NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... Our own neck of the woods in the cosmos is called the Local Group, and in it our Milky Way is joined by two other spiral galaxies that are visible even with the unaided eye in a rural, moonless sky (making them the largest objects you can see without aid!). They’re both in the same part of the sky, ...
... Our own neck of the woods in the cosmos is called the Local Group, and in it our Milky Way is joined by two other spiral galaxies that are visible even with the unaided eye in a rural, moonless sky (making them the largest objects you can see without aid!). They’re both in the same part of the sky, ...
star
... Giants are large bright stars that are smaller and fainter than supergiants. A white dwarf is the small dense remains of a low or medium-‐mass star. ...
... Giants are large bright stars that are smaller and fainter than supergiants. A white dwarf is the small dense remains of a low or medium-‐mass star. ...
File
... – what type of star it is, which give us… – its absolute brightness (among other things) • For example, the stars that are close enough to have their distance measured with parallax will have their spectrum analyzed. • From this, we can determine how bright a certain class of stars is supposed to be ...
... – what type of star it is, which give us… – its absolute brightness (among other things) • For example, the stars that are close enough to have their distance measured with parallax will have their spectrum analyzed. • From this, we can determine how bright a certain class of stars is supposed to be ...
Chapter 15 (Star Lives)
... A. all have the same age. B. all have the same mass. C. all have the same chemical composition. D. are at different stages of their lives. 2. In making a model of a star, an astronomer does NOT have to know or assume: A. that the energy given off is produced in the interior. B. the mass of the star. ...
... A. all have the same age. B. all have the same mass. C. all have the same chemical composition. D. are at different stages of their lives. 2. In making a model of a star, an astronomer does NOT have to know or assume: A. that the energy given off is produced in the interior. B. the mass of the star. ...
The winter triangle - NRC Publications Archive
... mass of the Sun, it is easy to see that it cannot keep this up for long. The Sun has been burning for around 4.5 billion years. Betelgeux cannot be more than about 10 million years old and is unlikely to last another ten million. Our star, along with Sirius and Procyon will end its life by sneezing ...
... mass of the Sun, it is easy to see that it cannot keep this up for long. The Sun has been burning for around 4.5 billion years. Betelgeux cannot be more than about 10 million years old and is unlikely to last another ten million. Our star, along with Sirius and Procyon will end its life by sneezing ...
Ursa Minor
... Contains the Big Dipper The line that connects Dubhe with Merak points to Polaris, the North Star ...
... Contains the Big Dipper The line that connects Dubhe with Merak points to Polaris, the North Star ...
Answers to Final Exam – Study Guide
... 83. The type of friction that an airplane that is flying experiences is called fluid friction 84. The property of a moving object that depends on its mass and velocity is called momentum 85. The two components of all forces are magnitude and direction 86. Large dark areas on the surface of the moon ...
... 83. The type of friction that an airplane that is flying experiences is called fluid friction 84. The property of a moving object that depends on its mass and velocity is called momentum 85. The two components of all forces are magnitude and direction 86. Large dark areas on the surface of the moon ...
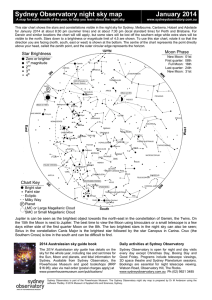
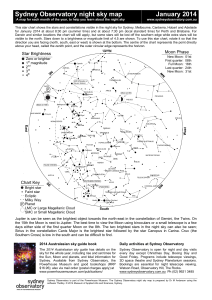
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
ASTR 200 : Lecture 15 Ensemble Properties of Stars
... on stellar surface temperature. ● Note, in practice that getting luminosity is tricky, and they used 'spectral class' as a proxy for temperature (see ASTR 205) ...
... on stellar surface temperature. ● Note, in practice that getting luminosity is tricky, and they used 'spectral class' as a proxy for temperature (see ASTR 205) ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.