Stellar Evolution
... wander up and down somewhat as its size shrinks. This process takes about 50 million years for a star like the sun, but may take a much shorter time for a more massive star since there will be more gravity. A ten solar mass star will only spend about 200,000 years in this initial stage. ...
... wander up and down somewhat as its size shrinks. This process takes about 50 million years for a star like the sun, but may take a much shorter time for a more massive star since there will be more gravity. A ten solar mass star will only spend about 200,000 years in this initial stage. ...
common constellations
... Members of the Underground Railroad were fully aware of the predicament of fleeing slaves. About 1831 the Railroad began to send travelers into the South to secretly teach slaves specific routes they could navigate using Polaris. By the beginning of the Civil War in 1861, about 500 people a year wer ...
... Members of the Underground Railroad were fully aware of the predicament of fleeing slaves. About 1831 the Railroad began to send travelers into the South to secretly teach slaves specific routes they could navigate using Polaris. By the beginning of the Civil War in 1861, about 500 people a year wer ...
Blowing Bubbles in Space: The Birth and Death of Practically
... ss Amherst/M.D. Stage et al. • Scale 420” • D 3067 pc ...
... ss Amherst/M.D. Stage et al. • Scale 420” • D 3067 pc ...
binary star
... • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
... • During their collapse from red giants to white dwarfs, medium-mass stars are thought to cast off their bloated outer layer, creating an expanding round cloud of gas called planetary nebula. ...
iClicker Questions
... Discovering the Universe, Eighth Edition by Neil F. Comins and William J. Kaufmann III Chapter 12 12-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust * c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are al ...
... Discovering the Universe, Eighth Edition by Neil F. Comins and William J. Kaufmann III Chapter 12 12-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust * c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are al ...
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit-
... A star plot on the diagonal line in the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R) which graphs luminosity and surface temperature. Once a star is stable and its gravitational inward pull overcomes the stars outward release of energy, it can be graphed on the Main Sequence. A star lives about 90% of its li ...
... A star plot on the diagonal line in the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R) which graphs luminosity and surface temperature. Once a star is stable and its gravitational inward pull overcomes the stars outward release of energy, it can be graphed on the Main Sequence. A star lives about 90% of its li ...
Toys Watch the Sky - The Sun is a close star
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
... centre of our Solar System. The Sun is located in an outer spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy, approximately 28,000 light-years from the galaxy's centre. (One light year is about 10 million million km.) In comparison with other stars, our Sun is very ordinary – it’s an average sized (1.4 million km ...
The Sun and Stars The Sun is a typical star with a mass of about 2
... I is measured in Watt/m2 . So, a star that is 10 times farther away appears 100 time less bright. The brightness is sometimes expressed not in Watt/m2 but in magnitudes. The magnitude of Sirius (the brightest star in our sky) is -1.46, of Canopus -0.72, of Vega 0.04, of Deneb 1.26,. . . more or less ...
... I is measured in Watt/m2 . So, a star that is 10 times farther away appears 100 time less bright. The brightness is sometimes expressed not in Watt/m2 but in magnitudes. The magnitude of Sirius (the brightest star in our sky) is -1.46, of Canopus -0.72, of Vega 0.04, of Deneb 1.26,. . . more or less ...
Candidate`s registration number: Desk number: ………………….. Date
... At the end of the examination, tie this paper to your answer book for Section B and hand them in together. Remember to fill in your registration number from your UCard in the space below. If you attempt additional questions in Section B, please indicate clearly on the cover of your answer book which ...
... At the end of the examination, tie this paper to your answer book for Section B and hand them in together. Remember to fill in your registration number from your UCard in the space below. If you attempt additional questions in Section B, please indicate clearly on the cover of your answer book which ...
deep space - altaastronomy
... Black Holes • Regular black holes are thought to form from heavy stars. When these stars end their lives in a supernova explosion, their cores collapse and gravity wins out over any other force that might be able to hold the star up. • Eventually, the star collapses so much that it is contained wit ...
... Black Holes • Regular black holes are thought to form from heavy stars. When these stars end their lives in a supernova explosion, their cores collapse and gravity wins out over any other force that might be able to hold the star up. • Eventually, the star collapses so much that it is contained wit ...
February 2012
... Mars offers especially curious behavior for the next couple months as the planet will execute a "retrograde loop" in the constellation of Leo the Lion. The word "planets" literally means "wanderers". In our view of the sky, planets appear to move or "wander" smoothly from one constellation to the ne ...
... Mars offers especially curious behavior for the next couple months as the planet will execute a "retrograde loop" in the constellation of Leo the Lion. The word "planets" literally means "wanderers". In our view of the sky, planets appear to move or "wander" smoothly from one constellation to the ne ...
Lecture 2 - Physics and Astronomy
... will find that it rises approximately 4 minutes earlier each night, or 2 hours earlier each month ...
