HW Set II– page 1 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions
... HW Set II– page 5 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions 5-50 Figure 5-46 shows a man sitting in a bosun's chair that dangles from a massless rope, which runs over a massless, frictionless pulley and back down to the man's hand. The combined mass of man and chair is 95.0 kg. With what force magni ...
... HW Set II– page 5 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions 5-50 Figure 5-46 shows a man sitting in a bosun's chair that dangles from a massless rope, which runs over a massless, frictionless pulley and back down to the man's hand. The combined mass of man and chair is 95.0 kg. With what force magni ...
17_LectureOutline
... In 1604, stars within a constellation were ranked in order of brightness and labeled with Greek letters (Alpha Centauri) In the early 18th century, stars were numbered from west to east in a constellation (61 Cygni) ...
... In 1604, stars within a constellation were ranked in order of brightness and labeled with Greek letters (Alpha Centauri) In the early 18th century, stars were numbered from west to east in a constellation (61 Cygni) ...
The Stars: Distance, Luminosity, Size
... The idea is that a large sample of stars will contain examples of all life stages (newborn, adult, moribund) and of all types of stars. The hope is that by looking at some carefully selected observable properties of the stars, we will see trends that are the telltale of stellar evolution A large sam ...
... The idea is that a large sample of stars will contain examples of all life stages (newborn, adult, moribund) and of all types of stars. The hope is that by looking at some carefully selected observable properties of the stars, we will see trends that are the telltale of stellar evolution A large sam ...
Station A Star Charts I
... D7. (2 pts) One of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way is Cygnus OB2#12. Based on its size and distance from the Earth astronomers expect that its apparent magnitude should be 1.5. However, interstellar dust causes its apparent magnitude to be 11.4. How many times brighter (or fainter) does the ...
... D7. (2 pts) One of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way is Cygnus OB2#12. Based on its size and distance from the Earth astronomers expect that its apparent magnitude should be 1.5. However, interstellar dust causes its apparent magnitude to be 11.4. How many times brighter (or fainter) does the ...
Globular Clusters
... even with 60mm. It is not as round and regular as other globs. In medium side scopes it can appear to have a brighter "bar" across the centre, perhaps an illusion created by a few brighter stars on opposite sides of the core or by a slighter darker regions on one side of the "bar". M4 sits far behin ...
... even with 60mm. It is not as round and regular as other globs. In medium side scopes it can appear to have a brighter "bar" across the centre, perhaps an illusion created by a few brighter stars on opposite sides of the core or by a slighter darker regions on one side of the "bar". M4 sits far behin ...
Chapter10 (with interactive links)
... Eclipsing binary: the total light coming from the star system decreases when one star passes in front of the other. This allows us to determine the relative sizes of the two stars. ...
... Eclipsing binary: the total light coming from the star system decreases when one star passes in front of the other. This allows us to determine the relative sizes of the two stars. ...
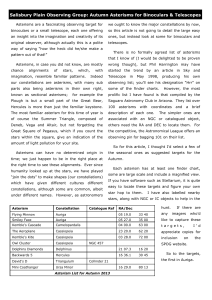
Autumn Asterisms for binoculars 2013
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in ...
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in ...
charts_set_7
... Stars can be single, double (binary), or multiple. Apparent binaries are happenstance alignments. True binaries orbit each other. ...
... Stars can be single, double (binary), or multiple. Apparent binaries are happenstance alignments. True binaries orbit each other. ...
Big Bear Valley Astronomical Society
... The chief star, Aldebaran is the 1st magnitude star referred to by Ptolemy as 'the Torch' on account of its bright, rose-colored luminance. It is positioned on the southern or left eye of the Bull and is known by early authors as 'the Bright Eye of the Bull', 'Bull's Eye', Occulus Taurii; or by some ...
... The chief star, Aldebaran is the 1st magnitude star referred to by Ptolemy as 'the Torch' on account of its bright, rose-colored luminance. It is positioned on the southern or left eye of the Bull and is known by early authors as 'the Bright Eye of the Bull', 'Bull's Eye', Occulus Taurii; or by some ...
The Solar Neighborhood
... Part 2: The Nearest and Brightest Stars Plot the stars from the two lists of brightest and nearest stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram on the next page. Use the intrinsic brightness (absolute magnitude) on the y-axis and the temperature on the x-axis. Note that the y-axis has negative magnitud ...
... Part 2: The Nearest and Brightest Stars Plot the stars from the two lists of brightest and nearest stars on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram on the next page. Use the intrinsic brightness (absolute magnitude) on the y-axis and the temperature on the x-axis. Note that the y-axis has negative magnitud ...
Standing in Awe - Auckland Astronomical Society
... VV 72, also catalogued as Me 2-1. By easy I mean reasonably bright, however, the size is only 5" or so, making it difficult to perceive as anything other than stellar without high magnification. An 8" telescope with a magnification of 200x will show a greyish disk around 44" to the east of a magnitu ...
... VV 72, also catalogued as Me 2-1. By easy I mean reasonably bright, however, the size is only 5" or so, making it difficult to perceive as anything other than stellar without high magnification. An 8" telescope with a magnification of 200x will show a greyish disk around 44" to the east of a magnitu ...
The Birth of Stars Guiding Questions • Because stars shine by
... 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve (bad use of term – this is about the birth, life and death of stars and that is NOT evolution)? 2. What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? 3. In what kind of nebulae do new stars form? 4. What steps are involved in forming a star like ...
... 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve (bad use of term – this is about the birth, life and death of stars and that is NOT evolution)? 2. What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? 3. In what kind of nebulae do new stars form? 4. What steps are involved in forming a star like ...
