Ch. 27 Stars & Galaxies
... • The core of the supernova may contract into a small dense area of neutrons = neutron star o Some may emit beams of radiation called pulsars ...
... • The core of the supernova may contract into a small dense area of neutrons = neutron star o Some may emit beams of radiation called pulsars ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? Blue and White 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? Blue and White (also, hottest) a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? The hotter the star, the more energy it has b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? Along ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? Blue and White 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? Blue and White (also, hottest) a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? The hotter the star, the more energy it has b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? Along ...
Astronomical terms and constants
... Mbol = 4.8 − 2.5 log (L/L⊙ ) = absolute bolometric magnitude of a star with a luminosity L . “Bolometric” means integrated over the entire stellar spectral energy distribution. Mbol,⊙ = +4.74. MV = Mbol − BC = absolute visual magnitude of a star; BC is a bolometric correction, and V indicates that w ...
... Mbol = 4.8 − 2.5 log (L/L⊙ ) = absolute bolometric magnitude of a star with a luminosity L . “Bolometric” means integrated over the entire stellar spectral energy distribution. Mbol,⊙ = +4.74. MV = Mbol − BC = absolute visual magnitude of a star; BC is a bolometric correction, and V indicates that w ...
The Sun . . .
... H-R Diagram: Diagram that classifies stars according to their luminosity/absolute magnitude, and spectral class based on color and surface temperature. Luminosity: The brightness of a star compared to the Sun. Absolute Magnitude: Compares the brightness of stars from a standard distance ...
... H-R Diagram: Diagram that classifies stars according to their luminosity/absolute magnitude, and spectral class based on color and surface temperature. Luminosity: The brightness of a star compared to the Sun. Absolute Magnitude: Compares the brightness of stars from a standard distance ...
How is a Star`s Color Related to Its temperature?
... How is a Star’s Color Related to Its temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than cthers. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russel ...
... How is a Star’s Color Related to Its temperature? On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than cthers. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue. and Betelgense is red. Capella and ore" Sun are yellow, in this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russel ...
Document
... from us than 1 pc. b. Star A is closer to us than Star B. Both are closer to us than 1 pc. c. Star A is closer to us than 1 pc. Star B is farther than 1 pc. d. Star B is closer to us than 1 pc. Star A is farther than 1 pc. e. Star B is closer to us than Star A. Both are farther away than 1 pc. ...
... from us than 1 pc. b. Star A is closer to us than Star B. Both are closer to us than 1 pc. c. Star A is closer to us than 1 pc. Star B is farther than 1 pc. d. Star B is closer to us than 1 pc. Star A is farther than 1 pc. e. Star B is closer to us than Star A. Both are farther away than 1 pc. ...
Stars
... from us than 1 pc. b. Star A is closer to us than Star B. Both are closer to us than 1 pc. c. Star A is closer to us than 1 pc. Star B is farther than 1 pc. d. Star B is closer to us than 1 pc. Star A is farther than 1 pc. e. Star B is closer to us than Star A. Both are farther away than 1 pc. ...
... from us than 1 pc. b. Star A is closer to us than Star B. Both are closer to us than 1 pc. c. Star A is closer to us than 1 pc. Star B is farther than 1 pc. d. Star B is closer to us than 1 pc. Star A is farther than 1 pc. e. Star B is closer to us than Star A. Both are farther away than 1 pc. ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth • Ex: calculating absolute magnitude by making all stars 1 light-year away ...
... • The brightness a star would have if it was a standard distance from Earth • This requires an astronomer to determine both the apparent magnitude and distance from Earth • Ex: calculating absolute magnitude by making all stars 1 light-year away ...
d 2
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
What are stars? - Manhasset Schools
... nothing can escape its gravity • Usually results from the supernova of a very massive star ...
... nothing can escape its gravity • Usually results from the supernova of a very massive star ...
The Lives of Stars
... The core will shrink and grow hocer, burning more Hydrogen. The increased oudlow of energy will push out the outer layers, which will cool and become red. The sun will become a “R ...
... The core will shrink and grow hocer, burning more Hydrogen. The increased oudlow of energy will push out the outer layers, which will cool and become red. The sun will become a “R ...
