STARS Chapter 8 Section 1
... • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the man on the left? • W ...
... • Parallax is the object’s apparent shift in motion when viewed from different locations. It is an optical effect. • Astronomers can measure parallax and use it to calculate exact distances to stars. • Does the man on the right(V2) see the moon as closer or farther away than the man on the left? • W ...
Sky Watching Talk
... of stars all in roughly the same direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
... of stars all in roughly the same direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
Measuring stars Part I
... If p is in arcsec and d is in parsecs A star with a parallax of 1 arcsec is 1 parsec distant ...
... If p is in arcsec and d is in parsecs A star with a parallax of 1 arcsec is 1 parsec distant ...
the life cycle of stars
... become giants or supergiants (Right) and then down to the left to become white dwarfs. ...
... become giants or supergiants (Right) and then down to the left to become white dwarfs. ...
ppt
... Brightest stars are about 1011 times fainter that the Sun… If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
... Brightest stars are about 1011 times fainter that the Sun… If same luminosity, this means that they are about 300,000 times further away (i.e. 300,000 AU, or about 5 light years). ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... Double Stars/Star Clusters/Nebulae/Galaxies. ...
... Double Stars/Star Clusters/Nebulae/Galaxies. ...
Star Life Cycles
... A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size; such a star is near its final stage of life. White dwarfs eventually become black dwarfs, which is a white dwarf that has cooled down enough that it no longer emits light. Interes ...
... A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size; such a star is near its final stage of life. White dwarfs eventually become black dwarfs, which is a white dwarf that has cooled down enough that it no longer emits light. Interes ...
Stellar Distances and Magnitudes
... Luminosity vs. Color of Stars • In 1911, Ejnar Hertzsprung investigated the relationship between luminosity and colors of stars in within clusters. • In 1913, Henry Norris Russell did a similar study of nearby stars. ...
... Luminosity vs. Color of Stars • In 1911, Ejnar Hertzsprung investigated the relationship between luminosity and colors of stars in within clusters. • In 1913, Henry Norris Russell did a similar study of nearby stars. ...
JPL Small-Body Database Browser
... Classification of Stars • Furthermore, the classifications are each divided into tenths, with labels going from 0 to 9 – e.g. If a star is said to be a G-class star, it could, at its brightest, be classified as a G9 star, and at its dimmest, be classified as a G0 star. • The Sun is classified as a ...
... Classification of Stars • Furthermore, the classifications are each divided into tenths, with labels going from 0 to 9 – e.g. If a star is said to be a G-class star, it could, at its brightest, be classified as a G9 star, and at its dimmest, be classified as a G0 star. • The Sun is classified as a ...
Lifecycle of a Star
... Massive main sequence stars fuse hydrogen much faster than small or medium stars ...
... Massive main sequence stars fuse hydrogen much faster than small or medium stars ...
Friday, November 7 - Otterbein University
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Stars Unit 1-2: Stars
... • The closest star to Earth is the Sun. • The average distance from the Earth to QuickTime™ and a the Sun (since it varies greatly) is decompressor are needed150 to seemillion this picture. approximately kilometers. – This distance is designated as 1 Astronomical Unit, or AU. ...
... • The closest star to Earth is the Sun. • The average distance from the Earth to QuickTime™ and a the Sun (since it varies greatly) is decompressor are needed150 to seemillion this picture. approximately kilometers. – This distance is designated as 1 Astronomical Unit, or AU. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
... exhausted its ability to fuse other elements like carbon and oxygen, it will become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telesc ...
answers - Salem State University
... larger. In instellar medium (ISM) where there is not sufficient gravity to force the materials of the ISM to contract, the pressure will be lower than in a star or on most planets. 10. There is larger nuclear fusion (more energy and emission) in a high mass due to gravity increasing the pressure and ...
... larger. In instellar medium (ISM) where there is not sufficient gravity to force the materials of the ISM to contract, the pressure will be lower than in a star or on most planets. 10. There is larger nuclear fusion (more energy and emission) in a high mass due to gravity increasing the pressure and ...
White Dwarf
... electrons holds the material of the core apart. • This compressed material is degenerate matter. – Core of giant stars – Sun mass in Earth size ...
... electrons holds the material of the core apart. • This compressed material is degenerate matter. – Core of giant stars – Sun mass in Earth size ...
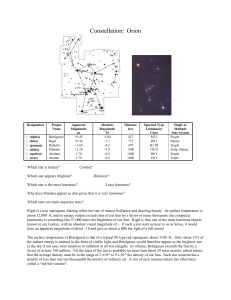
Orion
... luminosity is something like 57,000 times the brightness of our Sun. Rigel is thus one of the most luminous objects known in our Galaxy, with an absolute visual magnitude of -. If such a star were as near to us as Sirius, it would have an apparent magnitude of about –10 and give us about a fifth the ...
... luminosity is something like 57,000 times the brightness of our Sun. Rigel is thus one of the most luminous objects known in our Galaxy, with an absolute visual magnitude of -. If such a star were as near to us as Sirius, it would have an apparent magnitude of about –10 and give us about a fifth the ...
IB Precalculus
... (b) How many times louder does your normal speech seem as compared to your whisper? 4. Suppose your cell phone rings with a noise of 74 decibels, and you normally speak at 61 decibels. (a) What is the ratio of the sound intensity of your cell phone ring to the sound intensity of your normal speech? ...
... (b) How many times louder does your normal speech seem as compared to your whisper? 4. Suppose your cell phone rings with a noise of 74 decibels, and you normally speak at 61 decibels. (a) What is the ratio of the sound intensity of your cell phone ring to the sound intensity of your normal speech? ...
H-R Diagram - SFA Physics
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
... Now plot all the stars from Table 7 onto Figure 3. Table 7 is a list of the 30 stars nearest the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
Space Science Distance Definitions
... Earth would produce a parallax angle much, much too small to detect. We need to use as large a baseline as possible. The largest one we can easily use is the orbit of the Earth. In this case the baseline is the distance between the Earth and the Sun - an astronomical unit (AU) or 149.6 million kilom ...
... Earth would produce a parallax angle much, much too small to detect. We need to use as large a baseline as possible. The largest one we can easily use is the orbit of the Earth. In this case the baseline is the distance between the Earth and the Sun - an astronomical unit (AU) or 149.6 million kilom ...
7a Properties of Stars.pptx
... • Measured in light-‐years – distance light travels in one year (9.5 x 1012 or 9.5 trillion kilometers) ...
... • Measured in light-‐years – distance light travels in one year (9.5 x 1012 or 9.5 trillion kilometers) ...
common constellations
... also the stellar home of Sirius, which is the brightest star in the night sky. When Canis Major is visible, the brilliant white light of Sirius shines like a searchlight in the sky. Although Sirius is not a very large star, being only about one and one-half times as large as our own Sun, its young a ...
... also the stellar home of Sirius, which is the brightest star in the night sky. When Canis Major is visible, the brilliant white light of Sirius shines like a searchlight in the sky. Although Sirius is not a very large star, being only about one and one-half times as large as our own Sun, its young a ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most common shape Irregular galaxies—smaller, less common galaxies with various different shapes ...
... Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most common shape Irregular galaxies—smaller, less common galaxies with various different shapes ...
Life Cycle of a Star Notes
... together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is then called a black hole. We cannot see ...
... together to form heavier elements such as helium and release energy. If enough matter is left behind, this may be so dense, and its gravitational field so strong that nothing can escape from it, not even light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is then called a black hole. We cannot see ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.