Lecture 3
... Apparent magnitude : The apparent magnitude (symbol m) is a measure of the stars brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Scale originally devised by Hipparchus and later Ptolemy. Historically , stars were divided into 6 categories according to their brightness : brightest 1st magnitude, faintest ...
... Apparent magnitude : The apparent magnitude (symbol m) is a measure of the stars brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Scale originally devised by Hipparchus and later Ptolemy. Historically , stars were divided into 6 categories according to their brightness : brightest 1st magnitude, faintest ...
Lecture 6: Stellar Distances and Brightness
... Measure distances out to ~100 pc Get 10% distances only to a few parsecs But there are only a few hundred stars this close, so the errors are much bigger for most stars. Blurring caused by the atmosphere is the main reason for the limit from the ...
... Measure distances out to ~100 pc Get 10% distances only to a few parsecs But there are only a few hundred stars this close, so the errors are much bigger for most stars. Blurring caused by the atmosphere is the main reason for the limit from the ...
Newfoundland Sky in Summer
... room than in a dark one. The sun itself i s a star. Other stars are bigger and brighter than the sun but are much fainter because they are so far away. Some stars look brighter than others, but these are not necessarily the biggest, and many of the largest stars cannot be seen at all. One of the lar ...
... room than in a dark one. The sun itself i s a star. Other stars are bigger and brighter than the sun but are much fainter because they are so far away. Some stars look brighter than others, but these are not necessarily the biggest, and many of the largest stars cannot be seen at all. One of the lar ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
... to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
October 2014 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... with our Sun on the vertical scale on the left (therefore our Sun is classified as 1). The absolute magnitude is shown on the vertical scale on the right. This is the magnitude of a star (brightness) if it was located at a standard distance from us (32.6 light years). The colour of the stars indicat ...
... with our Sun on the vertical scale on the left (therefore our Sun is classified as 1). The absolute magnitude is shown on the vertical scale on the right. This is the magnitude of a star (brightness) if it was located at a standard distance from us (32.6 light years). The colour of the stars indicat ...
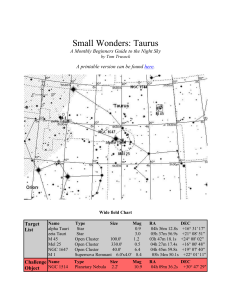
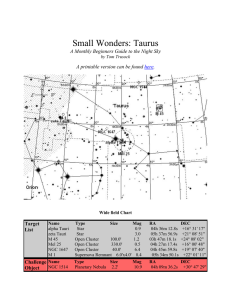
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
... obviously orange in color - even to the naked eye. Shining at 150 times the suns brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance ...
Lives of Stars - Amazon Web Services
... longer than stars with less mass. But the reverse is true. You can think of stars as being like cars. A small car has a small gas tank, but it also has a small engine that burns gas slowly. A large car has a larger gas tank, but it also has alarger engine that burns gas rapidly. So the small car can ...
... longer than stars with less mass. But the reverse is true. You can think of stars as being like cars. A small car has a small gas tank, but it also has a small engine that burns gas slowly. A large car has a larger gas tank, but it also has alarger engine that burns gas rapidly. So the small car can ...
Omega Centauri
... parameter problem (which have been there for decades), as well as the newly discovered multiple sequences in the CMD. 3) Finally, we should never forget that what we will learn on the origin and on the properties of multiple populations in star clusters has a deep impact on our understanding of the ...
... parameter problem (which have been there for decades), as well as the newly discovered multiple sequences in the CMD. 3) Finally, we should never forget that what we will learn on the origin and on the properties of multiple populations in star clusters has a deep impact on our understanding of the ...
Project 4: The HR diagram. Open clusters
... stars do not fall randomly on the graph; rather they are confined to specific regions. This tells you that there is some physical relationship between the luminosity and temperature of a star. From the figure, one sees that most stars fall along a diagonal strip from high temperature, high lumi ...
... stars do not fall randomly on the graph; rather they are confined to specific regions. This tells you that there is some physical relationship between the luminosity and temperature of a star. From the figure, one sees that most stars fall along a diagonal strip from high temperature, high lumi ...
Spectroscopy – the study of the colors of light (the spectrum) given
... The width of the spectral line seen in the spectra of stars is determined by the density of the gas producing the light. The densities of these gases is less for a red giant and more for a white dwarf. ...
... The width of the spectral line seen in the spectra of stars is determined by the density of the gas producing the light. The densities of these gases is less for a red giant and more for a white dwarf. ...
Photometry of star clusters with SalsaJ - Eu-Hou
... curves of objects such as variable stars and supernovae, where the interest is the variation of total light energy output by the system over time. It can also be used to discover exoplanets, by measuring the intensity of a stars light over a period of time. Deviations in the light output can indicat ...
... curves of objects such as variable stars and supernovae, where the interest is the variation of total light energy output by the system over time. It can also be used to discover exoplanets, by measuring the intensity of a stars light over a period of time. Deviations in the light output can indicat ...
Student Handout - Mr. vallee`s Class Site
... 8. It is important to recognize the ____________________ introduced in our vision of the sky by the selection of these constellations. 9. Many peoples also noticed that the ___________, the ________, and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, ...
... 8. It is important to recognize the ____________________ introduced in our vision of the sky by the selection of these constellations. 9. Many peoples also noticed that the ___________, the ________, and ________ moved through the sky in a different way than the stars. They noticed that, over time, ...
Chapter 13 (Properties of Stars)
... C. observed at shorter wavelength and lower luminosity. D. at lower luminosity and lower temperature. 16. The brightness magnitude scale for stars is arbitrary with: A. decreasing number associated with increased luminosity. B. decreasing number associated with increased wavelength. C. increasing nu ...
... C. observed at shorter wavelength and lower luminosity. D. at lower luminosity and lower temperature. 16. The brightness magnitude scale for stars is arbitrary with: A. decreasing number associated with increased luminosity. B. decreasing number associated with increased wavelength. C. increasing nu ...
Chapter 5 Galaxies and Star Systems
... Galaxy. One orbit of the solar system takes about 225 to 250 million years at a speed of half a million miles per hour. The solar system has orbited 20 to 25 times since it formed 4.6 billion years ago. The center of our galaxy is located about 28,000 light-years away, beyond the constellation Sagi ...
... Galaxy. One orbit of the solar system takes about 225 to 250 million years at a speed of half a million miles per hour. The solar system has orbited 20 to 25 times since it formed 4.6 billion years ago. The center of our galaxy is located about 28,000 light-years away, beyond the constellation Sagi ...
Assignment 7 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... ____ 31. A star that is quite hot and has a very small radius compared to most stars is called a. a mainsequence star b. an Otype star c. a red giant d. a white dwarf e. an Mtype star ____ 32. The apparent brightness of stars in general tells us nothing about their distances (i.e. we cannot assum ...
... ____ 31. A star that is quite hot and has a very small radius compared to most stars is called a. a mainsequence star b. an Otype star c. a red giant d. a white dwarf e. an Mtype star ____ 32. The apparent brightness of stars in general tells us nothing about their distances (i.e. we cannot assum ...
Chapter 14. Stellar Structure and Evolution
... Inevitably a star will exhaust the H in its core, having converted it to He. The Sun is about half way through that process. In the core of the Sun, we believe the present composition is about 50% He. As the He is created, the core of the star must move to slightly higher temperatures and pressures ...
... Inevitably a star will exhaust the H in its core, having converted it to He. The Sun is about half way through that process. In the core of the Sun, we believe the present composition is about 50% He. As the He is created, the core of the star must move to slightly higher temperatures and pressures ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.