1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... The surface temperature of Barnard’s star is about 3 500 K. Using this information and information about its luminosity, explain why Barnard’s star cannot be (i) ...
... The surface temperature of Barnard’s star is about 3 500 K. Using this information and information about its luminosity, explain why Barnard’s star cannot be (i) ...
Distance, Size, and Temperature of a Star
... Because blue stars are large, and compact, they burn their fuel quickly, which gives them a very high temperature. These stars often run out of fuel in only 10,000 - 100,000 years. A blue giant is very bright. Like a lighthouse, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are ra ...
... Because blue stars are large, and compact, they burn their fuel quickly, which gives them a very high temperature. These stars often run out of fuel in only 10,000 - 100,000 years. A blue giant is very bright. Like a lighthouse, they shine across a great distance. Even though blue giant stars are ra ...
Astronomy in 1936 The History of the Universe
... At each Rm , stars’ positions in epicycles are forced into a specific pattern by gravitational potential of spiral arm. Sum of positions of stars at this Rm forms an ellipse rotating at pattern speed. ...
... At each Rm , stars’ positions in epicycles are forced into a specific pattern by gravitational potential of spiral arm. Sum of positions of stars at this Rm forms an ellipse rotating at pattern speed. ...
Reflecting telescopes - School
... Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is. There are, however, two different ways of indicating a stars magnitude; apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The scale we use to measure magnitude is based on that created by the ancient Greeks which ran from 1 to 6. On the ancient Greek scale 1 ...
... Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is. There are, however, two different ways of indicating a stars magnitude; apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The scale we use to measure magnitude is based on that created by the ancient Greeks which ran from 1 to 6. On the ancient Greek scale 1 ...
stars-notes
... as seen from Earth. The absolute magnitude is the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 light-years from Earth. • If all stars were the same distance away, their absolute magnitudes would be the same as their apparent magnitudes. ...
... as seen from Earth. The absolute magnitude is the brightness that a star would have at a distance of 32.6 light-years from Earth. • If all stars were the same distance away, their absolute magnitudes would be the same as their apparent magnitudes. ...
Astronomy 160: Frontiers and Controversies in Astrophysics
... So, the Type I Cepheids would have to be ∼ 4 magnitudes brighter than Type II Cepheids to fully account for Hubble’s error. b) Suppose there had been no problem with the standard candles Hubble used, including the Cepheids, and that the error in the determination of Hubble constant was due to some b ...
... So, the Type I Cepheids would have to be ∼ 4 magnitudes brighter than Type II Cepheids to fully account for Hubble’s error. b) Suppose there had been no problem with the standard candles Hubble used, including the Cepheids, and that the error in the determination of Hubble constant was due to some b ...
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
... Our galaxy is a spiral galaxy. Here are two other spiral galaxies, one viewed from the side and the other from the top, which are thought to resemble the Milky Way: ...
... Our galaxy is a spiral galaxy. Here are two other spiral galaxies, one viewed from the side and the other from the top, which are thought to resemble the Milky Way: ...
Stars and Nebulae
... their spectral classifications (or, alternatively, to their temperatures). They knew that some stars were hotter and more luminous than the sun, and that others were cooler and less luminous. Hertzsprung and Russell found that 90% of the stars fell into a narrow band they termed the "main sequence." ...
... their spectral classifications (or, alternatively, to their temperatures). They knew that some stars were hotter and more luminous than the sun, and that others were cooler and less luminous. Hertzsprung and Russell found that 90% of the stars fell into a narrow band they termed the "main sequence." ...
Slide 1
... Observed rotation of E’s is too low to explain observed flattening To quantify this, define Vmax as maximum Vlos ...
... Observed rotation of E’s is too low to explain observed flattening To quantify this, define Vmax as maximum Vlos ...
September Globular Clusters - Salisbury Plain Observing Group
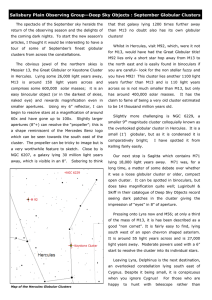
... Pressing onto Lyra now and M56; at only a third of the mass of M13, it is has been described as a good “non comet”. It is fairly easy to find, lying south west of an open chevron shaped asterism. It is around 55 light years across and is 27,000 light years away. Moderate powers used with a 6” start ...
... Pressing onto Lyra now and M56; at only a third of the mass of M13, it is has been described as a good “non comet”. It is fairly easy to find, lying south west of an open chevron shaped asterism. It is around 55 light years across and is 27,000 light years away. Moderate powers used with a 6” start ...
Building` a Galaxy SED
... Apparent magnitude of sun is mV~-26. Absolute magnitude.... of sun is MV~4.8. of a massive O-star is MV~-5 of a (Type 1a) supernova explosion MV~-19.3 of our Milky way as a whole MV~-20 ...
