January SKY Newsletter 2012
... clear night ─ you may see a very worthwhile shower. The count of meteors per hour varies greatly from year to year (60 to 200), with an average at peak time count of about 120 per hour. The shower appears to radiate from the constellation Boötes, but its name is derived from an earlier constellation ...
... clear night ─ you may see a very worthwhile shower. The count of meteors per hour varies greatly from year to year (60 to 200), with an average at peak time count of about 120 per hour. The shower appears to radiate from the constellation Boötes, but its name is derived from an earlier constellation ...
Characteristics of Stars
... 4. In relation to the brightness of other stars how bright is the Sun? What are the three characteristics astronomers use to classify stars? 5. What size is the Sun compared to other stars? What are very large stars called? How far would the supergiant Betelgeuse reach if it were to replace our Sun? ...
... 4. In relation to the brightness of other stars how bright is the Sun? What are the three characteristics astronomers use to classify stars? 5. What size is the Sun compared to other stars? What are very large stars called? How far would the supergiant Betelgeuse reach if it were to replace our Sun? ...
The Magnitude scale
... The Magnitude scale Relative brightness on a backwards (!) log scale. Dates to Hipparchus. E.g., apparent relative luminosities of stars a & b are given by, ...
... The Magnitude scale Relative brightness on a backwards (!) log scale. Dates to Hipparchus. E.g., apparent relative luminosities of stars a & b are given by, ...
Apparent Magnitude
... off 1000 times more light than Rigel!! SO..If Spica is giving off more light, why would it appear dimmer in the sky here at Earth? ...
... off 1000 times more light than Rigel!! SO..If Spica is giving off more light, why would it appear dimmer in the sky here at Earth? ...
HR Diagram - Geneva 304
... 56. Briefly describe the density and processes involved in each of the layers of a star. Include a diagram of the interior of a star with labeled layers. ...
... 56. Briefly describe the density and processes involved in each of the layers of a star. Include a diagram of the interior of a star with labeled layers. ...
LAB #6 - GEOCITIES.ws
... like the Celsius scale, but offset by 273. Thus something that is 273 Kelvins is 0 degrees Celsius.] PRE-LAB WARMUP QUESTION: A star gives out more blue light than yellow. Thus its B-V is (positive, negative, zero). The most likely spectral type for this star is (B, K, M). When one constructs an HR ...
... like the Celsius scale, but offset by 273. Thus something that is 273 Kelvins is 0 degrees Celsius.] PRE-LAB WARMUP QUESTION: A star gives out more blue light than yellow. Thus its B-V is (positive, negative, zero). The most likely spectral type for this star is (B, K, M). When one constructs an HR ...
Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics
... •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have more __self _gravity, they tend to have _higher_ ...
... •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have more __self _gravity, they tend to have _higher_ ...
Lecture 16
... A later scheme, called the B-V Index, classed stars according to a logarithmic ratio of the peak amount of radiation in the blue and violet colors. The current scheme is to class stars according to color in a way which is more or less logarithmically proportional to temperature. In this scheme stars ...
... A later scheme, called the B-V Index, classed stars according to a logarithmic ratio of the peak amount of radiation in the blue and violet colors. The current scheme is to class stars according to color in a way which is more or less logarithmically proportional to temperature. In this scheme stars ...
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
... EXAMPLE: The brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor is Polaris. In modern astronomy it is also called Alpha ( Ursa Minoris. The second brightest star Kocab (on the “bowl” itself) is known as Ursa Minoris If the Greek alphabet is used up, then Roman letters are used. ...
... EXAMPLE: The brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor is Polaris. In modern astronomy it is also called Alpha ( Ursa Minoris. The second brightest star Kocab (on the “bowl” itself) is known as Ursa Minoris If the Greek alphabet is used up, then Roman letters are used. ...
Teacher Subject Title Concept Context Tek/SE Verb
... Engage – Stars in the Night Sky. Construct a KLEW Chart in the class science notebook: What do you see when you look up at the sky? Does the sky look the same during the day as it does at night? Other than the Moon, what do we see in the night sky? What do you know about stars? Misconceptions: stude ...
... Engage – Stars in the Night Sky. Construct a KLEW Chart in the class science notebook: What do you see when you look up at the sky? Does the sky look the same during the day as it does at night? Other than the Moon, what do we see in the night sky? What do you know about stars? Misconceptions: stude ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will cover: Brief review
... Interlude: Naming stars Ordinary stars Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “ ...
... Interlude: Naming stars Ordinary stars Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “ ...
Test#3
... 1. A measurement of the parallax of a star allows us directly to determine the star's a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 2. How much brighter would a star be if an observer moved from 3 to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 3. The difference b ...
... 1. A measurement of the parallax of a star allows us directly to determine the star's a) rotation rate, b) temperature, c) distance, d) age 2. How much brighter would a star be if an observer moved from 3 to 1 parsec from the star? a) 3 times, b) 9 times, c) 27 times, d) 81 times 3. The difference b ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... P.S. You have noticed, haven’t you, that answers to even numbered problems are given on page 449 of your text? 6. Use the table below to answer the following questions. You may also consult a standard H-R diagram. For each question, give a brief explanation (in one sentence). Star Spectral Type Alde ...
