The Stars
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
... • Most stars are on the main sequence. – Stars spend most of their life on the main sequence – Most stars are faint and red • Giants and supergiants are visible from great distances. – Giants and supergiants are rare. ...
Star Maps and Constellations (pdf 3.7 Megs)
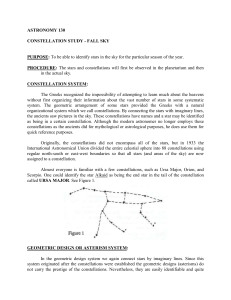
... 3. Division of the Sky into Constellations A constellation contains one or more asterisms (star groups) plus the surrounding region of the dark sky. Much the way that the United States is divided into 50 states, the sky is divided into 88 such constellations (i.e. regions). Each star technically bel ...
... 3. Division of the Sky into Constellations A constellation contains one or more asterisms (star groups) plus the surrounding region of the dark sky. Much the way that the United States is divided into 50 states, the sky is divided into 88 such constellations (i.e. regions). Each star technically bel ...
14.5 Yellow Giants and Pulsating Stars Variable Stars Not all stars
... 14.5 Yellow Giants and Pulsating Stars Variable Stars Not all stars have a constant luminosity. Stars that change in brightness are called variable stars, and many of these are associated with stages in the evolution of a star. For example, the red giant star Mira changes brightness over a regular p ...
... 14.5 Yellow Giants and Pulsating Stars Variable Stars Not all stars have a constant luminosity. Stars that change in brightness are called variable stars, and many of these are associated with stages in the evolution of a star. For example, the red giant star Mira changes brightness over a regular p ...
1 Astronomical Measurements and Quantities 2 Astronomical Objects
... method. A brief overview of different methods treated through the course to go from very nearby objects to very distant ones. [K],[BM] Galaxy Clusters: Morphological classification. Main properties. Clusters as multicomponent objects and their multivawelenght observations: optical, X-ray, gravitatio ...
... method. A brief overview of different methods treated through the course to go from very nearby objects to very distant ones. [K],[BM] Galaxy Clusters: Morphological classification. Main properties. Clusters as multicomponent objects and their multivawelenght observations: optical, X-ray, gravitatio ...
The Life Cycle of a Star and the Hertzsprung
... tells us two things about each star: its luminosity (brightness) and its temperature. The majority of stars, including our Sun, are found along a region called the Main Sequence. Main Sequence stars vary widely in effective temperature but the hotter they are, the more luminous (brighter) they are, ...
... tells us two things about each star: its luminosity (brightness) and its temperature. The majority of stars, including our Sun, are found along a region called the Main Sequence. Main Sequence stars vary widely in effective temperature but the hotter they are, the more luminous (brighter) they are, ...
read in advance to speed your work
... questions. Note that spectral class D indicates white dwarfs and T indicates brown dwarfs. 6a. ...
... questions. Note that spectral class D indicates white dwarfs and T indicates brown dwarfs. 6a. ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
... the ancients saw pictures in the sky. These constellations have names and a star may be identified as being in a certain constellation. Although the modern astronomer no longer employs these constellations as the ancients did for mythological or astrological purposes, he does use them for quick refe ...
... the ancients saw pictures in the sky. These constellations have names and a star may be identified as being in a certain constellation. Although the modern astronomer no longer employs these constellations as the ancients did for mythological or astrological purposes, he does use them for quick refe ...
Document
... Globular cluster – tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars Open cluster - contain less than a few hundred members, and are often very young - may eventually become disrupted over time and no longer gravitational bound – move in same direction in space – referred to as stellar ass ...
... Globular cluster – tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars Open cluster - contain less than a few hundred members, and are often very young - may eventually become disrupted over time and no longer gravitational bound – move in same direction in space – referred to as stellar ass ...
May 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... the Lion with the bright star, Regulas, marking his chin. On the 15th, if you look to the east of the moon with a pair of binoculars, you will find the Beehive cluster - a cluster of stars in the constellation of Cancer. They are an awesome sight in binoculars. Follow the curve of the Big Dipper’s h ...
... the Lion with the bright star, Regulas, marking his chin. On the 15th, if you look to the east of the moon with a pair of binoculars, you will find the Beehive cluster - a cluster of stars in the constellation of Cancer. They are an awesome sight in binoculars. Follow the curve of the Big Dipper’s h ...