... Apparent magnitude of sun is mV~-26. Absolute magnitude.... of sun is MV~4.8. of a massive O-star is MV~-5 of a (Type 1a) supernova explosion MV~-19.3 of our Milky way as a whole MV~-20 ...
May 2017 Astronomy Calendar by Dave Mitsky
... http://www.popastro.com/meteor/activity/activity.php?id_pag=485 for additional information. Information on Iridium flares and passes of the ISS, the Tiangong-1, the USAF’s X-37B, the HST, and other satellites can be found at http://www.heavens-above.com/ The Moon is 6.2 days old, is illuminated 44.6 ...
... http://www.popastro.com/meteor/activity/activity.php?id_pag=485 for additional information. Information on Iridium flares and passes of the ISS, the Tiangong-1, the USAF’s X-37B, the HST, and other satellites can be found at http://www.heavens-above.com/ The Moon is 6.2 days old, is illuminated 44.6 ...
Document
... • Interstellar gas clouds emit intense microwaves at specific frequencies. • Doppler shift gives speed • True speed plus proper motion gives distance • Maybe 10s of Mpc but new technique ...
... • Interstellar gas clouds emit intense microwaves at specific frequencies. • Doppler shift gives speed • True speed plus proper motion gives distance • Maybe 10s of Mpc but new technique ...
Which Constellation is Which?
... long handle. Orion is named after a great hunter. You can see his belt, marked by three bright stars. Constellations are imaginary pictures in the sky. The stars look like they are all the same distance away. That’s not true. The stars in the sky are different distances from Earth. ...
... long handle. Orion is named after a great hunter. You can see his belt, marked by three bright stars. Constellations are imaginary pictures in the sky. The stars look like they are all the same distance away. That’s not true. The stars in the sky are different distances from Earth. ...
colour
... • measure stellar flux (i.e. f = L/4 D2, L: luminosity, D: distance) . for Sun: L¯ = 3.86 × 1026 W, f = 1.360 × 103 W m−2 (solar constant) . luminosity measurement requires distance determination (1A.U. = 1.50 × 1011 m) • define apparent magnitudes of two stars, m1, m2, by m1 − m2 = 2.5 log f2/f1 • ...
... • measure stellar flux (i.e. f = L/4 D2, L: luminosity, D: distance) . for Sun: L¯ = 3.86 × 1026 W, f = 1.360 × 103 W m−2 (solar constant) . luminosity measurement requires distance determination (1A.U. = 1.50 × 1011 m) • define apparent magnitudes of two stars, m1, m2, by m1 − m2 = 2.5 log f2/f1 • ...
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... • define bolometric correction: B.C. = Mbol − MV (usually tabulated as a function of B − V colour) • visual extinction AV : absorption of visual star light due to extinction by interstellar gas/dust (can vary from ∼ 0 to 30 magnitudes [Galactic centre]) • distance modulus: (m − M)V = 5 × log D/10pc ...
... • define bolometric correction: B.C. = Mbol − MV (usually tabulated as a function of B − V colour) • visual extinction AV : absorption of visual star light due to extinction by interstellar gas/dust (can vary from ∼ 0 to 30 magnitudes [Galactic centre]) • distance modulus: (m − M)V = 5 × log D/10pc ...
Binary Orbits
... determine parameters e.g. period and line of sight velocities – masses – done in optical and X-ray • Fact that a large fraction of stars are found in binaries indicate stars are formed in groups through gravitational collapse of ...
... determine parameters e.g. period and line of sight velocities – masses – done in optical and X-ray • Fact that a large fraction of stars are found in binaries indicate stars are formed in groups through gravitational collapse of ...
Name: Astronomy Lab: The Hertzsprung-Russell (H
... Sometimes the student of astronomy starts to become overwhelmed trying to understand the many measurements and observations astronomers make. Data concerning distance, brightness, color, spectral class, mass, temperature, motion, etc. all seem to be gathered in an attempt to impress the student with ...
... Sometimes the student of astronomy starts to become overwhelmed trying to understand the many measurements and observations astronomers make. Data concerning distance, brightness, color, spectral class, mass, temperature, motion, etc. all seem to be gathered in an attempt to impress the student with ...
Document
... Students will learn the different types of supernovae observed and the physical theories of their production. ...
... Students will learn the different types of supernovae observed and the physical theories of their production. ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412
... Students will learn the different types of supernovae observed and the physical theories of their production. ...
... Students will learn the different types of supernovae observed and the physical theories of their production. ...
HW Set II– page 1 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions
... HW Set II– page 5 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions 5-50 Figure 5-46 shows a man sitting in a bosun's chair that dangles from a massless rope, which runs over a massless, frictionless pulley and back down to the man's hand. The combined mass of man and chair is 95.0 kg. With what force magni ...
... HW Set II– page 5 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 (1) homework solutions 5-50 Figure 5-46 shows a man sitting in a bosun's chair that dangles from a massless rope, which runs over a massless, frictionless pulley and back down to the man's hand. The combined mass of man and chair is 95.0 kg. With what force magni ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.