15.4 Star Systems and Galaxies
... I. Star Systems and Planets A. Star system-groups of two or more stars 1. Binary stars - two stars or double stars a. Eclipsing binary-a system in which one star blocks the light from another II. Planets Around Other Stars A. Astronomers study gravitational effects on stars to see if there is a pla ...
... I. Star Systems and Planets A. Star system-groups of two or more stars 1. Binary stars - two stars or double stars a. Eclipsing binary-a system in which one star blocks the light from another II. Planets Around Other Stars A. Astronomers study gravitational effects on stars to see if there is a pla ...
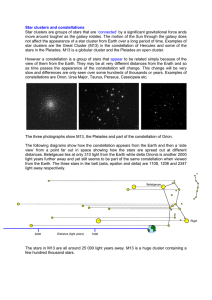
Star clusters and constellations
... Star clusters are groups of stars that are ‘connected’ by a significant gravitational force ands move around tougher as the galaxy rotates. The motion of the Sun through the galaxy does not affect the appearance of a star cluster from Earth over a long period of time. Examples of star clusters are t ...
... Star clusters are groups of stars that are ‘connected’ by a significant gravitational force ands move around tougher as the galaxy rotates. The motion of the Sun through the galaxy does not affect the appearance of a star cluster from Earth over a long period of time. Examples of star clusters are t ...
HW 5 Solutions What are “black smokers?” Where in our solar
... Figure 11.10: NGC 4414 is a spiral galaxy, with no bar, and numerous arms. Sc Figure 11.11: NGC 1300 is a spiral galaxy, barred, and with two distinct arms. SBb Figure 11.12: M87 is an elliptical galaxy that is almost entirely spherical. E0. 4. How did Edwin Hubble use Cepheid variables to determine ...
... Figure 11.10: NGC 4414 is a spiral galaxy, with no bar, and numerous arms. Sc Figure 11.11: NGC 1300 is a spiral galaxy, barred, and with two distinct arms. SBb Figure 11.12: M87 is an elliptical galaxy that is almost entirely spherical. E0. 4. How did Edwin Hubble use Cepheid variables to determine ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... The term magnitude is used to describe the brightness of a star' Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the ...
... The term magnitude is used to describe the brightness of a star' Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the ...
How Bright is that Star?
... (Notice that the lower the number is the brighter the star is.) Modern astronomy still uses this system, but has refined it. ...
... (Notice that the lower the number is the brighter the star is.) Modern astronomy still uses this system, but has refined it. ...
Chapter 24 Test:Stars/Galaxies
... the remnants of a larger galaxy we collided with over years ago. (a) elliptical, (b) normal spiral, (c) (d) barred spiral. ...
... the remnants of a larger galaxy we collided with over years ago. (a) elliptical, (b) normal spiral, (c) (d) barred spiral. ...
Figure 10-6 The same star field shown in Figure
... Hipparchus misjudged the magnitudes of some of the brighter stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. ...
... Hipparchus misjudged the magnitudes of some of the brighter stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
... hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
... hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
Physical properties of stars
... Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their apparent magnitude. Absolute motion- the actual motion of stars in spa ...
... Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their apparent magnitude. Absolute motion- the actual motion of stars in spa ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
Sky Notes - April 2012 - North Devon Astronomical Society
... moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
... moderate telescopes is NGC 188. This small open cluster is the closest object of it’s type to the Northern Celestial Pole and is one of the oldest open clusters known to astronomers. ...
Regulus the Star njw
... The star’s name regulus comes from the Latin word Rex which means King It is associated with many cultures like the Greeks , Arabs, and Ancient Babylon It also is know as one of the four Royal Stars of the Heavens ...
... The star’s name regulus comes from the Latin word Rex which means King It is associated with many cultures like the Greeks , Arabs, and Ancient Babylon It also is know as one of the four Royal Stars of the Heavens ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
... 3. What is the name of the galaxy our solar system is located in? 4. What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 5. The ________ is the largest star in our solar system. 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light ye ...
THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF
... serious students of astrology. Opening page of Tetrabiblos, published in 1484. ...
... serious students of astrology. Opening page of Tetrabiblos, published in 1484. ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
The Constellation Microscopium, the Microscope Microscopium is a
... brightest star. It is a yellow giant of spectral type G6III. Lying 381 light years away, It depicts the eyepiece of the microscope. Alpha Microscopii is also a yellow giant, though in this case a variable Johann Bode in his Uranographia atlas of star, which ranges between apparent magnitudes 4.88 an ...
... brightest star. It is a yellow giant of spectral type G6III. Lying 381 light years away, It depicts the eyepiece of the microscope. Alpha Microscopii is also a yellow giant, though in this case a variable Johann Bode in his Uranographia atlas of star, which ranges between apparent magnitudes 4.88 an ...
One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
File
... crosses the celestial equator from north to south) because of this, the Babylonians identified it to be the starting point of the zodiac ("Aries Constellation"). However, this is credited to the revisions the Neo-Babylonians did to the Babylonian zodiac, which placed Alpha Arietis, Hamal, very close ...
... crosses the celestial equator from north to south) because of this, the Babylonians identified it to be the starting point of the zodiac ("Aries Constellation"). However, this is credited to the revisions the Neo-Babylonians did to the Babylonian zodiac, which placed Alpha Arietis, Hamal, very close ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... Astronomical distances and stellar magnitudes 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate dis ...
... Astronomical distances and stellar magnitudes 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate dis ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.