Notes 6 - University of Northern Iowa
... Hot, surface temperatures ranging from 5000 – 80,000 K Core temperature of ~107 K. Temperature decreases as it ages Small radius, approximately the size of the Earth, around 6000 km. Masses are not too diverse, typically only 0.6 M Maximum mass defined by the Chandrasekhar limit (equati ...
... Hot, surface temperatures ranging from 5000 – 80,000 K Core temperature of ~107 K. Temperature decreases as it ages Small radius, approximately the size of the Earth, around 6000 km. Masses are not too diverse, typically only 0.6 M Maximum mass defined by the Chandrasekhar limit (equati ...
The star Epsilon UMa, or more commonly known as Alioth
... horse”), is the third star from the tail-end of the Big Dipper located approximately 80.9 ± 1.2 light years away.9 Alioth and the Big Dipper are also a part of the constellation Ursa Major, also known as The Great Bear. In Greek mythology, it is said that there once was a daughter of King Lycaon nam ...
... horse”), is the third star from the tail-end of the Big Dipper located approximately 80.9 ± 1.2 light years away.9 Alioth and the Big Dipper are also a part of the constellation Ursa Major, also known as The Great Bear. In Greek mythology, it is said that there once was a daughter of King Lycaon nam ...
First Stars II
... Formation of the second generation of stars is still quite uncertain. Metallicity/ radiation can induce the transition from massive to low-mass star formation mode. ...
... Formation of the second generation of stars is still quite uncertain. Metallicity/ radiation can induce the transition from massive to low-mass star formation mode. ...
PSC100 Summary Chapters 1 to Chapter 9
... you must multiply this basic number by ten if the superscript is positive, or the number of times you must divide it by ten if the superscript is negative. Because you will see numbers written in this notation quite often during your study of astronomy, you should take a few minutes now to familiar ...
... you must multiply this basic number by ten if the superscript is positive, or the number of times you must divide it by ten if the superscript is negative. Because you will see numbers written in this notation quite often during your study of astronomy, you should take a few minutes now to familiar ...
B LOG - Science Centre
... Betelgeuse (alpha Orionis) is a massive red supergiant that varies in brightness. Bellatrix (gamma Orionis), is blue giant star. Its name means “female warrior”, indicating that Orion may not have always been seen as a male hunter. Bellatrix is the closest of Orion’s stars (243 light years away). Ri ...
... Betelgeuse (alpha Orionis) is a massive red supergiant that varies in brightness. Bellatrix (gamma Orionis), is blue giant star. Its name means “female warrior”, indicating that Orion may not have always been seen as a male hunter. Bellatrix is the closest of Orion’s stars (243 light years away). Ri ...
The Hipparcos Star Globe Booklet - Cosmos
... the globe, there would be on average over 24 000 stars per square degree - and no space left for sky! The globe draws on the Hipparcos map of the sky: a colour, all-sky map in Galactic coordinates synthesised from Hipparcos and Tycho data products. The full-size map shows around 2.5 million of the b ...
... the globe, there would be on average over 24 000 stars per square degree - and no space left for sky! The globe draws on the Hipparcos map of the sky: a colour, all-sky map in Galactic coordinates synthesised from Hipparcos and Tycho data products. The full-size map shows around 2.5 million of the b ...
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM
... Sun, is the solar system’s source of heat and light as well as its central mass, a gravitational anchor holding everything together as we travel around the galaxy. Its warmth naturally divides the planetary system into two zones of disparate size: one hot, bright, and compact, and the other cold, da ...
... Sun, is the solar system’s source of heat and light as well as its central mass, a gravitational anchor holding everything together as we travel around the galaxy. Its warmth naturally divides the planetary system into two zones of disparate size: one hot, bright, and compact, and the other cold, da ...
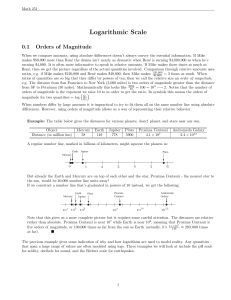
Log Scale Notes
... But already the Earth and Mercury are on top of each other and the star, Proxima Centauri - the nearest star to the sun, would be 40,000 number line units away! If we construct a number line that’s graduated in powers of 10 instead, we get the following: Mercury ...
... But already the Earth and Mercury are on top of each other and the star, Proxima Centauri - the nearest star to the sun, would be 40,000 number line units away! If we construct a number line that’s graduated in powers of 10 instead, we get the following: Mercury ...
Life and Death of Stars - UM Research Repository
... circulation can be measured, hence they can be referred for directions, as well as the measurement of time. Stars are one of the beautiful objects which come out at night which becomes the symbolic of the hundreds of thousands of the members of heaven. The stars life cycles are following some stages ...
... circulation can be measured, hence they can be referred for directions, as well as the measurement of time. Stars are one of the beautiful objects which come out at night which becomes the symbolic of the hundreds of thousands of the members of heaven. The stars life cycles are following some stages ...
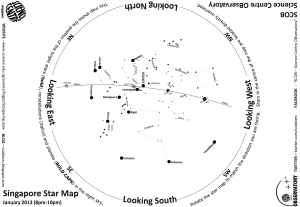
Sky Maps Teacher`s Guide - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Circumpolar Constellations and Stars are the constellations and stars that never set. The number of circumpolar constellations you see depends on your latitude. The further north or south you travel from the equator, the more stars become circumpolar. At the equator, no stars are circumpolar. At the ...
... Circumpolar Constellations and Stars are the constellations and stars that never set. The number of circumpolar constellations you see depends on your latitude. The further north or south you travel from the equator, the more stars become circumpolar. At the equator, no stars are circumpolar. At the ...
Galaxy Questions Info
... A spiral galaxy consists of a flattened disk containing spiral (pinwheel-shaped) arms, a bulge at its center, and a halo. Spiral galaxies have a variety of shapes, and they are classified according to the size of the bulge and the tightness and appearance of the arms. The spiral arms, which wrap aro ...
... A spiral galaxy consists of a flattened disk containing spiral (pinwheel-shaped) arms, a bulge at its center, and a halo. Spiral galaxies have a variety of shapes, and they are classified according to the size of the bulge and the tightness and appearance of the arms. The spiral arms, which wrap aro ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 11-20
... massive star in our Milky Way Galaxy – Eta Carinae. It radiates five million times more brightly than the Sun and is about 120 times more massive. It sheds about two Earth masses each day in its stellar wind. If the Sun gave off this much mass it would be gone in a mere 300 years. The star lies with ...
... massive star in our Milky Way Galaxy – Eta Carinae. It radiates five million times more brightly than the Sun and is about 120 times more massive. It sheds about two Earth masses each day in its stellar wind. If the Sun gave off this much mass it would be gone in a mere 300 years. The star lies with ...
CHP 13
... d. a white dwarf in a close binary system. e. a solar like star that has exhausted its hydrogen and helium. The Algol paradox is explained by considering a. the degenerate nature of the hydrogen on the surface of the white dwarf. b. that iron is the most tightly bound of all atomic nuclei. c. the ra ...
... d. a white dwarf in a close binary system. e. a solar like star that has exhausted its hydrogen and helium. The Algol paradox is explained by considering a. the degenerate nature of the hydrogen on the surface of the white dwarf. b. that iron is the most tightly bound of all atomic nuclei. c. the ra ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.