... P.S. You have noticed, haven’t you, that answers to even numbered problems are given on page 449 of your text? 6. Use the table below to answer the following questions. You may also consult a standard H-R diagram. For each question, give a brief explanation (in one sentence). Star Spectral Type Alde ...
Lecture 11 - Stars and Atomic Spectra
... • Up to now, we have been discussing the wavelength of light as determining it color • However, light comes in discrete packets called photons and the energy of each photon is set by its color or wavelength • From Einstein, we known that the photon energy is inversely proportional to its wavelength ...
... • Up to now, we have been discussing the wavelength of light as determining it color • However, light comes in discrete packets called photons and the energy of each photon is set by its color or wavelength • From Einstein, we known that the photon energy is inversely proportional to its wavelength ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
a star is born reading
... burn fuel very quickly. It runs out in ten thousand to 100 thousand years. Even though they are very rare, many of the stars we see at night are blue giants. They burn brightly, and their light shines a very long distance. Blue giant stars die as a supernova. This is a spectacular explosion in space ...
... burn fuel very quickly. It runs out in ten thousand to 100 thousand years. Even though they are very rare, many of the stars we see at night are blue giants. They burn brightly, and their light shines a very long distance. Blue giant stars die as a supernova. This is a spectacular explosion in space ...
test - Scioly.org
... to the other, as illustrated above. What type of star is shown on the left side of this illustration? 14. What type of star is shown on the right side of this illustration? 15. What is the name of the material spiraling around and into the left hand star? 16. Expressed in solar masses, a type 1a sup ...
... to the other, as illustrated above. What type of star is shown on the left side of this illustration? 14. What type of star is shown on the right side of this illustration? 15. What is the name of the material spiraling around and into the left hand star? 16. Expressed in solar masses, a type 1a sup ...
The Solar System and Beyond
... 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult to predict how long it would take to run that ...
... 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult to predict how long it would take to run that ...
First Ever STEREO Images of the Entire Sun NASA Deputy
... Follow a line from Sirius to the tip of Canis Major's nose (Theta Canis Majoris), continue nearly as far exactly straight onward, and there you are. M50 is magnitude 5.9, quite a bit fainter than M41's magnitude 4.5. In the same field with M50 is another, the fainter cluster: NGC 2343, a tougher cat ...
... Follow a line from Sirius to the tip of Canis Major's nose (Theta Canis Majoris), continue nearly as far exactly straight onward, and there you are. M50 is magnitude 5.9, quite a bit fainter than M41's magnitude 4.5. In the same field with M50 is another, the fainter cluster: NGC 2343, a tougher cat ...
Stars
... • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one ‘Earth’ year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
... • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one ‘Earth’ year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
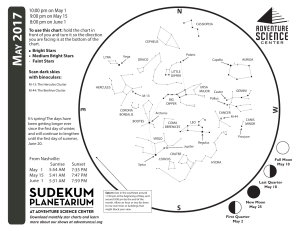
1705 chart front
... astronomers sometimes call an asterism. The Big Dipper is a familiar name for this pattern of stars, especially known to observers in the United States, but it’s not one of the 88 constellations recognized by astronomers worldwide. Ursa Major the Great Bear is the official constellation here, but yo ...
... astronomers sometimes call an asterism. The Big Dipper is a familiar name for this pattern of stars, especially known to observers in the United States, but it’s not one of the 88 constellations recognized by astronomers worldwide. Ursa Major the Great Bear is the official constellation here, but yo ...
Distance to Stars
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
Canis Minor

Canis Minor /ˌkeɪnɨs ˈmaɪnər/ is a small constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. In the second century, it was included as an asterism, or pattern, of two stars in Ptolemy's 48 constellations, and it is counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name is Latin for ""lesser dog"", in contrast to Canis Major, the ""greater dog""; both figures are commonly represented as following the constellation of Orion the hunter.Canis Minor contains only two stars brighter than the fourth magnitude, Procyon (Alpha Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 0.34, and Gomeisa (Beta Canis Minoris), with a magnitude of 2.9. The constellation's dimmer stars were noted by Johann Bayer, who named eight stars including Alpha and Beta, and John Flamsteed, who numbered fourteen. Procyon is the seventh-brightest star in the night sky, as well as one of the closest. A yellow-white main sequence star, it has a white dwarf companion. Gomeisa is a blue-white main sequence star. Luyten's Star is a ninth-magnitude red dwarf and the Solar System's next closest stellar neighbour in the constellation after Procyon. The fourth-magnitude HD 66141, which has evolved into an orange giant towards the end of its life cycle, was discovered to have a planet in 2012. There are two faint deep sky objects within the constellation's borders. The 11 Canis-Minorids are a meteor shower that can be seen in early December.








![Test ticket - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010793453_1-3f96ef5ee7d4646c2142d92e4dc3c3f6-300x300.png)