Star Name __Direction ___ Degrees
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
... 21. Name three stars that are second magnitude or brighter. Give their location in direction and degrees above the horizon on the celestial sphere. Star Name __Direction Example: Polaris North ___________ ____________ ...
Chapter 25 Study guide Answer Key
... Which sequence of events describes the big bang theory? Begin with the earliest event. a. Explosion; atoms form; stars form; all matter concentrated at a single point. b. All matter concentrated at a single point; explosion; atoms form; stars form. c. Explosion; stars form; all matter concentrated a ...
... Which sequence of events describes the big bang theory? Begin with the earliest event. a. Explosion; atoms form; stars form; all matter concentrated at a single point. b. All matter concentrated at a single point; explosion; atoms form; stars form. c. Explosion; stars form; all matter concentrated a ...
Circle of Letters on Good Will Spiritual Astrology /1 Aries
... course of the day it corresponds to noontime. Aries is the seed, the first vibration emerging as a new idea. It is the first impulse from the background of eternity, the impetus for a new beginning. This is represented by the head of the ram shooting ahead with full power. This sign is fresh, elated ...
... course of the day it corresponds to noontime. Aries is the seed, the first vibration emerging as a new idea. It is the first impulse from the background of eternity, the impetus for a new beginning. This is represented by the head of the ram shooting ahead with full power. This sign is fresh, elated ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Define main sequence stars: • Major grouping of stars • Form a narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
... Define main sequence stars: • Major grouping of stars • Form a narrow band from the upper left to the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
Surface Environments of the Planets o+ our Solar System
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
Section 25.1 Properties of Stars
... A binary star is one of two stars revolving around a common center of mass under their mutual gravitational attraction. Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate—its mass. Common Center of Mass ...
... A binary star is one of two stars revolving around a common center of mass under their mutual gravitational attraction. Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate—its mass. Common Center of Mass ...
The Constellation Lepus, the Hare
... its striking red color. It varies in magnitude from a minimum of 9.8 to a maximum of 7.3, with a period of 420 days. R Leporis is at a distance of 1500 light-years. The colour intensifies as the star brightens. It was named for John Russell Hind and has been reputed to be the most beautiful star in ...
... its striking red color. It varies in magnitude from a minimum of 9.8 to a maximum of 7.3, with a period of 420 days. R Leporis is at a distance of 1500 light-years. The colour intensifies as the star brightens. It was named for John Russell Hind and has been reputed to be the most beautiful star in ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are the letters of the Greek alphabet used to name stars in a constellation? Give five illustrations of the use of the letters of the Greek alphabet ...
... 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are the letters of the Greek alphabet used to name stars in a constellation? Give five illustrations of the use of the letters of the Greek alphabet ...
Weekly Homework Questions #3, Sep. 14, 2010
... 6. The star Fomalhaut is visible in the evening now, and will be more prominent later in the fall. Its apparent magnitude is 1.15. Is it brighter or fainter than Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a ...
... 6. The star Fomalhaut is visible in the evening now, and will be more prominent later in the fall. Its apparent magnitude is 1.15. Is it brighter or fainter than Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a ...
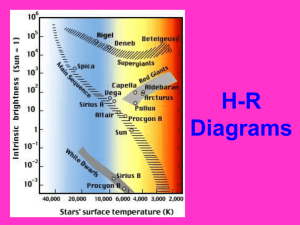
H-R Diagrams
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
CONSTELLATION TUCANA, THE TOUCAN
... Globular Cluster 47 Tucana is the second-brightest globular cluster in the sky after Omega Centauri, 47 Tucanae (NGC 104) lies just west of the Small Magellanic Cloud. Only 14,700 light-years distant from Earth, it is thought to be around 12 billion years old. Mostly composed of old, yellow stars, i ...
... Globular Cluster 47 Tucana is the second-brightest globular cluster in the sky after Omega Centauri, 47 Tucanae (NGC 104) lies just west of the Small Magellanic Cloud. Only 14,700 light-years distant from Earth, it is thought to be around 12 billion years old. Mostly composed of old, yellow stars, i ...
Chapter 30.1
... Measure light from star using telescopes Measurement is then assigned a number Brightest stars have lowest numbers Dimmest stars have highest numbers ...
... Measure light from star using telescopes Measurement is then assigned a number Brightest stars have lowest numbers Dimmest stars have highest numbers ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Apparent Magnitude The measurement of brightness is assigned a number on a scale – Brightest stars have lowest numbers – Dimmest stars have highest numbers ...
... Apparent Magnitude The measurement of brightness is assigned a number on a scale – Brightest stars have lowest numbers – Dimmest stars have highest numbers ...
F03HW09
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
The Big Dipper is a
... Each of the following lists a constellation and a bright star. In all cases but one, the star is part of the constellation. Which one is the mismatch? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... Each of the following lists a constellation and a bright star. In all cases but one, the star is part of the constellation. Which one is the mismatch? a. b. c. d. e. ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 3) As you move across the X axis of the diagram, what happens to surface temperature? Surface temperature decreases 4) Where is the sun found within the H-R diagram? In the Main Sequence 5) Sketch an H-R diagram and label the main sequence, white dwarf, and giant/super giant regions on the diagram. ...
... 3) As you move across the X axis of the diagram, what happens to surface temperature? Surface temperature decreases 4) Where is the sun found within the H-R diagram? In the Main Sequence 5) Sketch an H-R diagram and label the main sequence, white dwarf, and giant/super giant regions on the diagram. ...
THE STAR - physics.udel.edu
... The four brightest stars of Cassiopeia are all brighter than the third magnitude. Alpha Cassiopeiae, traditionally called Shedir (from the Arabic Al Sadr, "the breast"), is a double star. The primary is an orange-hued giant of magnitude 2.2, 229 light-years from Earth. The secondary is widely separa ...
... The four brightest stars of Cassiopeia are all brighter than the third magnitude. Alpha Cassiopeiae, traditionally called Shedir (from the Arabic Al Sadr, "the breast"), is a double star. The primary is an orange-hued giant of magnitude 2.2, 229 light-years from Earth. The secondary is widely separa ...
Slide 1
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
labex7
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) Star ...
Grade 6 Standard 4 - Murray School District
... 5. When Earth is in this location, which constellations would be visible at night? A. Scorpius and Sagitarius B. Libra and Virgo C. Libra and Capricorn D. Taurus and Aries 6. When Earth is in this location, which constellation would not be visible at night? A. Gemini B. Scorpius C. Cancer D. Aries 7 ...
... 5. When Earth is in this location, which constellations would be visible at night? A. Scorpius and Sagitarius B. Libra and Virgo C. Libra and Capricorn D. Taurus and Aries 6. When Earth is in this location, which constellation would not be visible at night? A. Gemini B. Scorpius C. Cancer D. Aries 7 ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.