Measuring the Stars
... The spectroscopic parallax calculation can be misleading if the star is not on the main sequence. The width of spectral lines can be used to define luminosity classes: ...
... The spectroscopic parallax calculation can be misleading if the star is not on the main sequence. The width of spectral lines can be used to define luminosity classes: ...
Stars
... sky, called Sirius. It is also the “Dog Star” because it forms the eye of the Great Dog, Canis Majoris. Sirius is bright for two reasons: first, because it is has a spectral class of A1, it is intrinsically bright. Its surface temperature is about 10,000 K. If Sirius were to somehow trade places wit ...
... sky, called Sirius. It is also the “Dog Star” because it forms the eye of the Great Dog, Canis Majoris. Sirius is bright for two reasons: first, because it is has a spectral class of A1, it is intrinsically bright. Its surface temperature is about 10,000 K. If Sirius were to somehow trade places wit ...
THE METER STICK MODEL OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult to predict how long it would take to run that ...
... 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult to predict how long it would take to run that ...
Lesson #5: Constellations - Center for Learning in Action
... Ask the students what they know about stars. Try to lead them towards the definition: Stars are massive shining spheres of hot gas. The stars you can see with your naked eye in the night sky are part of the Milky Way Galaxy, a huge system of stars that contains our solar system. Use pictures or over ...
... Ask the students what they know about stars. Try to lead them towards the definition: Stars are massive shining spheres of hot gas. The stars you can see with your naked eye in the night sky are part of the Milky Way Galaxy, a huge system of stars that contains our solar system. Use pictures or over ...
Stars
... Color of Stars • Look at the candle and Bunsen burner. Which is hotter? • The blue flame of the Bunsen burner is much hotter than the yellow flame of the candle. • Stars are different colors too, so we know they are different ...
... Color of Stars • Look at the candle and Bunsen burner. Which is hotter? • The blue flame of the Bunsen burner is much hotter than the yellow flame of the candle. • Stars are different colors too, so we know they are different ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Constellations 1
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
constellations[1]
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
Summer 2001 Day 07: Intro to Solar System
... 4) What does the brightness of a star depend on? A) Define brightness as the watts/m2 received from a star. B) Brightness follows an inverse square relation B=L/(4πR2). Draw the picture (see figure 54.2 C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightn ...
... 4) What does the brightness of a star depend on? A) Define brightness as the watts/m2 received from a star. B) Brightness follows an inverse square relation B=L/(4πR2). Draw the picture (see figure 54.2 C) Calculate the brightness of the Sun as seen from Earth B=1,355 W/m2 i) Typical stellar brightn ...
Stars and Universe Test Review - Garnet Valley School District
... produced from a distant star. Which conclusion can be made by comparing the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? A. The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. B. The star’s spectral lines have s ...
... produced from a distant star. Which conclusion can be made by comparing the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? A. The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. B. The star’s spectral lines have s ...
The Ursa Major Moving Cluster, Collinder 285
... approximately in the same spatial direction, and thus drift commonly through their cosmic neighborhood - a property typically found for members of a physical star cluster. The cluster is currently approaching us at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluste ...
... approximately in the same spatial direction, and thus drift commonly through their cosmic neighborhood - a property typically found for members of a physical star cluster. The cluster is currently approaching us at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluste ...
Stars - Madison County Schools
... up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star • Most of its life is in this phase ...
... up. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass and nuclear fusion begins. • Begins the main sequence phase of the star • Most of its life is in this phase ...
File
... –The Earth’s orbit around the Sun causes different stars and constellations to be visible at different times during the year. ...
... –The Earth’s orbit around the Sun causes different stars and constellations to be visible at different times during the year. ...
Chapter 28.3 Topic questions
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
... 11. Red Super Giant stars have surface temperatures that are cooler than our earth, so why do they have greater luminosity than the sun? 12. The H-R diagram also includes which stars that are near the end of their life, what are these stars called? 13. A star begins it life in a cloud of gas and dus ...
this article as a PDF
... Hunter, rests brilliant Rigel. In classical mythology, Rigel marks the spot where Scorpio, the Scorpion stung Orion after a brief and fierce battle. Its Arabic name means the Foot. Rigel is a multiple star system. The brighter component, Rigel A, is a blue super giant that shines a remarkable 40,000 ...
