Project 3. Colour in Astronomy
... U=B=V=R=I=0 This does not mean that Vega show the same brightness through all filters. It is an arbitrary decision taken by the astronomers who have agreed on taking Vega as the zero point for the magnitude scale. Exercise 2: Spica and Antares are two well-known stars with colour indices (B-V)=0.13 ...
... U=B=V=R=I=0 This does not mean that Vega show the same brightness through all filters. It is an arbitrary decision taken by the astronomers who have agreed on taking Vega as the zero point for the magnitude scale. Exercise 2: Spica and Antares are two well-known stars with colour indices (B-V)=0.13 ...
How to Plot the H-R Diagram and Use its Applications
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
death_low_mass
... • Most stars form in the spiral arms of galaxies • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type ...
... • Most stars form in the spiral arms of galaxies • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type ...
FREE Sample Here
... Ursa Major), the Great Square (part of Pegasus), the Water Jug (part of Aquarius), the Summer Triangle (composed of three bright stars in the constellations of Lyra, Cygnus, and Aquilla), Medusa's Head (part of Perseus. ...
... Ursa Major), the Great Square (part of Pegasus), the Water Jug (part of Aquarius), the Summer Triangle (composed of three bright stars in the constellations of Lyra, Cygnus, and Aquilla), Medusa's Head (part of Perseus. ...
PDF - BYU Studies
... pass away. Modern astrophysics teaches that stars are formed, enjoy an enormously long “summer” as they fuse hydrogen to helium in their core, then undergo major changes as nuclear fuel runs low, and finally fade away (occasionally with grand fireworks). The sun is enjoying its glorious summer, but ...
... pass away. Modern astrophysics teaches that stars are formed, enjoy an enormously long “summer” as they fuse hydrogen to helium in their core, then undergo major changes as nuclear fuel runs low, and finally fade away (occasionally with grand fireworks). The sun is enjoying its glorious summer, but ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... Ursa Major), the Great Square (part of Pegasus), the Water Jug (part of Aquarius), the Summer Triangle (composed of three bright stars in the constellations of Lyra, Cygnus, and Aquilla), Medusa's Head (part of Perseus. ...
... Ursa Major), the Great Square (part of Pegasus), the Water Jug (part of Aquarius), the Summer Triangle (composed of three bright stars in the constellations of Lyra, Cygnus, and Aquilla), Medusa's Head (part of Perseus. ...
Oct 06, 2001
... 13. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two stars marked α and β? A. Star α is hotter than star β. B. Star α is less luminous than star β. C. Star α is larger in radius than star β. D. Star α appears brighter that star β. 14. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two st ...
... 13. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two stars marked α and β? A. Star α is hotter than star β. B. Star α is less luminous than star β. C. Star α is larger in radius than star β. D. Star α appears brighter that star β. 14. Which of the statements below is true regarding the two st ...
V = 3 d3 = 4188.8 pc N = ρV = 0.1 pc χ 4188.8 pc = 419
... where M is the mass of the star. For what primary masses will any planets in the optimistic habitable zone be tidally locked? (Hint: Adopt the mass-luminosity relationship I showed in class to derive a relationship between the habitable zone distance and primary mass.) a) 0.11 MSun and below b) 0.25 ...
... where M is the mass of the star. For what primary masses will any planets in the optimistic habitable zone be tidally locked? (Hint: Adopt the mass-luminosity relationship I showed in class to derive a relationship between the habitable zone distance and primary mass.) a) 0.11 MSun and below b) 0.25 ...
ASTROPHYSICS UNIVERSE - Physics
... their poles. This acts a little like a lighthouse, it appears to “pulse” when the pole points at us. ...
... their poles. This acts a little like a lighthouse, it appears to “pulse” when the pole points at us. ...
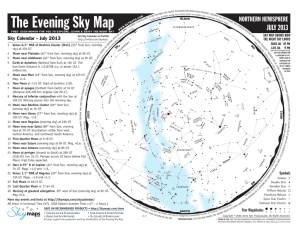
The Evening Sky Map
... Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances f ...
... Constellation – A defined area of the sky containing a star pattern. Diffuse Nebula – A cloud of gas illuminated by nearby stars. Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances f ...
Constellation Classification Cards*
... brightness is used. In the second set, B, more advanced students are introduced to the additional term, magnitude. In addition, several stars are what are called binaries (a star system with two stars orbiting around their center of mass). In Set B both stars are shown, along with their combined bri ...
... brightness is used. In the second set, B, more advanced students are introduced to the additional term, magnitude. In addition, several stars are what are called binaries (a star system with two stars orbiting around their center of mass). In Set B both stars are shown, along with their combined bri ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.