スライド 1 - STScI
... monitoring an area of 3 square degrees along the bar in the LMC, and also an area of 1 square degree in the central part of the SMC. In the last 10 years, we observed these areas about 80-90 and 100-110 times for LMC and SMC, respectively. As a result, we obtained time series data with more than 3,0 ...
... monitoring an area of 3 square degrees along the bar in the LMC, and also an area of 1 square degree in the central part of the SMC. In the last 10 years, we observed these areas about 80-90 and 100-110 times for LMC and SMC, respectively. As a result, we obtained time series data with more than 3,0 ...
Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... The first step is to obtain instrumental and absolute BVR magnitudes. This is accomplished by observing at least one standard star with known magnitudes on the standard system along with your night’s data and using it to determine the transformation equations. Often the st ...
... The first step is to obtain instrumental and absolute BVR magnitudes. This is accomplished by observing at least one standard star with known magnitudes on the standard system along with your night’s data and using it to determine the transformation equations. Often the st ...
Build your own Galaxy - McDonald Observatory
... dust, and stars. Generally, it is flat like the brim of a wide hat. Astronomers estimate that the galaxy’s disk is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. Stars: glitter. The hottest and brightest stars are blue and white. But these stars live short lives — only ten million to a few hundred million y ...
... dust, and stars. Generally, it is flat like the brim of a wide hat. Astronomers estimate that the galaxy’s disk is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. Stars: glitter. The hottest and brightest stars are blue and white. But these stars live short lives — only ten million to a few hundred million y ...
The Case against Copernicus
... This new “geoheliocentric” cosmology had two major advantages going for it: it squared with deep intuitions about how the world appeared to behave, and it fit the available data better than Copernicus’s system did. Brahe was a towering figure. He ran a huge research program with a castlelike observa ...
... This new “geoheliocentric” cosmology had two major advantages going for it: it squared with deep intuitions about how the world appeared to behave, and it fit the available data better than Copernicus’s system did. Brahe was a towering figure. He ran a huge research program with a castlelike observa ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... • Scientists think the centre of the galaxy contains a super massive black hole. • The Milky Way is full of dust, gas and stars. • The Milky Way, along with everything else, is moving through space. ...
... • Scientists think the centre of the galaxy contains a super massive black hole. • The Milky Way is full of dust, gas and stars. • The Milky Way, along with everything else, is moving through space. ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... 1 minute of longitude = 1 nautical mile * cosine(latitude) Lines of longitude converge at the north and south poles To find longitude typically requires a clock, although there is a technique, called the lunar method that relies on the fact that the moon moves ½ of a degree per hour. ...
... 1 minute of longitude = 1 nautical mile * cosine(latitude) Lines of longitude converge at the north and south poles To find longitude typically requires a clock, although there is a technique, called the lunar method that relies on the fact that the moon moves ½ of a degree per hour. ...
Three Coordinate Systems
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
... Declination – angle from celestial equator (=0o), positive going north (north celestial pole = + 90o), negative going south (south celestial pole = - 90o) Right ascension (RA) – angle from celestial “prime meridian” – equivalent of celestial longitude RA – typically expressed as a time going east – ...
Physics- HSC- Module 9.7 Astrophysics
... The wonders of the Universe are revealed through technological advances based on tested principles of physics. Our understanding of the cosmos draws upon models, theories and laws in our endeavour to seek explanations for the myriad of observations made by various instruments at many different wavel ...
... The wonders of the Universe are revealed through technological advances based on tested principles of physics. Our understanding of the cosmos draws upon models, theories and laws in our endeavour to seek explanations for the myriad of observations made by various instruments at many different wavel ...
Lecture 10: Stellar Evolution
... stories of stars comes from comparing mathematical models of stars with observations • Star clusters are particularly useful because they contain stars of different mass that were born about the same time ...
... stories of stars comes from comparing mathematical models of stars with observations • Star clusters are particularly useful because they contain stars of different mass that were born about the same time ...
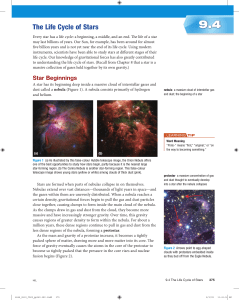
The Life Cycle of Stars
... the shape of the band in the H–R diagram in Figure 4. The hotter these stars are, the more luminous they are. Astronomers have determined that hotter, more luminous main sequence stars are more massive, while cooler, less luminous stars are less massive. Main sequence stars fuse hydrogen to produce ...
... the shape of the band in the H–R diagram in Figure 4. The hotter these stars are, the more luminous they are. Astronomers have determined that hotter, more luminous main sequence stars are more massive, while cooler, less luminous stars are less massive. Main sequence stars fuse hydrogen to produce ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... wind that is believed to be an effect of the young star’s magnetic field. The effect is to propel material away from the star’s photosphere at speeds up to 100 km/s. It is this strong stellar wind the sweeps away the surrounding gas and dust from which the star formed. 5. What is happening in the co ...
... wind that is believed to be an effect of the young star’s magnetic field. The effect is to propel material away from the star’s photosphere at speeds up to 100 km/s. It is this strong stellar wind the sweeps away the surrounding gas and dust from which the star formed. 5. What is happening in the co ...
Can we detect asteroid impacts with rocky extrasolar planets?
... solar system, so we can expect one to be hit every 25 million years. However, half of these impacts will be on the side facing away from the Earth so a visible impact occurs, on average, once every 50 million years. During the first billion years of our solar system, though, the impact rate was at l ...
... solar system, so we can expect one to be hit every 25 million years. However, half of these impacts will be on the side facing away from the Earth so a visible impact occurs, on average, once every 50 million years. During the first billion years of our solar system, though, the impact rate was at l ...
Galactic Star Formation Science with Integral Field
... – Bow-shock apex shows extremely high temperature T~6000K - revealing that the H2 molecule persists in these very high temperature regions Giannini et al. “Near-infrared, IFU spectroscopy unravels the bow-shock HH99B“ 2008, A&A v.481, 123 ...
... – Bow-shock apex shows extremely high temperature T~6000K - revealing that the H2 molecule persists in these very high temperature regions Giannini et al. “Near-infrared, IFU spectroscopy unravels the bow-shock HH99B“ 2008, A&A v.481, 123 ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... Example: Betelgeuse 300 times larger radius than the Sun • If further away but a binary star, get size of stars when they eclipse each other length of time one star passes in front or behind each other ...
... Example: Betelgeuse 300 times larger radius than the Sun • If further away but a binary star, get size of stars when they eclipse each other length of time one star passes in front or behind each other ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.