... will find that it rises approximately 4 minutes earlier each night, or 2 hours earlier each month ...
reach for the stars
... older Pop II stars formed when there was little in the Universe but H and He. After these stars had fused H and He into heavier elements, they often scattered material back into space (through supernovae and planetary nebula). The younger Pop I stars then formed out of gaseous clouds of H, He, and t ...
... older Pop II stars formed when there was little in the Universe but H and He. After these stars had fused H and He into heavier elements, they often scattered material back into space (through supernovae and planetary nebula). The younger Pop I stars then formed out of gaseous clouds of H, He, and t ...
PDF - Interactive Stars
... May 16th to May 31 If you were born between these dates, your guiding star is Mirfak, a yellow supergiant, marking the hero's side. It is said to give courage and success through perseverance. Nearby, lies Algol, the Demon Star that marks the head of the petrifying gorgon that Perseus overcame. The ...
... May 16th to May 31 If you were born between these dates, your guiding star is Mirfak, a yellow supergiant, marking the hero's side. It is said to give courage and success through perseverance. Nearby, lies Algol, the Demon Star that marks the head of the petrifying gorgon that Perseus overcame. The ...
MBuzaTalk2
... Star begins to fuse iron, which eats up energy. Causes the star to contract, gravity taking over Varying densities causes pressure build up, and then the ‘bounce’ (degenerate core), the star violently ejects large amounts of the star into space. ...
... Star begins to fuse iron, which eats up energy. Causes the star to contract, gravity taking over Varying densities causes pressure build up, and then the ‘bounce’ (degenerate core), the star violently ejects large amounts of the star into space. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... in the prime of their lives . . 16.ln these stars, the force of Jlravity pushing in equals the force of nuclear _fusion__ pushing out and so the star is stable. 17. When a nebula grows and the force of gravity attracts more and more dust and gas, the temperature warms and a -protostar is formed. 18. ...
... in the prime of their lives . . 16.ln these stars, the force of Jlravity pushing in equals the force of nuclear _fusion__ pushing out and so the star is stable. 17. When a nebula grows and the force of gravity attracts more and more dust and gas, the temperature warms and a -protostar is formed. 18. ...
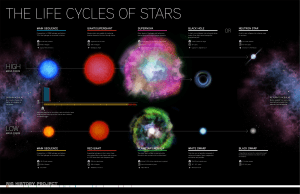
Life Cycles of Stars
... The outer layers of gas are ejected while the star's core contracts into a white dwarf. ...
... The outer layers of gas are ejected while the star's core contracts into a white dwarf. ...
RMH_Stellar_Evolution_Ast2001_09_29_09
... Indirect: -- must know distance Luminosity – depends on surface area (size) and temperature (Stefan-Boltzman Law) Mass -- with luminosity + physics , mass – luminosity relation ...
... Indirect: -- must know distance Luminosity – depends on surface area (size) and temperature (Stefan-Boltzman Law) Mass -- with luminosity + physics , mass – luminosity relation ...
What tool do astronomers use to understand the evolution of stars?
... Mass-Lifetime relation • The lifetime of a star (on the main sequence) is longer if more fuel is available and shorter if that fuel is burned more rapidly • The available fuel is (roughly) proportional to the mass of the star • From the previous, we known that luminosity is much higher for higher m ...
... Mass-Lifetime relation • The lifetime of a star (on the main sequence) is longer if more fuel is available and shorter if that fuel is burned more rapidly • The available fuel is (roughly) proportional to the mass of the star • From the previous, we known that luminosity is much higher for higher m ...
guide to orion 3-d flythrough
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
... The central area of the nebula is called the Trapezium cluster. It is dominated by four young, massive stars in a kite-like arrangement. The brightest of these stars, which has a luminosity 100,000 times that of the Sun, provides the energy that creates the nebula as we see it. It produces a flood o ...
Problem Set #3
... a. Is your galaxy in solid body rotation? How do you know? b. What is the local rotation speed at your position? c. Is the rotation curve locally flat? How do you know? d. What is the mass of the Galaxy contained within R0? e. Do you think this Galaxy is likely to be more or less massive than the Mi ...
... a. Is your galaxy in solid body rotation? How do you know? b. What is the local rotation speed at your position? c. Is the rotation curve locally flat? How do you know? d. What is the mass of the Galaxy contained within R0? e. Do you think this Galaxy is likely to be more or less massive than the Mi ...
Astronomy 20 Homework # 2
... Å wide. How many counts per resolution element are detected from the galaxy alone in a 1-hour exposure? From the foreground sky? If a blank piece of sky is measured at the same time in order to subtract the sky spectrum from the total, what is the signal-to-noise ratio per resolution element in the ...
... Å wide. How many counts per resolution element are detected from the galaxy alone in a 1-hour exposure? From the foreground sky? If a blank piece of sky is measured at the same time in order to subtract the sky spectrum from the total, what is the signal-to-noise ratio per resolution element in the ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.