2 magnitude difference is an apparent brightness difference of 2.51 x 2.51 = ...
... To find brightness b using apparent magnitude; raise 2.51 to power Dm (mag). Ex 3: A 2 magnitude difference is an apparent brightness difference of 2.51 x 2.51 = ...
chapter 24 instructor notes
... orginator of the BD catalogue, was able to derive an apex for the solar motion from studying stellar proper motions. His result is very similar to that recognized today. Also in 1837, Frederick Struve found evidence for interstellar extinction in star count data, which was considered necessary at th ...
... orginator of the BD catalogue, was able to derive an apex for the solar motion from studying stellar proper motions. His result is very similar to that recognized today. Also in 1837, Frederick Struve found evidence for interstellar extinction in star count data, which was considered necessary at th ...
January-February-March - WVU Planetarium
... About: Are all stars white? Looking up at the stars on a fine clear evening, at first glance we might think that all the stars are white, but on closer inspection we can see that is really not so. As an example, in the constellation Orion, the Hunter, the star that marks his upper left hand shoulde ...
... About: Are all stars white? Looking up at the stars on a fine clear evening, at first glance we might think that all the stars are white, but on closer inspection we can see that is really not so. As an example, in the constellation Orion, the Hunter, the star that marks his upper left hand shoulde ...
3.1 Using Technology
... – The apparent shift in position of an object when the object is viewed from two different places. – Astronomers use a star’s apparent shift in position relative to the background stars to determine what angles to use when triangulating the stars distance from Earth. ...
... – The apparent shift in position of an object when the object is viewed from two different places. – Astronomers use a star’s apparent shift in position relative to the background stars to determine what angles to use when triangulating the stars distance from Earth. ...
Interstellar medium, birth and life of stars
... How do stars form? How do we know? How will our Sun evolve as a star? What will its final state be? Compare its predicted evolution to that of higher-mass stars. How do they end? How do we know? ...
... How do stars form? How do we know? How will our Sun evolve as a star? What will its final state be? Compare its predicted evolution to that of higher-mass stars. How do they end? How do we know? ...
The Classification of Stellar Spectra
... In 1802, William Wollaston noted that the spectrum of sunlight did not appear to be a continuous band of colours, but rather had a series of dark lines superimposed on it. Wollaston attributed the lines to natural boundaries between colours. Joseph Fraunhofer made a more careful set of observations ...
... In 1802, William Wollaston noted that the spectrum of sunlight did not appear to be a continuous band of colours, but rather had a series of dark lines superimposed on it. Wollaston attributed the lines to natural boundaries between colours. Joseph Fraunhofer made a more careful set of observations ...
Stefan-Boltzmann`s law Wien`s law
... light-years from us. And the observable part of the universe contains too few stars to fill up the sky with light. Calculation shows that the helium produced by nuclear fusion within stars cannot account for the real amount of helium in Universe (24%). In 1960 it was proposed that sometime during th ...
... light-years from us. And the observable part of the universe contains too few stars to fill up the sky with light. Calculation shows that the helium produced by nuclear fusion within stars cannot account for the real amount of helium in Universe (24%). In 1960 it was proposed that sometime during th ...
dtu7ech01 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... grid lines that circle the globe N-S and E-W and that intersect at right angles…These grid lines are called ...
... grid lines that circle the globe N-S and E-W and that intersect at right angles…These grid lines are called ...
Characteristics of Main Sequence Stars
... • The interiors of stars are extremely hot (T > 106 K). The fall-off to surface temperatures (T ∼ 104 K) takes place in a very thin region near the surface. • The region of nuclear energy generation is restricted to a very small mass range near the center of the star. The rapid fall-off of ²n with ...
... • The interiors of stars are extremely hot (T > 106 K). The fall-off to surface temperatures (T ∼ 104 K) takes place in a very thin region near the surface. • The region of nuclear energy generation is restricted to a very small mass range near the center of the star. The rapid fall-off of ²n with ...
Astronomy
... 3. If you live on the equator, where would the celestial equator be in your sky? It would run from East to West and directly overhead through your zenith 4. What is the difference between 1st magnitude and 2nd magnitude stars? 1st magnitude are brighter ...
... 3. If you live on the equator, where would the celestial equator be in your sky? It would run from East to West and directly overhead through your zenith 4. What is the difference between 1st magnitude and 2nd magnitude stars? 1st magnitude are brighter ...
Lecture 22 - Seattle Central
... What are the main stages in a high mass star’s life? What happens in the core of a high mass star at the end of its life? Why does fusion stop at Iron in high mass stars? Where do elements heavier than Iron come from? What are the two possibilities when the electron degeneracy pressure in a high mas ...
... What are the main stages in a high mass star’s life? What happens in the core of a high mass star at the end of its life? Why does fusion stop at Iron in high mass stars? Where do elements heavier than Iron come from? What are the two possibilities when the electron degeneracy pressure in a high mas ...
What would the sky look like from the North Pole
... d) Saturn is presently at a distance of about 10 AU from the Earth. How long does it take a radio signal from the Cassini spacecraft to reach the mission control center in California? Radio waves travel at the speed of light, which is 3 x 105 km/s. 1 AU is 1.5 x 108 km. ...
... d) Saturn is presently at a distance of about 10 AU from the Earth. How long does it take a radio signal from the Cassini spacecraft to reach the mission control center in California? Radio waves travel at the speed of light, which is 3 x 105 km/s. 1 AU is 1.5 x 108 km. ...
ASTR 105 Intro Astronomy: The Solar System
... c) The image to the left shows a configuration in which the Sun is never to the zenith. Are there locations on Earth at which the Sun reaches the Zenith? If so, at what latitudes are they? At which time of the year do they reach the zenith? [hint: remember the tilt angle of the spin axis of the Eart ...
... c) The image to the left shows a configuration in which the Sun is never to the zenith. Are there locations on Earth at which the Sun reaches the Zenith? If so, at what latitudes are they? At which time of the year do they reach the zenith? [hint: remember the tilt angle of the spin axis of the Eart ...
Recap: High Mass Stars
... Neutron Star • Star with a core from 1.4 to 3 times the size of the Sun becomes a neutron. • Electrons and neutrons combine into neutrons. • 10 km (6 mi) in diameter with a mass more than our Sun! • A teaspoon of neutron star would be about 10 million tons • Acts like a huge magnet with magnetic p ...
... Neutron Star • Star with a core from 1.4 to 3 times the size of the Sun becomes a neutron. • Electrons and neutrons combine into neutrons. • 10 km (6 mi) in diameter with a mass more than our Sun! • A teaspoon of neutron star would be about 10 million tons • Acts like a huge magnet with magnetic p ...
Activity 1: The Scientific Method
... 1) Start by becoming aware of your own biases. Do you believe any of the data is correlated? If so how? Relationship Example: radial motion of the stars and temperature Should state relationships that you believe might exist ...
... 1) Start by becoming aware of your own biases. Do you believe any of the data is correlated? If so how? Relationship Example: radial motion of the stars and temperature Should state relationships that you believe might exist ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.