Place in Space
... space. Light can travel about seven times around Earth in one second. Astronomers use the speed of light to measure how far away things are in space. They use light years. A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So ...
... space. Light can travel about seven times around Earth in one second. Astronomers use the speed of light to measure how far away things are in space. They use light years. A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... The second and longest stage in the life of a star is the main-sequence stage Main-sequence stars do not expand because the force of gravity pulls the ...
... The second and longest stage in the life of a star is the main-sequence stage Main-sequence stars do not expand because the force of gravity pulls the ...
Star Formation
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • The chart of the stars’ luminosity vs. temperature is called the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. • This is the H-R diagram for hundreds of nearby stars. – Temperature decreases to the right ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • The chart of the stars’ luminosity vs. temperature is called the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. • This is the H-R diagram for hundreds of nearby stars. – Temperature decreases to the right ...
The Lives of Stars
... • White dwarfs are only about the size of Earth, but they have about as much mass as the sun. • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truc ...
... • White dwarfs are only about the size of Earth, but they have about as much mass as the sun. • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truc ...
Science 8 Name: Unit 2 Astronomy Date: Period: LAB
... The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is actually an elaborate graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. Absolute magnitude is how bright stars would appear to be if they were all the same distance away from Earth. Ra ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram is actually an elaborate graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. Absolute magnitude is how bright stars would appear to be if they were all the same distance away from Earth. Ra ...
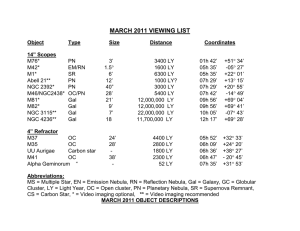
March
... Alpha Geminorum commonly known as the star Castor in the constellation Gemini (GEM-in-eye) is a fascinating triple star with a secret. Each of the stars in this triple system is itself a spectroscopic double star. So when we gaze at Castor we are in fact looking at a six star system. Star A (Magnitu ...
... Alpha Geminorum commonly known as the star Castor in the constellation Gemini (GEM-in-eye) is a fascinating triple star with a secret. Each of the stars in this triple system is itself a spectroscopic double star. So when we gaze at Castor we are in fact looking at a six star system. Star A (Magnitu ...
100 X size of Sun - East Penn School District
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF
... serious students of astrology. Opening page of Tetrabiblos, published in 1484. ...
... serious students of astrology. Opening page of Tetrabiblos, published in 1484. ...
Star and Sun Properties
... • As stars age and pass through different stages, their positions on the H-R diagram change. ...
... • As stars age and pass through different stages, their positions on the H-R diagram change. ...
Properties of Stars
... • Color is a clue to a star’s temperature • Very hot (30,000 K) stars emit their light in the blue spectrum, red stars are much cooler, stars with temperatures between 5000 and 6000 K appear yellow • Binary Stars – pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbit each other • Binary stars are ...
... • Color is a clue to a star’s temperature • Very hot (30,000 K) stars emit their light in the blue spectrum, red stars are much cooler, stars with temperatures between 5000 and 6000 K appear yellow • Binary Stars – pairs of stars, pulled together by gravity, that orbit each other • Binary stars are ...
Astronomy
... 23. Stars spend most of their lives in this stage 24. Powerful explosions that blast away the outer layers of massive stars near the end of their ...
... 23. Stars spend most of their lives in this stage 24. Powerful explosions that blast away the outer layers of massive stars near the end of their ...
HR Diagram Activity
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500°C are red. Shade a vertical column from 2,000°C to 3,500°C red. 4. Shade other color columns as follows: Stars up to 5,000°C are orange-red; up to 6,000°C yellow; 6000°C to 10,000°C are white (don’t shade); up to 20,000°C blue-white, and up to 40,000°C ...
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500°C are red. Shade a vertical column from 2,000°C to 3,500°C red. 4. Shade other color columns as follows: Stars up to 5,000°C are orange-red; up to 6,000°C yellow; 6000°C to 10,000°C are white (don’t shade); up to 20,000°C blue-white, and up to 40,000°C ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.