Document
... changes. From an observed line profile, one can construct an image of the surface of the star. This technique has been applied to many different types of stars. ...
... changes. From an observed line profile, one can construct an image of the surface of the star. This technique has been applied to many different types of stars. ...
C H A P T E R 2
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
Lecture 14
... What would happen to a contracting cloud fragment if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change. B. Its mass would increase. C. Its internal pressure would increase. ...
... What would happen to a contracting cloud fragment if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change. B. Its mass would increase. C. Its internal pressure would increase. ...
L11
... The evolution of massive stars have the following general characteristics and differences to lower mass evolution 1. The electrons in their cores do not become degenerate until the final burning stages, when iron core is reached 2. Mass-loss plays an important role in the entire evolution (we will c ...
... The evolution of massive stars have the following general characteristics and differences to lower mass evolution 1. The electrons in their cores do not become degenerate until the final burning stages, when iron core is reached 2. Mass-loss plays an important role in the entire evolution (we will c ...
FREE Sample Here
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
Astronomical Toolkit
... stars. Some appear bright and others very faint as seen from Earth. Some of the faint stars are intrinsically very bright, but are very distant. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are very faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When observing, we are forced to stay on Earth or nea ...
... stars. Some appear bright and others very faint as seen from Earth. Some of the faint stars are intrinsically very bright, but are very distant. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are very faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When observing, we are forced to stay on Earth or nea ...
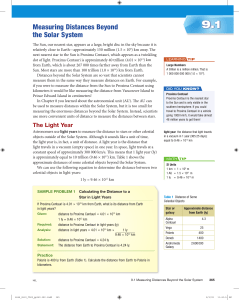
Measuring Distances Beyond the Solar System
... distances—the distances between stars in the Universe. One method, parallax, relies on geometry. Parallax is the apparent change in position of an object against a fixed background when viewed from two different lines of sight (or locations). You can observe parallax when you hold your thumb upright ...
... distances—the distances between stars in the Universe. One method, parallax, relies on geometry. Parallax is the apparent change in position of an object against a fixed background when viewed from two different lines of sight (or locations). You can observe parallax when you hold your thumb upright ...
Ch. S1 - Relativity Group
... because of Earth’s rotation • You also need to know day of year because of Earth’s orbit • Accurate measurement of longitude requires an accurate clock. ...
... because of Earth’s rotation • You also need to know day of year because of Earth’s orbit • Accurate measurement of longitude requires an accurate clock. ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
1/20/09 301 Physics Chapter 12 The Family of Stars Triangulation
... – Superimposed on this orbital motion are small random motions of about 20 km/sec – In addition to their motion through space, stars spin on their axes and this spin can be measured using the Doppler shift technique – young stars are found to rotate faster than old stars ...
... – Superimposed on this orbital motion are small random motions of about 20 km/sec – In addition to their motion through space, stars spin on their axes and this spin can be measured using the Doppler shift technique – young stars are found to rotate faster than old stars ...
Stellar Spectral Classes
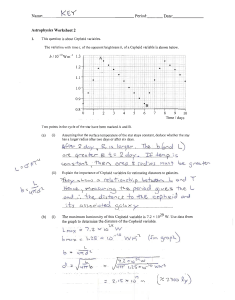
... Using these data, describe and explain one similarity and one difference in the appearance of the two stars as seen with the unaided eye by an observer on the Earth. similarity................................................................................................. ...
... Using these data, describe and explain one similarity and one difference in the appearance of the two stars as seen with the unaided eye by an observer on the Earth. similarity................................................................................................. ...
- saspcsus
... D. Students know that Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun and that the Moon orbits Earth. E. Students know the position of the Sun in the sky changes during the course of the day and from season to season. Grade 5 Standards: 5. The solar system consists of planets and other bodies tha ...
... D. Students know that Earth is one of several planets that orbit the Sun and that the Moon orbits Earth. E. Students know the position of the Sun in the sky changes during the course of the day and from season to season. Grade 5 Standards: 5. The solar system consists of planets and other bodies tha ...
DTU 8e Chap 11 Characterizing Stars
... spectral types (or, equivalently, their absolute magnitudes are plotted against surface temperatures). The H-R diagram reveals the existence of four major groupings of stars: main-sequence stars, giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation betwe ...
... spectral types (or, equivalently, their absolute magnitudes are plotted against surface temperatures). The H-R diagram reveals the existence of four major groupings of stars: main-sequence stars, giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs. The mass-luminosity relation expresses a direct correlation betwe ...
Characteristics of Stars
... distance from Earth and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in two different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent brightness is its brightness as seen from Earth. Astronomers can measure apparent brightness fairly easily using el ...
... distance from Earth and how bright the star actually is. The brightness of a star can be described in two different ways: apparent brightness and absolute brightness. A star’s apparent brightness is its brightness as seen from Earth. Astronomers can measure apparent brightness fairly easily using el ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
... 10. The binary star, Mizar A, is shown with the motion of the members around one another. The mass of a visual binary pair of stars can be obtained from a. the time in years for them to orbit one another. b. the size of their orbit. c. their location in space. * d. both a and b 11. We know the white ...
... 10. The binary star, Mizar A, is shown with the motion of the members around one another. The mass of a visual binary pair of stars can be obtained from a. the time in years for them to orbit one another. b. the size of their orbit. c. their location in space. * d. both a and b 11. We know the white ...
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
... • Core becomes so dense that the protons and electrons fuse into neutrons • Inner part of the core bounces and produces a shockwave that triggers a ...
... • Core becomes so dense that the protons and electrons fuse into neutrons • Inner part of the core bounces and produces a shockwave that triggers a ...
the life cycles of stars (5) - U3A Bendigo Courses / Activities
... sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Our sun emits a solar wind of protons and electrons which can cause aurorae and in certain cases disrupt our electricity supply lines. In its later post main sequenc ...
... sequence these stars emit material from their surface due to sheer radiation pressure. The strong light radiation carries gas with it. Our sun emits a solar wind of protons and electrons which can cause aurorae and in certain cases disrupt our electricity supply lines. In its later post main sequenc ...
slides
... The central core (which, in the most massive stars, is made of iron) undergoes a sudden gravitational collapse, reducing in size until all the electrons in the atoms are smashed down into the nulcei. ...
... The central core (which, in the most massive stars, is made of iron) undergoes a sudden gravitational collapse, reducing in size until all the electrons in the atoms are smashed down into the nulcei. ...
Star Maps and Constellations
... made by project a ball onto a cylinder (problems at the poles!) ...
... made by project a ball onto a cylinder (problems at the poles!) ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
PHYS3380_102615_bw
... Computer simulations can reproduce most of the observed motions We have observed disks around other stars. These could be new planetary systems in formation. ...
... Computer simulations can reproduce most of the observed motions We have observed disks around other stars. These could be new planetary systems in formation. ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe Fall 2001 Professor: ER Capriotti
... C. weighs more than the atom. D. is moving more slowly than a normal atom. E. None of the other answers is correct. 46. If we compare several objects at the same temperature, all glowing because they are hot, the one that emits the most light from each unit area of surface will also A. absorb light ...
... C. weighs more than the atom. D. is moving more slowly than a normal atom. E. None of the other answers is correct. 46. If we compare several objects at the same temperature, all glowing because they are hot, the one that emits the most light from each unit area of surface will also A. absorb light ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.