The Mighty Hunter in the Winter Sky By Shannon Jackson
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
... Five constellations are always in our northern sky. Other groupings appear seasonally, and then disappear as they fall below the horizon. There are five constellations, however, which seem to circle Polaris (po LAR us), also known as the North Star. The North Star always stays put while the other st ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... contain O and B stars (newly made, short-lived stars), it is apparent that spiral arms are where star formation takes place. Because O and B stars are very luminous, spiral arms are very prominent in snapshots of galaxies similar to our own. For instance, the image below is of a galaxy called the Wh ...
... contain O and B stars (newly made, short-lived stars), it is apparent that spiral arms are where star formation takes place. Because O and B stars are very luminous, spiral arms are very prominent in snapshots of galaxies similar to our own. For instance, the image below is of a galaxy called the Wh ...
Tutor Marked Assignment
... (a) Express the distances of the stars Sirius A and Antares in light years. ...
... (a) Express the distances of the stars Sirius A and Antares in light years. ...
Comets and more
... When a space rock enters Earth’s Atmosphere, the friction as it falls through air produces heat and light. The light being created is called a meteor. The rock itself is still called a meteoroid. ...
... When a space rock enters Earth’s Atmosphere, the friction as it falls through air produces heat and light. The light being created is called a meteor. The rock itself is still called a meteoroid. ...
Constellation Guide Book
... cultures. It's also got some features of interest for us today. The Facts Image of: A jumping or running ram Time best visible: in December Rank in constellation size: 39th Brightest star: Alpha Arietis, also known as Hamal or El Nath, with an apparent magnitude of 2.0. ...
... cultures. It's also got some features of interest for us today. The Facts Image of: A jumping or running ram Time best visible: in December Rank in constellation size: 39th Brightest star: Alpha Arietis, also known as Hamal or El Nath, with an apparent magnitude of 2.0. ...
2017 March Celestial Timings
... sunset. Mercury is passing 2.2° to the right of Uranus (+5.9 magnitude at the very edge of our ability to see it without aid). Mars continues to hover in the western sky after sunset from twilight to late evening setting about three hours after the Sun. Mars is to the upper left of Mercury and ...
... sunset. Mercury is passing 2.2° to the right of Uranus (+5.9 magnitude at the very edge of our ability to see it without aid). Mars continues to hover in the western sky after sunset from twilight to late evening setting about three hours after the Sun. Mars is to the upper left of Mercury and ...
Rotation Curves:
... compare this to the light, we find that M/L ~ 5-25. (But since the rotation curve is still flat, this is a lower limit.) • For the observed stars in a galaxy, M/L ~3, so between 50% and 90% of a galaxy mass is in dark matter!! – What is it?? We’ll come back to this question later on too. ...
... compare this to the light, we find that M/L ~ 5-25. (But since the rotation curve is still flat, this is a lower limit.) • For the observed stars in a galaxy, M/L ~3, so between 50% and 90% of a galaxy mass is in dark matter!! – What is it?? We’ll come back to this question later on too. ...
same
... Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the constellations are not actually physically associated but are just patterns that resemble or honor animals, mythological characters, etc. Many of the constellation names are Greek in origin (e.g., Orion, He ...
... Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the constellations are not actually physically associated but are just patterns that resemble or honor animals, mythological characters, etc. Many of the constellation names are Greek in origin (e.g., Orion, He ...
Test - Scioly.org
... B. It was detected very early C. It was first classified as a Type II supernova D. It had a much higher absolute magnitude than expected E. It had a much lower absolute magnitude than expected 49. Which of the following are true about Tycho’s SNR? A. It was one of eight supernovae visible to the nak ...
... B. It was detected very early C. It was first classified as a Type II supernova D. It had a much higher absolute magnitude than expected E. It had a much lower absolute magnitude than expected 49. Which of the following are true about Tycho’s SNR? A. It was one of eight supernovae visible to the nak ...
What is a Hertzsprung
... • The light curve of this pulsating variable star shows that its brightness alternately rises and falls over a 50-day period ...
... • The light curve of this pulsating variable star shows that its brightness alternately rises and falls over a 50-day period ...
November Celestial Calendar by Dave Mitsky All times are UT
... through southern Aries. It lies a bit more than two degrees south of the sixth-magnitude star 19 Arietis on the nights of November 11 and November 12. Asteroid 216 Kleopatra is at opposition in Taurus on November 16. For information on this year’s bright asteroids and upcoming asteroid occultation e ...
... through southern Aries. It lies a bit more than two degrees south of the sixth-magnitude star 19 Arietis on the nights of November 11 and November 12. Asteroid 216 Kleopatra is at opposition in Taurus on November 16. For information on this year’s bright asteroids and upcoming asteroid occultation e ...
The Extragalactic Distance Database: Color–Magnitude Diagrams
... are, among others, columns that describe a star’s position on the image, and its apparent magnitude in both flight and groundbased filters, as well as several characterizations of the quality of the measurement. If there are several images per filter available then these values are displayed for eac ...
... are, among others, columns that describe a star’s position on the image, and its apparent magnitude in both flight and groundbased filters, as well as several characterizations of the quality of the measurement. If there are several images per filter available then these values are displayed for eac ...
