Climbing the Distance Ladder
... We don’t directly measure a star’s luminosity. We measure its flux (f): the wattage collected per square meter of our telescope mirror. ...
... We don’t directly measure a star’s luminosity. We measure its flux (f): the wattage collected per square meter of our telescope mirror. ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... 3. Students incorrectly think that our Sun will end as a supernova explosion. All stars that are about 8 MSun or greater will end as a supernova, leaving some kind of stellar remnant (e.g., a neutron star or black hole). Specifically, these massive stars will end as a Type II supernova. In massive ...
... 3. Students incorrectly think that our Sun will end as a supernova explosion. All stars that are about 8 MSun or greater will end as a supernova, leaving some kind of stellar remnant (e.g., a neutron star or black hole). Specifically, these massive stars will end as a Type II supernova. In massive ...
Stars 3
... Nebula. These include wisp-like structures that move outward away from the pulsar at half the speed of light, as well as a mysterious “halo” which remains stationary, but grows brighter then fainter over time. Also seen are the effects of two polar jets that move out along the rotation axis of the p ...
... Nebula. These include wisp-like structures that move outward away from the pulsar at half the speed of light, as well as a mysterious “halo” which remains stationary, but grows brighter then fainter over time. Also seen are the effects of two polar jets that move out along the rotation axis of the p ...
Stellar Evolution
... In which order will a single star of one solar mass progress through the various stages of stellar evolution? 1. Planetary nebula, main-sequence star, white dwarf, black hole 2. Proto-star, main-sequence star, planetary nebula, white dwarf 3. Proto-star, red giant, supernova, planetary nebula 4. Pr ...
... In which order will a single star of one solar mass progress through the various stages of stellar evolution? 1. Planetary nebula, main-sequence star, white dwarf, black hole 2. Proto-star, main-sequence star, planetary nebula, white dwarf 3. Proto-star, red giant, supernova, planetary nebula 4. Pr ...
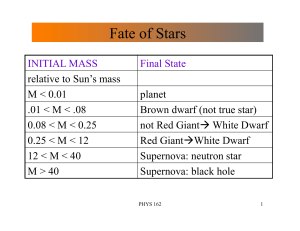
Fate of Stars
... • Usually leaves neutron star For high mass stars • Fusion continues beyond C,O • Core of degenerate electrons builds up - opposes gravity • If Mass(core) > 1.4 M(Sun) core collapses in SUPERNOVA (II) • Leaves either Neutron Star or Black Hole PHYS 162 ...
... • Usually leaves neutron star For high mass stars • Fusion continues beyond C,O • Core of degenerate electrons builds up - opposes gravity • If Mass(core) > 1.4 M(Sun) core collapses in SUPERNOVA (II) • Leaves either Neutron Star or Black Hole PHYS 162 ...
Part I Light, Telescopes, Atoms and Stars
... Near the center (the core) of the sun nuclear fusion is proceeding generating tremendous energy (4.7 million tons per second from E=mc2 and 3.9x1026 J/s luminosity) This is surrounded by the radiation zone – photons must take the energy out – random walk – 500,000 years! ...
... Near the center (the core) of the sun nuclear fusion is proceeding generating tremendous energy (4.7 million tons per second from E=mc2 and 3.9x1026 J/s luminosity) This is surrounded by the radiation zone – photons must take the energy out – random walk – 500,000 years! ...
observing cards - NC Science Festival
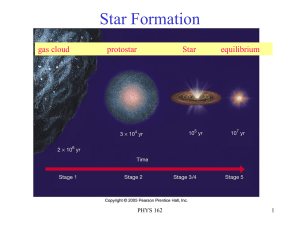
... was given to this class of object because they appear small & round and possibly planet-like through primitive telescopes. It was very quickly recognized that these were not planets, but the name stuck. The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life represents a short but important time in the life of ...
... was given to this class of object because they appear small & round and possibly planet-like through primitive telescopes. It was very quickly recognized that these were not planets, but the name stuck. The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life represents a short but important time in the life of ...
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
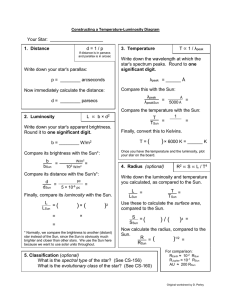
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
Stellarium Astronomy Software
... Although we can’t feel it, the Earth rotates eastward at about 800 miles an hour at its surface. The stars, sun, and moon appear to us to move westward when, in fact, we are the ones that are moving eastward. Because of this, it seems like any given constellation or star takes about 24 hours to make ...
... Although we can’t feel it, the Earth rotates eastward at about 800 miles an hour at its surface. The stars, sun, and moon appear to us to move westward when, in fact, we are the ones that are moving eastward. Because of this, it seems like any given constellation or star takes about 24 hours to make ...
27B Star Life Cycle and the HR Diagram
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
chapter 14 - Astronomy
... 3. Electron degeneracy is the state of a gas in which its electrons are packed as densely as nature permits. The temperature of such a high-density gas is not dependent on the pressure as it is in a “normal” gas. 4. In the case of the degenerate core of a red giant, the more massive the core is, the ...
... 3. Electron degeneracy is the state of a gas in which its electrons are packed as densely as nature permits. The temperature of such a high-density gas is not dependent on the pressure as it is in a “normal” gas. 4. In the case of the degenerate core of a red giant, the more massive the core is, the ...
Stars
... The brightest star in the sky (besides the Sun) is Sirius. It is 2.6 pc from Earth. How long does it take light from Sirius to reach us? ...
... The brightest star in the sky (besides the Sun) is Sirius. It is 2.6 pc from Earth. How long does it take light from Sirius to reach us? ...
second grade - Math/Science Nucleus
... scorpion rises, Orion sets, so that they are never visible at the same time. The Big Dipper is actually part of the Ursa Major (Big Bear) constellation, and represents a cup with a long handle. These points of light in the sky, and the shapes they represented, were also important for traveling at ni ...
... scorpion rises, Orion sets, so that they are never visible at the same time. The Big Dipper is actually part of the Ursa Major (Big Bear) constellation, and represents a cup with a long handle. These points of light in the sky, and the shapes they represented, were also important for traveling at ni ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.