Andromeda *ruler of men*
... Andromeda is an autumn constellation that is V shaped the best time of year to view Andromeda is during the month of November with the suggested time being 9pm. It occupies 722 square degrees and is located close to the North Pole in the first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere. Andromeda can be s ...
... Andromeda is an autumn constellation that is V shaped the best time of year to view Andromeda is during the month of November with the suggested time being 9pm. It occupies 722 square degrees and is located close to the North Pole in the first quadrant of the Northern Hemisphere. Andromeda can be s ...
Ch. 5 The Universe and Solar System
... Our Sun: An Average Star • The Sun is a stable, average size yellow star in the main sequence. • Has a surface temperature of 5500°C. • Largest object in our solar system—a million Earths could fit inside it. • Light takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach the Earth. • Much of what we know about th ...
... Our Sun: An Average Star • The Sun is a stable, average size yellow star in the main sequence. • Has a surface temperature of 5500°C. • Largest object in our solar system—a million Earths could fit inside it. • Light takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach the Earth. • Much of what we know about th ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctly. An eclipsing binary reveals its binary nature because of periodic dimming that occurs when one sta ...
... determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctly. An eclipsing binary reveals its binary nature because of periodic dimming that occurs when one sta ...
16. Properties of Stars
... determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctly. An eclipsing binary reveals its binary nature because of periodic dimming that occurs when one sta ...
... determines its luminosity and spectral type at each stage of its life. What are the three major classes of binary star systems? • A visual binary is a pair of orbiting stars that we can see distinctly. An eclipsing binary reveals its binary nature because of periodic dimming that occurs when one sta ...
Astronomy Basics
... massive as Earth. These cores are so massive that they accrete gas, forming gas giant planets. ...
... massive as Earth. These cores are so massive that they accrete gas, forming gas giant planets. ...
Star`s ReadingStar`s Reading(es)
... Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. The main characteristics used to classify stars are size, temperature, and brightness. Sizes of Stars When you look at stars in the sky, they all appear to be the same size. Many stars are actually about the size of the sun, whi ...
... Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics. The main characteristics used to classify stars are size, temperature, and brightness. Sizes of Stars When you look at stars in the sky, they all appear to be the same size. Many stars are actually about the size of the sun, whi ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... Throughout its life, these two forces determine the stages of a star’s life. ...
... Throughout its life, these two forces determine the stages of a star’s life. ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
Slide 1
... can collide and form H2 molecules. This also is facilitated on dust--for other molecules as well. It increases gravitation enough for stars to form in reasonable time. --Different sized clumps form stars of differing mass. --Disk with central sphere (protostar) formed. Gravity heats by ...
... can collide and form H2 molecules. This also is facilitated on dust--for other molecules as well. It increases gravitation enough for stars to form in reasonable time. --Different sized clumps form stars of differing mass. --Disk with central sphere (protostar) formed. Gravity heats by ...
Characteristics of Stars (Ph)
... Imagine you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. To travel from Earth to the sun would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is much farther away—a trip to Proxima Centauri would take 4.2 years! Most stars are much fart ...
... Imagine you could travel to the stars at the speed of light. To travel from Earth to the sun would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet the next nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is much farther away—a trip to Proxima Centauri would take 4.2 years! Most stars are much fart ...
Stars and Temperature and Color
... • The color indicates the temperature of the surface of the star. • The same is true for the filament in a light bulb or any other hot object. In general, we call radiation from a hot body `black body’ radiation (do demonstration 6B40.10). ...
... • The color indicates the temperature of the surface of the star. • The same is true for the filament in a light bulb or any other hot object. In general, we call radiation from a hot body `black body’ radiation (do demonstration 6B40.10). ...
Astronomy 1020 Exam 1 Review Questions
... 4. The evil Death Star has gone into an elliptical orbit about the Sun with an eccentricity of 0.90. At its closest approach to the Sun, it comes within 0.5 AU from our star. What is the orbital period of the Death Star? 5. Describe Newton’s 3 laws of motion and Newton’s law of gravity. 6. The brigh ...
... 4. The evil Death Star has gone into an elliptical orbit about the Sun with an eccentricity of 0.90. At its closest approach to the Sun, it comes within 0.5 AU from our star. What is the orbital period of the Death Star? 5. Describe Newton’s 3 laws of motion and Newton’s law of gravity. 6. The brigh ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.