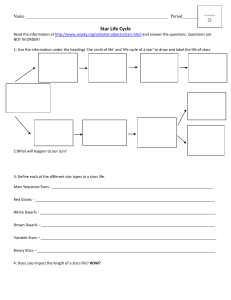
Life Cycle of Stars Flipbook Assignment
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Measuring distances to stars • Measure parallax – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. • Knowing the angle that the star’s position changes and the size of Earth’s orbit, astronomers can calculate the distance of the star from earth. ...
... Measuring distances to stars • Measure parallax – the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. • Knowing the angle that the star’s position changes and the size of Earth’s orbit, astronomers can calculate the distance of the star from earth. ...
The Milky Way
... physically close to each other in space. They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different cultures grouped stars differently. Example: The Paw ...
... physically close to each other in space. They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different cultures grouped stars differently. Example: The Paw ...
Problem set 1 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56Fe is 8.8MeV
... can detect a star of apparent magnitude 6). The apparent magnitude, m, is related to the absolute magnitude, M , by m = M + 5 log ...
... can detect a star of apparent magnitude 6). The apparent magnitude, m, is related to the absolute magnitude, M , by m = M + 5 log ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
Astronomy Toolkit
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
The magnitudes of stars
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
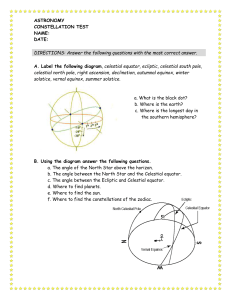
ASTRONOMY
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What looks like a potato, orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter, and is made of rock ? _________________________ A rock that hits the Earth’s surface is called a _______________________. A rock that is flying through space is called a _____________________________. A rock that burns up in our atmo ...
... What looks like a potato, orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter, and is made of rock ? _________________________ A rock that hits the Earth’s surface is called a _______________________. A rock that is flying through space is called a _____________________________. A rock that burns up in our atmo ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Different stars produce different amounts of energy. The amount of energy produced by a star determines the star’s color and surface temperature. Stars differ in composition, age, and size. *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
... Different stars produce different amounts of energy. The amount of energy produced by a star determines the star’s color and surface temperature. Stars differ in composition, age, and size. *young stars are rich in hydrogen *older stars use up hydrogen to produce more helium ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... The fact that the spectra of stars are shifted towards the red suggests that the stars are moving _away____ Diagram the correct sequence of a star’s life cycle. ...
... The fact that the spectra of stars are shifted towards the red suggests that the stars are moving _away____ Diagram the correct sequence of a star’s life cycle. ...
Southern cross Crux - The Southern Cross Crux, the Southern Cross
... α1 Cru is magnitude 1.40 and α2 Cru is magnitude 2.09, both hot class B1 V main sequence stars, with surface temperatures of about 28,000 and 26,000 K respectively. Their luminosities are 25,000 and 16,000 times the Sun's. α1 and α2 Cru orbit over such a long period that motion is only barely seen. ...
... α1 Cru is magnitude 1.40 and α2 Cru is magnitude 2.09, both hot class B1 V main sequence stars, with surface temperatures of about 28,000 and 26,000 K respectively. Their luminosities are 25,000 and 16,000 times the Sun's. α1 and α2 Cru orbit over such a long period that motion is only barely seen. ...
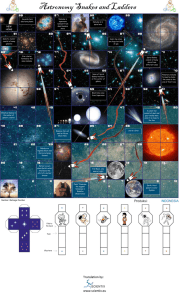
Astronomy Snakes and Ladders Earth, third planet in Solar System
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
1/2016
... Description: Delta Cephei is the prototype of the Cepheid class of variable stars. With a change in visual magnitude of 3.5 to 4.4, delta Cephei’s entire range of variability can be observed with the unaided eye. Its period of 5.366 days makes it an attractive candidate for anyone anxious to obtain ...
... Description: Delta Cephei is the prototype of the Cepheid class of variable stars. With a change in visual magnitude of 3.5 to 4.4, delta Cephei’s entire range of variability can be observed with the unaided eye. Its period of 5.366 days makes it an attractive candidate for anyone anxious to obtain ...
Astronomy Problems – Color Index Nov. 2011
... Astronomy Problems – Color Index Nov. 2011 Colors of Stars Astronomers measure the brightness of stars at three colors of light: The "U" band at 360 nm The "B" band at 440 nm The "V" band at 540 nm The "color index" of a star is defined as the magnitude in the B filter, minus the magnitude in ...
... Astronomy Problems – Color Index Nov. 2011 Colors of Stars Astronomers measure the brightness of stars at three colors of light: The "U" band at 360 nm The "B" band at 440 nm The "V" band at 540 nm The "color index" of a star is defined as the magnitude in the B filter, minus the magnitude in ...
CONSTELLATION CASSIOPEIA named after the
... the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to th ...
... the northern sky and one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to th ...
9 spectroscopic parallax
... Absolute magnitude = how bright (what magnitude) a star would appear at 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) ...
... Absolute magnitude = how bright (what magnitude) a star would appear at 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
chap17_s05_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
chap17_f04_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
The Stellar Luminosity Function
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
Astronomy Objectives
... Doppler effect and measuring motion of stars with their absorption spectra: Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence that supports it Big Bang Theory: be able to explain how the universe was formed according to this theory; know ...
... Doppler effect and measuring motion of stars with their absorption spectra: Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence that supports it Big Bang Theory: be able to explain how the universe was formed according to this theory; know ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.