Week 6
... has a radius 936 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What is the luminosity of this star? If Betelgeuse is 640 ly from Earth, what is the brightness of the light from Betelgeuse that reaches Earth? ...
... has a radius 936 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 3500 K. What is the luminosity of this star? If Betelgeuse is 640 ly from Earth, what is the brightness of the light from Betelgeuse that reaches Earth? ...
slides
... Q: Which is larger? A. K-type main sequence star B. K-type giant C. they are about the same ...
... Q: Which is larger? A. K-type main sequence star B. K-type giant C. they are about the same ...
Colour - Magnitude Diagram for M 45
... Colour - Magnitude Diagram for M 45 (Pleiades) Introduction The Pleiades is a relatively close open cluster. The six or seven stars visible to the naked eye form a tight grouping of stars (an asterism) near the even closer Hyades cluster. They are easily visible in the winter sky in the northern hem ...
... Colour - Magnitude Diagram for M 45 (Pleiades) Introduction The Pleiades is a relatively close open cluster. The six or seven stars visible to the naked eye form a tight grouping of stars (an asterism) near the even closer Hyades cluster. They are easily visible in the winter sky in the northern hem ...
Is the Sun a Star? - Classroom Websites
... The probe is primarily designed for students in upper elementary grades or middle school, although it can be used with students in high school as well, both to learn abour students' current thinking and to spark conversation as an introduction to a unit on stars. If students aren't sure what is mean ...
... The probe is primarily designed for students in upper elementary grades or middle school, although it can be used with students in high school as well, both to learn abour students' current thinking and to spark conversation as an introduction to a unit on stars. If students aren't sure what is mean ...
Geography
... The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
OUR COSMIC NEIGHBORS Story of the Stars
... This constellation is found directly across the Pole from Ursa Major. Both are circumpolar constellations, so when one is high in the sky, the other is low over the northern point. Cassiopeia is characterized by a zigzag row of second magnitude stars, forming an irregular “M” or “W” according to the ...
... This constellation is found directly across the Pole from Ursa Major. Both are circumpolar constellations, so when one is high in the sky, the other is low over the northern point. Cassiopeia is characterized by a zigzag row of second magnitude stars, forming an irregular “M” or “W” according to the ...
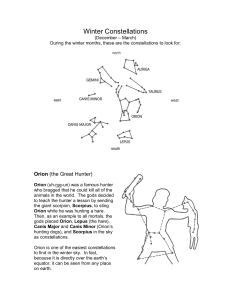
seven winter constellations
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
... animals in the world. The gods decided to teach the hunter a lesson by sending the giant scorpion, Scorpius, to sting Orion while he was hunting a hare. Then, as an example to all mortals, the gods placed Orion, Lepus (the hare), Canis Major and Canis Minor (Orion’s hunting dogs), and Scorpius in th ...
Chapter 30 Notes
... As the planetary nebula disperses; gravity causes the remaining matter in the star to collapse inward until it cannot be pressed further together. A hot, extremely dense core of matter is left behind. This mass is called a white dwarf and can shine for billions of years before it cools completely. S ...
... As the planetary nebula disperses; gravity causes the remaining matter in the star to collapse inward until it cannot be pressed further together. A hot, extremely dense core of matter is left behind. This mass is called a white dwarf and can shine for billions of years before it cools completely. S ...
Wednesday, April 17 - Otterbein University
... – get the luminosity. This is your y-coordinate. – Then take the spectral type as your x-coordinate, e.g. K5 for Aldebaran. First letter is the spectral type: K (one of OBAFGKM), the arab number (5) is like a second digit to the spectral type, so K0 is very close to G, K9 is very close to M. ...
... – get the luminosity. This is your y-coordinate. – Then take the spectral type as your x-coordinate, e.g. K5 for Aldebaran. First letter is the spectral type: K (one of OBAFGKM), the arab number (5) is like a second digit to the spectral type, so K0 is very close to G, K9 is very close to M. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram—key to understanding properties of stars. 26 Sept
... – A show highlighting the current sky, spectacular gatherings of Venus with the moon and other planets in coming months. See what Galileo saw through his telescope 400 years ago— the Milky Way and the Pleiades, details on the moon, the four moons of Jupiter, the phases of Venus, and the mysterious d ...
... – A show highlighting the current sky, spectacular gatherings of Venus with the moon and other planets in coming months. See what Galileo saw through his telescope 400 years ago— the Milky Way and the Pleiades, details on the moon, the four moons of Jupiter, the phases of Venus, and the mysterious d ...
The Temperatures of Stars
... This information doesn’t decay or expire as the light travels through space. By examining the light of distant objects (stars, galaxies, or anything else), we can learn a great deal about the objects without touching them. Today we understand the information that light carries, but that wasn’t the c ...
... This information doesn’t decay or expire as the light travels through space. By examining the light of distant objects (stars, galaxies, or anything else), we can learn a great deal about the objects without touching them. Today we understand the information that light carries, but that wasn’t the c ...
Astrophysics E1. This question is about stars.
... Option E — Astrophysics E1. This question is about the relative population density of stars and galaxies. The number of stars around the Sun, within a distance of 17 ly, is 75. The number of galaxies in the local group, within a distance of 4.0 x 106 ly from the Sun, is 26. (a) Calculate the average ...
... Option E — Astrophysics E1. This question is about the relative population density of stars and galaxies. The number of stars around the Sun, within a distance of 17 ly, is 75. The number of galaxies in the local group, within a distance of 4.0 x 106 ly from the Sun, is 26. (a) Calculate the average ...
Stars - HMXEarthScience
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
Chapter11
... understand how stars work. For instance, what stops a contracting star and gives it stability? We can understand this phenomenon because we understand some of the basic laws of physics. ...
... understand how stars work. For instance, what stops a contracting star and gives it stability? We can understand this phenomenon because we understand some of the basic laws of physics. ...
Slide 1 - Typepad
... Auriga contains an nteresting variety: many open clusters and nebulous regions simply because the Milky Way runs through it. 3 Open clusters in/out of pentagon of Constellation Auriga south of Capella. M37 the richest cluster containing over 500 stars spread across 20 arcminutes and is the brightest ...
... Auriga contains an nteresting variety: many open clusters and nebulous regions simply because the Milky Way runs through it. 3 Open clusters in/out of pentagon of Constellation Auriga south of Capella. M37 the richest cluster containing over 500 stars spread across 20 arcminutes and is the brightest ...
Cassiopeia (constellation)

Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopeia was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it has a 'W' shape, formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper.In northern locations above 34ºN latitude it is visible year-round and in the (sub)tropics it can be seen at its clearest from September to early November in its characteristic 'M' shape. Even in low southern latitudes below 25ºS is can be seen low in the North.