
How Close is our Nearest Neighbor
... From Shapley’s experiment we have learned that our Sun is located about halfway from the center of the Milky Way to its outer edge. Our Milky Way contains hundreds of billions of stars and is one of billions of galaxies in the universe. The universe is vast, and most of the universe is empty – no st ...
... From Shapley’s experiment we have learned that our Sun is located about halfway from the center of the Milky Way to its outer edge. Our Milky Way contains hundreds of billions of stars and is one of billions of galaxies in the universe. The universe is vast, and most of the universe is empty – no st ...
a new isotopic abundance anomaly in chemically peculiar stars
... The stars with isotopic anomalies are members of a diverse group with unusual and sometimes bizarre surface compositions. They are now called CP stars, where the “CP” stands for chemically peculiar. This notation was introduced to describe chemically peculiar main-sequence stars – stars still conver ...
... The stars with isotopic anomalies are members of a diverse group with unusual and sometimes bizarre surface compositions. They are now called CP stars, where the “CP” stands for chemically peculiar. This notation was introduced to describe chemically peculiar main-sequence stars – stars still conver ...
objects in telescope are farther than they appear
... the aperture (the telescope in this case). The outer rings of the pattern are very faint, so essentially the diameter of a star image is just twice the Airy Disk radius. In theory all stars have the same diameter image because all have the same Airy Disk radius. However, the star image diameter see ...
... the aperture (the telescope in this case). The outer rings of the pattern are very faint, so essentially the diameter of a star image is just twice the Airy Disk radius. In theory all stars have the same diameter image because all have the same Airy Disk radius. However, the star image diameter see ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... I soon joined the American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO) and discovered I was drawn to stars with wild, unpredictable swings in brightness. So-called cataclysmic variable stars soon became my focus and one in particular, SS Cygni, an all-time favorite. Cataclysmics, also known as dw ...
... I soon joined the American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO) and discovered I was drawn to stars with wild, unpredictable swings in brightness. So-called cataclysmic variable stars soon became my focus and one in particular, SS Cygni, an all-time favorite. Cataclysmics, also known as dw ...
Name: Astronomy Lab: The Hertzsprung-Russell (H
... Sometimes the student of astronomy starts to become overwhelmed trying to understand the many measurements and observations astronomers make. Data concerning distance, brightness, color, spectral class, mass, temperature, motion, etc. all seem to be gathered in an attempt to impress the student with ...
... Sometimes the student of astronomy starts to become overwhelmed trying to understand the many measurements and observations astronomers make. Data concerning distance, brightness, color, spectral class, mass, temperature, motion, etc. all seem to be gathered in an attempt to impress the student with ...
ph507lecnote06
... Most stars have properties within the shaded region known as the main sequence. The points plotted here are for stars lying within about 5 pc of the Sun. The diagonal lines correspond to constant stellar radius, so that stellar size can be represented on the same diagram as luminosity and temperatur ...
... Most stars have properties within the shaded region known as the main sequence. The points plotted here are for stars lying within about 5 pc of the Sun. The diagonal lines correspond to constant stellar radius, so that stellar size can be represented on the same diagram as luminosity and temperatur ...
H-RDiagramSE
... diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. What are the characteristics of giants and supergiants? _____________________________ ...
... diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer parts expand outwards. What are the characteristics of giants and supergiants? _____________________________ ...
The Lives of Stars
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar associat ...
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or “evaporate,” from such a cluster • A stellar associat ...
PDF of story and photos
... appear close to each other, they formed geometric patterns that represented features of gods, heroes, animals, and mythological creatures. Often, ancient people created myths or stories about why these creatures appear in the sky. The constellation tales not only provided amusement but also helped t ...
... appear close to each other, they formed geometric patterns that represented features of gods, heroes, animals, and mythological creatures. Often, ancient people created myths or stories about why these creatures appear in the sky. The constellation tales not only provided amusement but also helped t ...
Chapter 13 section 3
... sequence star. It continues to use its hydrogen fuel. The different stages in the life of a star are shown in the illustration on this page and the next page. When hydrogen in the core of the star runs out, the core contracts and temperatures inside the star increase. The outer layers of the star ex ...
... sequence star. It continues to use its hydrogen fuel. The different stages in the life of a star are shown in the illustration on this page and the next page. When hydrogen in the core of the star runs out, the core contracts and temperatures inside the star increase. The outer layers of the star ex ...
David`s Mapping the Heavens[1]
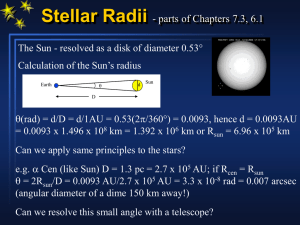
... Complete the following table. In each column outline what theory each astronomer came up with. Shapley ...
... Complete the following table. In each column outline what theory each astronomer came up with. Shapley ...
Gizmos: H-R Diagrams
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
Oct 06, 2001
... C) it stops fusing hydrogen in its core and starts to expand. D) it forms planets. ...
... C) it stops fusing hydrogen in its core and starts to expand. D) it forms planets. ...
The Rigel Star - Emmi
... angry about the death of her companion, but forgave Apollo when he helped her hang his image in the sky so that he wouldn’t be forgotten. The Greeks said that this is why the constellation of Orion is visible in the winter, but wavers and vanishes when Scorpio appears in the summer. ...
... angry about the death of her companion, but forgave Apollo when he helped her hang his image in the sky so that he wouldn’t be forgotten. The Greeks said that this is why the constellation of Orion is visible in the winter, but wavers and vanishes when Scorpio appears in the summer. ...
H-R Diagram
... cores of giants and supergiants. 7. Classify: Proxima Centauri is the nearest star to the Sun. It has a luminosity of 0.0017 and a temperature of 3,000 K. A. Which star group does Proxima Centauri belong to? _________________________ B. On the H-R diagram, which star would Proxima Centauri be near? ...
... cores of giants and supergiants. 7. Classify: Proxima Centauri is the nearest star to the Sun. It has a luminosity of 0.0017 and a temperature of 3,000 K. A. Which star group does Proxima Centauri belong to? _________________________ B. On the H-R diagram, which star would Proxima Centauri be near? ...
Astrophysics notes
... A continuous spectrum upon which dark lines appear due to missing wavelengths. Produced by a cool, non-luminous gas in front of a continuous spectrum source. ...
... A continuous spectrum upon which dark lines appear due to missing wavelengths. Produced by a cool, non-luminous gas in front of a continuous spectrum source. ...
SRP_Space_Lesson 5 - Scientist in Residence Program
... A constellation is an identifiable cluster of stars that make a given shape. Constellations are not real, that is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and ...
... A constellation is an identifiable cluster of stars that make a given shape. Constellations are not real, that is to say, the stars do not really form that shape. The first observers of the sky thought that the stars in a constellation when connected resembled a shape that was familiar to them, and ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.
















![David`s Mapping the Heavens[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008084229_1-877ead4b57cbb51d927fdcd6d06ce5c8-300x300.png)