... Hunter, rests brilliant Rigel. In classical mythology, Rigel marks the spot where Scorpio, the Scorpion stung Orion after a brief and fierce battle. Its Arabic name means the Foot. Rigel is a multiple star system. The brighter component, Rigel A, is a blue super giant that shines a remarkable 40,000 ...
ASTRONOMY 313
... 6. When the Sun has swollen to full red-giant size (R 0.5 A.U. = 107.5 R), its luminosity will be about 2000 times greater than it is now (i.e. L/L = 2000). Assume that the size of the Earth’s orbit remains unchanged. a. Calculate the Sun’s angular diameter at that time as seen from the Earth. ...
... 6. When the Sun has swollen to full red-giant size (R 0.5 A.U. = 107.5 R), its luminosity will be about 2000 times greater than it is now (i.e. L/L = 2000). Assume that the size of the Earth’s orbit remains unchanged. a. Calculate the Sun’s angular diameter at that time as seen from the Earth. ...
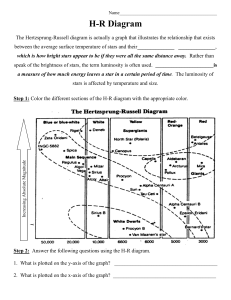
H-R Diagram Student
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... home to one of the loveliest open clusters in the sky, Praesepe, now more commonly known as the Beehive Cluster or M44. This lovely group of stars is just visible to the naked-eye even from Bristol, and a stunning sight in binoculars To the southeast of Leo lies the large faint constellation of Virg ...
... home to one of the loveliest open clusters in the sky, Praesepe, now more commonly known as the Beehive Cluster or M44. This lovely group of stars is just visible to the naked-eye even from Bristol, and a stunning sight in binoculars To the southeast of Leo lies the large faint constellation of Virg ...
Unit 6--Astronomy
... b. blue d. orange 3.Gamma rays, X-rays, visible light, and radio waves are all types of ____. a. nuclear energy c. ultraviolet radiation b. chromatic aberration d. electromagnetic radiation 4.Which of the following refers to the change in wavelength that occurs when an object moves toward or away fr ...
... b. blue d. orange 3.Gamma rays, X-rays, visible light, and radio waves are all types of ____. a. nuclear energy c. ultraviolet radiation b. chromatic aberration d. electromagnetic radiation 4.Which of the following refers to the change in wavelength that occurs when an object moves toward or away fr ...
Astronomy Quiz 12 “Stars
... _____3. Which of the following is the brightest star in the nighttime sky? A. Polaris B. Sirius C. Procyon ...
... _____3. Which of the following is the brightest star in the nighttime sky? A. Polaris B. Sirius C. Procyon ...
October 2013
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
... and is typical of areas where new stars can form. Between the Scorpion and the Centaur are the Altar, the Level and the Wolf, while to the east of the Milky Way stretches a great expanse of sky with relatively few bright stars, dominated by birds and 'water constellations'. In the south these includ ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Eagle Nebula and other nebulae (stars in formation) on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while, WHY? Realize that once our Sun starts to ...
... Eagle Nebula and other nebulae (stars in formation) on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to other stars like Sirius, and Proxima Centauri. Based on its mass, will our sun be around for a while, WHY? Realize that once our Sun starts to ...
Astronomy Study Guide #2
... 21. How do we know there exists material between the stars (interstellar gas)? Compare direct and indirect evidence. 22. What are the main interactions between radiation and matter? ...
... 21. How do we know there exists material between the stars (interstellar gas)? Compare direct and indirect evidence. 22. What are the main interactions between radiation and matter? ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.






![constellations[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081352_2-f872c73597ccdde4cfed49c9b322d3b2-300x300.png)