The Sculptor dwarf irregular galaxy SDIG: present and past
... indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of other late-type galaxies, suggesting that SDIG has faded by less than a magnitude in B since it stopped forming stars. Highly luminous red stars have been discovered ...
... indicating that the galaxy is now in a relatively quiescent state. However, the ratio of the H I mass to blue luminosity is typical of other late-type galaxies, suggesting that SDIG has faded by less than a magnitude in B since it stopped forming stars. Highly luminous red stars have been discovered ...
Arcturus - bYTEBoss
... Exactly whom Boötes is supposed to represent is not clear. According to one version, he was a ploughman who drove the oxen in the constellation Ursa Major using his two dogs Chara and Asterion (from the constellation Canes Venatici). The oxen were tied to the polar axis and so the action of Boötes k ...
... Exactly whom Boötes is supposed to represent is not clear. According to one version, he was a ploughman who drove the oxen in the constellation Ursa Major using his two dogs Chara and Asterion (from the constellation Canes Venatici). The oxen were tied to the polar axis and so the action of Boötes k ...
The Great Nebula in Orion
... Hubble’s high resolution enables us to separate the light of the closely packed stars in Orion. Its high stability and lightmeasuring accuracy overcome the challenge of the non-uniform brightness of nebula. In the Hubble images, we can precisely compare the stellar signals through many filters. We c ...
... Hubble’s high resolution enables us to separate the light of the closely packed stars in Orion. Its high stability and lightmeasuring accuracy overcome the challenge of the non-uniform brightness of nebula. In the Hubble images, we can precisely compare the stellar signals through many filters. We c ...
A Search for New Solar-Type Post-T Tauri Stars in
... 1. Those meeting the safety standards of the observatory based on the bright star and background web tools have been included in the table given in the “Description of Observations” section. Because our relatively low galactic latitude fields are expected to be rich in stars we have not attempted to ...
... 1. Those meeting the safety standards of the observatory based on the bright star and background web tools have been included in the table given in the “Description of Observations” section. Because our relatively low galactic latitude fields are expected to be rich in stars we have not attempted to ...
The Life Cycle of A Star
... electrons in the core of the star repulsing each other. With no fuel left to burn, the hot star radiates its remaining heat into the coldness of space for many billions of years. In the end, it will just sit in space as a cold dark mass sometimes referred to as a black dwarf. B. The Fate of Massive ...
... electrons in the core of the star repulsing each other. With no fuel left to burn, the hot star radiates its remaining heat into the coldness of space for many billions of years. In the end, it will just sit in space as a cold dark mass sometimes referred to as a black dwarf. B. The Fate of Massive ...
Document
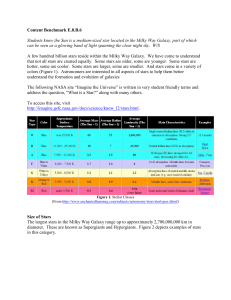
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision
... showing flattened shape – (camera angle zoom-out) Andromeda and M33 heading towards Milky Way – (4 billion years) Direct Milky Way – Andromeda collision ...
... showing flattened shape – (camera angle zoom-out) Andromeda and M33 heading towards Milky Way – (4 billion years) Direct Milky Way – Andromeda collision ...
Low mass stars
... The Mass-Luminosity Relationship Mass is the most important physical characteristic of stars - it determines luminosity, temperature, lifetime etc. How do we obtain the mass of stars? – use binary star systems and Kepler’s 3rd Law (for visible binaries – for spectroscopic binaries the orbital inclin ...
... The Mass-Luminosity Relationship Mass is the most important physical characteristic of stars - it determines luminosity, temperature, lifetime etc. How do we obtain the mass of stars? – use binary star systems and Kepler’s 3rd Law (for visible binaries – for spectroscopic binaries the orbital inclin ...
Presentation - Relativity Group
... What have we learned? • How can we learn about the lives of stars, which last millions to billions of years? • By taking observations of many stars, we can study stars in many phases of life, just as we might study how humans age by observing the humans living in a village at one time. • What two ba ...
... What have we learned? • How can we learn about the lives of stars, which last millions to billions of years? • By taking observations of many stars, we can study stars in many phases of life, just as we might study how humans age by observing the humans living in a village at one time. • What two ba ...
Introduction and first data set
... faint fuzzballs are very hard to observe: you need a huge telescope and a lot of exposure time. The time allocation committee therefore chose to give them observations of the five faintest fuzzballs in the New Fuzzball Catalogue, a catalogue of the thousand brightest fuzzballs in the sky. All observ ...
... faint fuzzballs are very hard to observe: you need a huge telescope and a lot of exposure time. The time allocation committee therefore chose to give them observations of the five faintest fuzzballs in the New Fuzzball Catalogue, a catalogue of the thousand brightest fuzzballs in the sky. All observ ...
Structure of the solar system
... Be A Fine Girl/Guy Kiss Me”. The systems is based on the surface temperature of the star. O ≥ 30,000 K blue (most massive) B 10,000–30,000 K blue to blue white A 7,500–10,000 K white F 6,000–7,500 K yellowish white G 5,200–6,000 K yellow K 3,700–5,200 K orange M ≤ 3,700 K red (least massive) Our sta ...
... Be A Fine Girl/Guy Kiss Me”. The systems is based on the surface temperature of the star. O ≥ 30,000 K blue (most massive) B 10,000–30,000 K blue to blue white A 7,500–10,000 K white F 6,000–7,500 K yellowish white G 5,200–6,000 K yellow K 3,700–5,200 K orange M ≤ 3,700 K red (least massive) Our sta ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.