Integrated Science
... A neutron star is about 20 km in diameter and has the mass of about 1.4 times that of our Sun. This means that a neutron star is so dense that on Earth, one teaspoonful would weigh a billion tons! Because of its small size and high density, a neutron star possesses a surface gravitational field ab ...
... A neutron star is about 20 km in diameter and has the mass of about 1.4 times that of our Sun. This means that a neutron star is so dense that on Earth, one teaspoonful would weigh a billion tons! Because of its small size and high density, a neutron star possesses a surface gravitational field ab ...
The Birth of Stars
... the reddish emission nebulae called H II regions • Ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from the O and B stars at the core of an H II region create shock waves that move outward through the gas cloud, compressing the gas and triggering the formation of more protostars ...
... the reddish emission nebulae called H II regions • Ultraviolet radiation and stellar winds from the O and B stars at the core of an H II region create shock waves that move outward through the gas cloud, compressing the gas and triggering the formation of more protostars ...
Characteristics of Stars - Laconia School District
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • People say about 100 years ago, two scientists were working alone and ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram • People say about 100 years ago, two scientists were working alone and ...
Bright versus Nearby Stars
... • The 269 Brightest stars are: – 381 light years away on average • Max Distance = 3400 light years – 75% are late stage giant stars – 25% are young hot (most probably B) stars. – Average absolute magnitude = -1.2 – Average luminosity = 300 solar luminosities. – Short lived stars or stars near the of ...
... • The 269 Brightest stars are: – 381 light years away on average • Max Distance = 3400 light years – 75% are late stage giant stars – 25% are young hot (most probably B) stars. – Average absolute magnitude = -1.2 – Average luminosity = 300 solar luminosities. – Short lived stars or stars near the of ...
Chapter 11: Stars
... Measuring a star’s surface T • Astronomers measure the surface temperature because the interior temperature can only be inferred from models. • Surface T is easier to measure than its luminosity because it does not depend on distance. ...
... Measuring a star’s surface T • Astronomers measure the surface temperature because the interior temperature can only be inferred from models. • Surface T is easier to measure than its luminosity because it does not depend on distance. ...
Observing the Night Sky - Constellations
... binoculars available to assist you in seeing the fainter stars. 3. Determine Limiting Magnitude - Your instructor will point out a constellation with a large variety of stellar magnitudes. The constellation should be located high above the horizon, where Earth's atmosphere cannot dim the star's brig ...
... binoculars available to assist you in seeing the fainter stars. 3. Determine Limiting Magnitude - Your instructor will point out a constellation with a large variety of stellar magnitudes. The constellation should be located high above the horizon, where Earth's atmosphere cannot dim the star's brig ...
Galaxies – Island universes
... How can you possibly get 1000 galaxies worth of luminosity out of something only as big as our solar system? • Only one mechanism can do it – a massive black hole with an accretion disk of infalling matter being heated to millions of degrees and giving off a ton of radiation at all ...
... How can you possibly get 1000 galaxies worth of luminosity out of something only as big as our solar system? • Only one mechanism can do it – a massive black hole with an accretion disk of infalling matter being heated to millions of degrees and giving off a ton of radiation at all ...
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache
... aspect, the native is reduced to being a door-keeper, admitting and saluting guests. [2] Ptolemy attributes a mercurial-saturnine nature to the constellation as a whole, but notes the principal star Arcturus (from Arktouros 'Bear Guard': arktos, bear + ouros, guard - from its position behind Ursa Ma ...
... aspect, the native is reduced to being a door-keeper, admitting and saluting guests. [2] Ptolemy attributes a mercurial-saturnine nature to the constellation as a whole, but notes the principal star Arcturus (from Arktouros 'Bear Guard': arktos, bear + ouros, guard - from its position behind Ursa Ma ...
Catching Andromeda`s Light
... arms give birth to stars. The brightest newborn stars are hot and blue, so spiral arms are blue. The blue stars give off ultraviolet radiation—light waves that are shorter than your eye can see. This ultraviolet light carries lots of energy and makes gas glow red. So, strangely enough, gas can turn ...
... arms give birth to stars. The brightest newborn stars are hot and blue, so spiral arms are blue. The blue stars give off ultraviolet radiation—light waves that are shorter than your eye can see. This ultraviolet light carries lots of energy and makes gas glow red. So, strangely enough, gas can turn ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... – What does a hot, dense source do? – Radiate a continuous spectrum, specifically blackbody radiation. A prediction! – The Universe has expanded quite a bit since the beginning, and so has the light. Big Bang theory predicted that we should see blackbody radiation from the beginning of the Univers ...
... – What does a hot, dense source do? – Radiate a continuous spectrum, specifically blackbody radiation. A prediction! – The Universe has expanded quite a bit since the beginning, and so has the light. Big Bang theory predicted that we should see blackbody radiation from the beginning of the Univers ...
What is a star?
... mean the actual brightness of a star. They measure it on a scale called absolute magnitude. • Absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would be if the star were located at a standard distance. • Absolute magnitude is a measure of the brightness of a star whose distance from Earth is know ...
... mean the actual brightness of a star. They measure it on a scale called absolute magnitude. • Absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would be if the star were located at a standard distance. • Absolute magnitude is a measure of the brightness of a star whose distance from Earth is know ...
Part A
... • Many stars exist in large groupings called clusters. • Stars in a cluster all formed at about the same time and are the same distance from Earth. ...
... • Many stars exist in large groupings called clusters. • Stars in a cluster all formed at about the same time and are the same distance from Earth. ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.