Pulsating variable stars and the Hertzsprung
... Hyde Wollaston (1766-1828) reported dark gaps between colors in the continuous spectrum. Later, Joseph von Fraunhofer (1787-1826) observed the Solar spectra more detailed and found that the dark gaps are different in strength. German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff (1824-1887) published his fundamental w ...
... Hyde Wollaston (1766-1828) reported dark gaps between colors in the continuous spectrum. Later, Joseph von Fraunhofer (1787-1826) observed the Solar spectra more detailed and found that the dark gaps are different in strength. German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff (1824-1887) published his fundamental w ...
Summary: Star Formation Near and Far
... other outflows are in fact much more conspicuous properties of newly formed stars than is any evidence for continuing gas infall, and for some years they seemed to contradict the theoretical models in this respect. Now it is clear that infall, outflow, and rotation are all present simultaneously in ...
... other outflows are in fact much more conspicuous properties of newly formed stars than is any evidence for continuing gas infall, and for some years they seemed to contradict the theoretical models in this respect. Now it is clear that infall, outflow, and rotation are all present simultaneously in ...
MAIN SEQUENCE STARS, Red Giants and White Dwarfs
... • 16O + 4He 20Ne + • 20Ne + 4He 24Mg + • We’ll come back to this type of onion-layer model star when we talk about supernova explosions and neutron stars. • The elements cooked here are needed for life ...
... • 16O + 4He 20Ne + • 20Ne + 4He 24Mg + • We’ll come back to this type of onion-layer model star when we talk about supernova explosions and neutron stars. • The elements cooked here are needed for life ...
PPS
... with a small volume and small surface area may be hot and white, it cannot be very bright because there is a limit to how much energy can escape across its surface each second without blowing the star apart. But on the main sequence all the stars are more or less the same size (they are all dwarf st ...
... with a small volume and small surface area may be hot and white, it cannot be very bright because there is a limit to how much energy can escape across its surface each second without blowing the star apart. But on the main sequence all the stars are more or less the same size (they are all dwarf st ...
white dwarfs, neutron stars, black hole
... Stellar masses and luminosities increase from the lower right of the main sequence to the upper left. From this relationship, the mass of a main sequence star can be estimated by its position on the H-R diagram. Unfortunately, there is no such rule between luminosity and mass for the approximately 1 ...
... Stellar masses and luminosities increase from the lower right of the main sequence to the upper left. From this relationship, the mass of a main sequence star can be estimated by its position on the H-R diagram. Unfortunately, there is no such rule between luminosity and mass for the approximately 1 ...
star - Cloudfront.net
... the region of space around them. 2. Although the stars that make up a pattern appear to be close together, they are not all the same distance from Earth. ...
... the region of space around them. 2. Although the stars that make up a pattern appear to be close together, they are not all the same distance from Earth. ...
Properties of Stars - Montana State University Extended University
... In order to better understand how stars are constructed, astronomers look for correlations between stellar properties. The easiest way to do this is make a plot of one intrinsic property vs. another intrinsic property. An intrinsic property is one that does not depend on the distance the star is fro ...
... In order to better understand how stars are constructed, astronomers look for correlations between stellar properties. The easiest way to do this is make a plot of one intrinsic property vs. another intrinsic property. An intrinsic property is one that does not depend on the distance the star is fro ...
Big Bang Theory
... “nebulae” and determined that these objects were located far outside the Milky Way. This confirmed that these “nebulae” were in fact other galaxies much like our own Milky Way. In 1912 another American astronomer, Vesto Slipher, analyzed spectrographs of galaxies and measured their redshift. Hubble ...
... “nebulae” and determined that these objects were located far outside the Milky Way. This confirmed that these “nebulae” were in fact other galaxies much like our own Milky Way. In 1912 another American astronomer, Vesto Slipher, analyzed spectrographs of galaxies and measured their redshift. Hubble ...
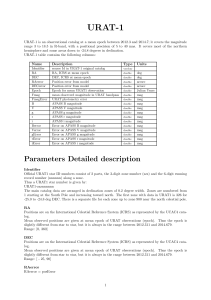
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
The Star Finder Book - Starpath School of Navigation
... New navigators soon learn that these unknown stars may offer the only sights available for several days, and that this can occur much more often than was suspected. This is not just true in high-latitude oceans, famous for cloudy skies; it is a potential problem in all oceans including those of the ...