Searching for stars in high-velocity clouds
... at similar distances to that of M31. In Fig. 1 we show the colour– magnitude plot for the three HVC fields and offsets. For a similar distance to M31 we would expect a cluster of stars (tip of red giant branch) around m I = 21–22 with colours of (V − I ) = 1.2–1.8 (box in Fig. 1). None of the colour ...
... at similar distances to that of M31. In Fig. 1 we show the colour– magnitude plot for the three HVC fields and offsets. For a similar distance to M31 we would expect a cluster of stars (tip of red giant branch) around m I = 21–22 with colours of (V − I ) = 1.2–1.8 (box in Fig. 1). None of the colour ...
CONSTELLATION POWER POINT PROJECT
... Brightest Stars: 1) Aldebaran, RA: 04h 35 min DEC: +16.18’ MAG: 0.85 2) Alnath, RA: 5h 26.292m DEC: 28 degrees 36.450’ MAG: 1.65 3) Hyadum 1, RA: 4h 19.8m DEC: +15 degrees 37.8’ MAG: 2.48 5 stars within the Taurus have a magnitude less than 3, which are the Aldebaran, Alnath, Hyadum 1, Elnath, and t ...
... Brightest Stars: 1) Aldebaran, RA: 04h 35 min DEC: +16.18’ MAG: 0.85 2) Alnath, RA: 5h 26.292m DEC: 28 degrees 36.450’ MAG: 1.65 3) Hyadum 1, RA: 4h 19.8m DEC: +15 degrees 37.8’ MAG: 2.48 5 stars within the Taurus have a magnitude less than 3, which are the Aldebaran, Alnath, Hyadum 1, Elnath, and t ...
StarIntro_sb12
... whole number) for an amount greater than or (X a decimal number) for an amount less than the AM of the Sun. ...
... whole number) for an amount greater than or (X a decimal number) for an amount less than the AM of the Sun. ...
October 2014 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... Sun its outer layers would extend to half way between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It is so big that it is the only star that can be seen as a disc using giant telescopes. However the surface temperature is cool for a star at 3100°K when compared with the brighter surface of our Sun at 5500°K and ...
... Sun its outer layers would extend to half way between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It is so big that it is the only star that can be seen as a disc using giant telescopes. However the surface temperature is cool for a star at 3100°K when compared with the brighter surface of our Sun at 5500°K and ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... The 'Game' of Science The following example is from Richard Feynman, "What do we mean when we claim to 'understand' the Universe? We may imagine the enormously complicated situation of changing things we call the physical universe is a chess game played by the gods; we are not permitted to play, bu ...
... The 'Game' of Science The following example is from Richard Feynman, "What do we mean when we claim to 'understand' the Universe? We may imagine the enormously complicated situation of changing things we call the physical universe is a chess game played by the gods; we are not permitted to play, bu ...
Orionids meteor shower is in the morning sky and Comet of Century
... early morning. The meteors will appear to be originating out of the constellation of Orionids and hence known as the Orionid shower. That’s because all the meteors appear to “rain” into the atmosphere from a corner of Orion, the hunter. The constellation climbs into v ...
... early morning. The meteors will appear to be originating out of the constellation of Orionids and hence known as the Orionid shower. That’s because all the meteors appear to “rain” into the atmosphere from a corner of Orion, the hunter. The constellation climbs into v ...
1. What is parallax? What unit is it measured in? 1a. Parallax is the
... 1a. Parallax is the change in the direction to a star due to the Earth’s motion around the Sun. Its usually measured in arcseconds. 2. Draw a labelled diagram showing a star with a 1 arcsecond parallax. What about a star with a 2 arcsecond parallax? 2a. See class. 3. How many arcseconds in a degree? ...
... 1a. Parallax is the change in the direction to a star due to the Earth’s motion around the Sun. Its usually measured in arcseconds. 2. Draw a labelled diagram showing a star with a 1 arcsecond parallax. What about a star with a 2 arcsecond parallax? 2a. See class. 3. How many arcseconds in a degree? ...
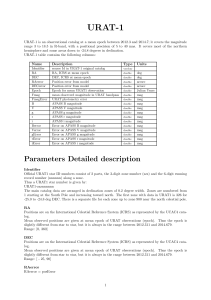
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
Properties of Stars - Indiana State University
... – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radius, the smaller the temperature – Therefore, as one moves right on the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must increase – The net effect of this is that the smal ...
... – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given luminosity, the larger the radius, the smaller the temperature – Therefore, as one moves right on the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must increase – The net effect of this is that the smal ...
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars
... • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: w ...
... • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and supergiants • Most stars end up small and white after fusion has ceased: w ...
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
... This infrared view of our Galaxy shows much more detail of the galactic center than the visible-light view does, as infrared is not as much absorbed by gas and dust. ...
... This infrared view of our Galaxy shows much more detail of the galactic center than the visible-light view does, as infrared is not as much absorbed by gas and dust. ...
Description of Pictures In the Dome
... of Orion's Belt. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of 1,344 ± 20 light years and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light years across. Older texts frequently ...
... of Orion's Belt. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of 1,344 ± 20 light years and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light years across. Older texts frequently ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.