Document
... Option E — Astrophysics E1. This question is about the relative population density of stars and galaxies. The number of stars around the Sun, within a distance of 17 ly, is 75. The number of galaxies in the local group, within a distance of 4.0 x 106 ly from the Sun, is 26. (a) Calculate the average ...
... Option E — Astrophysics E1. This question is about the relative population density of stars and galaxies. The number of stars around the Sun, within a distance of 17 ly, is 75. The number of galaxies in the local group, within a distance of 4.0 x 106 ly from the Sun, is 26. (a) Calculate the average ...
Ch 19 Directed Reading
... 17. A huge explosion in which a large star dies is called a _____________________________. 18. A star made up of neutrons is called a _____________________________. 19. A spinning neutron star that emits pulses of energy is called a _____________________________. 20. An object so massive and dense t ...
... 17. A huge explosion in which a large star dies is called a _____________________________. 18. A star made up of neutrons is called a _____________________________. 19. A spinning neutron star that emits pulses of energy is called a _____________________________. 20. An object so massive and dense t ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Why does the North Star appear to be fixed in the sky while all other object move? What would be the view of the night sky from the North pole? Why can't we see the same constellations in the evening sky throughout the year? Why haven’t constellation patters changed since they have been established ...
... Why does the North Star appear to be fixed in the sky while all other object move? What would be the view of the night sky from the North pole? Why can't we see the same constellations in the evening sky throughout the year? Why haven’t constellation patters changed since they have been established ...
luminosity1
... Spectral typing Summary • Spectral typing can be used to find the surface temperature of a star. (Along with color and Wien’s Law) • Spectral typing can also be used to find out how much of a given element is in a star. • HD 161817 has much less of all the elements, other than Hydrogen and Helium, ...
... Spectral typing Summary • Spectral typing can be used to find the surface temperature of a star. (Along with color and Wien’s Law) • Spectral typing can also be used to find out how much of a given element is in a star. • HD 161817 has much less of all the elements, other than Hydrogen and Helium, ...
A little bit more to do. Stefan
... is made of steel and is being heated from inside. We move a light collector (maybe a huge bundle of fiber optic cables) that is 1meter X 1meter, right up close to one of the surfaces so we can capture all the light being emitted from that side of the cube. The cube begins to glow, and we send the li ...
... is made of steel and is being heated from inside. We move a light collector (maybe a huge bundle of fiber optic cables) that is 1meter X 1meter, right up close to one of the surfaces so we can capture all the light being emitted from that side of the cube. The cube begins to glow, and we send the li ...
Groups of Stars
... the light from reaching Earth, the star system is called an eclipsing binary. The brightness of an eclipsing binary varies over time in a regular pattern. ...
... the light from reaching Earth, the star system is called an eclipsing binary. The brightness of an eclipsing binary varies over time in a regular pattern. ...
NASAexplores 9-12 Lesson: Classified Stars - Science
... American Henry Russell, determined a pattern in the life of stars. They arranged stars on a chart according to their color and brightness. The most amazing thing is that they did not even know one other, and did their experiments completely independent of each other. Therefore, this chart is called ...
... American Henry Russell, determined a pattern in the life of stars. They arranged stars on a chart according to their color and brightness. The most amazing thing is that they did not even know one other, and did their experiments completely independent of each other. Therefore, this chart is called ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
... in the lower right corner called red dwarfs. The more massive the star, the faster the rate of fusion, and the less time is remains on the main sequence. The amount of time that a star spends on the main sequence is also a function of its mass and luminosity and is defined as: T(years) = 1010M. L Th ...
... in the lower right corner called red dwarfs. The more massive the star, the faster the rate of fusion, and the less time is remains on the main sequence. The amount of time that a star spends on the main sequence is also a function of its mass and luminosity and is defined as: T(years) = 1010M. L Th ...
Astronomy Review revised Key
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
Deep Space (PDF: 224k)
... of the visible disk of stars. Most astronomers believe there is a black hole in the center of the Milky Way, but ours is only about a thousandth of the ...
... of the visible disk of stars. Most astronomers believe there is a black hole in the center of the Milky Way, but ours is only about a thousandth of the ...
After Dark M S
... and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binar ...
... and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binar ...
Define the following terms in the space provided
... sidereal year 365.2564 days tropical year 365.2422 days Gregorian year 365.2425 days Earth mass 5.9736× 1024 kilograms Sun mass 1.9891× 1030 kg = 332,980 × Earth mean Earth radius 6371 kilometers Sun radius 6.96265 × 105 km = 109 × Earth Sun luminosity 3.827× 1026 watts ...
... sidereal year 365.2564 days tropical year 365.2422 days Gregorian year 365.2425 days Earth mass 5.9736× 1024 kilograms Sun mass 1.9891× 1030 kg = 332,980 × Earth mean Earth radius 6371 kilometers Sun radius 6.96265 × 105 km = 109 × Earth Sun luminosity 3.827× 1026 watts ...
Way Milky the MAPPING
... In their work, Quillen and her colleagues focused on the forces acting on the stars in or near the bulge. As the stars go through their orbits, they also move above and below the plane of the bar. And like a child on a swing, each time a star crosses the plane of the bar at what’s known as the reson ...
... In their work, Quillen and her colleagues focused on the forces acting on the stars in or near the bulge. As the stars go through their orbits, they also move above and below the plane of the bar. And like a child on a swing, each time a star crosses the plane of the bar at what’s known as the reson ...
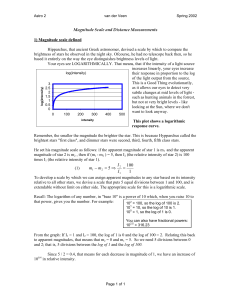
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... 2) Finding the distance to a star from its absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude: The visual magnitude you observe for a star depends both on its intrinsic luminosity and its distance. In order to bring all stars to the same "reference distance" so that we can really compare their magnitudes, we ...
... 2) Finding the distance to a star from its absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude: The visual magnitude you observe for a star depends both on its intrinsic luminosity and its distance. In order to bring all stars to the same "reference distance" so that we can really compare their magnitudes, we ...
Stars are made of very hot gas. This gas is mostly hydrogen and
... Like a light house, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are rare, they make up many of the stars we see at night Blue giant stars die in a spectacular way They grow larger just like the Sun sized stars, but then instead of shrinking and forming a planetary nebula they ex ...
... Like a light house, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are rare, they make up many of the stars we see at night Blue giant stars die in a spectacular way They grow larger just like the Sun sized stars, but then instead of shrinking and forming a planetary nebula they ex ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.