... New navigators soon learn that these unknown stars may offer the only sights available for several days, and that this can occur much more often than was suspected. This is not just true in high-latitude oceans, famous for cloudy skies; it is a potential problem in all oceans including those of the ...
STELLAR CLASSIFICATIONS: TYPE “O” STARS
... The one biggest plus to “M” class stars is that they live a very long time. 56 billion years on average. With lifespans more than 5 times that of the sun, there’s plenty of time for life to evolve around a star such as this. Color: These stars appear orange-red in the visible spectrum, but emit most ...
... The one biggest plus to “M” class stars is that they live a very long time. 56 billion years on average. With lifespans more than 5 times that of the sun, there’s plenty of time for life to evolve around a star such as this. Color: These stars appear orange-red in the visible spectrum, but emit most ...
My power point presentation on spectroscopy of stars (ppt file)
... • This star shows strong Zeeman splitting in almost every spectral line, due to a magnetic field of 14.5 kG (1.45 Tesla) • The trace elements in the atmosphere are stratified vertically and horizontally patchy. I have not included enough of these effects in my model to reproduce the observed spectru ...
... • This star shows strong Zeeman splitting in almost every spectral line, due to a magnetic field of 14.5 kG (1.45 Tesla) • The trace elements in the atmosphere are stratified vertically and horizontally patchy. I have not included enough of these effects in my model to reproduce the observed spectru ...
mass loss of massive stars - of /proceedings
... Although short, the RSG phase strongly impacts on the neighbouring environment. In that phase, mass loss rates range from 10−7 to 10−4 M and the wind velocities are typically of 10 to 40 km s−1 . Hence, the wind density is about a thousand times larger than in the OB phase. Fig. 2 shows mass loss r ...
... Although short, the RSG phase strongly impacts on the neighbouring environment. In that phase, mass loss rates range from 10−7 to 10−4 M and the wind velocities are typically of 10 to 40 km s−1 . Hence, the wind density is about a thousand times larger than in the OB phase. Fig. 2 shows mass loss r ...
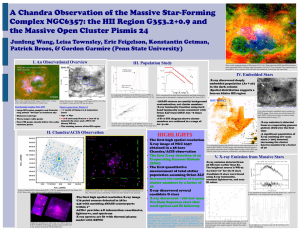
A Chandra Observation of the Massive Star-Forming
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
Lect15-3-23-11-stars..
... energy that escaped from the surface of the core with heat energy generated in the collapse from release of gravitational potential energy. But this cannot be true, since the collapse makes the core smaller. The core’s mass is still the same, but now its smaller size means that its gravity is strong ...
... energy that escaped from the surface of the core with heat energy generated in the collapse from release of gravitational potential energy. But this cannot be true, since the collapse makes the core smaller. The core’s mass is still the same, but now its smaller size means that its gravity is strong ...
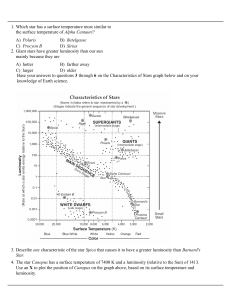
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
... than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel 55. The coolest stars appear A) white B) red C) yellow D) blue 56. Most of the radiant energy released by the sun results from the process of A) nuclear fission B) nuclea ...
... than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel 55. The coolest stars appear A) white B) red C) yellow D) blue 56. Most of the radiant energy released by the sun results from the process of A) nuclear fission B) nuclea ...
A billion pixels, a billion stars
... The stars in the Milky Way disc primarily form in small clusters inside larger star-forming regions (such as the Orion nebula) before diffusing away from their origins. During this spatial diffusion, their velocities remained clustered. Hence, if we know their distances and velocities very precisely ...
... The stars in the Milky Way disc primarily form in small clusters inside larger star-forming regions (such as the Orion nebula) before diffusing away from their origins. During this spatial diffusion, their velocities remained clustered. Hence, if we know their distances and velocities very precisely ...
Latitude and Longitude - Harvard University Laboratory for
... – Observe height of two or more celestial bodies, where you know their declination and SHA – Know time of observation – Gives two lines of position – Intersection of two lines gives position. – Process is called “sight reduction” ...
... – Observe height of two or more celestial bodies, where you know their declination and SHA – Know time of observation – Gives two lines of position – Intersection of two lines gives position. – Process is called “sight reduction” ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.