Autumn Asterisms for binoculars 2013
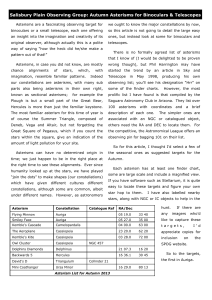
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in Auriga ...
... (the Giraffe) is not one of the brightest constellations, but the Cascade is one of its showpiece objects, with the open cluster NGC 1502 to its end. It is an easy object in binoculars and a favourite of mine. You can find it by taking a line from Capella in Auriga ...
IB_Op_F_04 - Effectsmeister
... corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall into this category of stars are called main sequence stars . Does our Sun fit into this category? White dwarfs are hot dim stars while red giants are bright cool stars. Where (i.e. in which regions) should these two types of stars be in the diagram? Identif ...
... corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall into this category of stars are called main sequence stars . Does our Sun fit into this category? White dwarfs are hot dim stars while red giants are bright cool stars. Where (i.e. in which regions) should these two types of stars be in the diagram? Identif ...
Stellar Evolution and the Herzsprung-Russell Diagram
... • Details depend sensitively on total mass: consider “low mass” stars like the sun, and “high mass” stars over 8 Msun. • “Very low mass” stars end their lives after the main sequence with no further nuclear fuels. • Post-M-S evolution may last 1/10 as long as M-S did • (Sun: 1 billion vs. 10 billion ...
... • Details depend sensitively on total mass: consider “low mass” stars like the sun, and “high mass” stars over 8 Msun. • “Very low mass” stars end their lives after the main sequence with no further nuclear fuels. • Post-M-S evolution may last 1/10 as long as M-S did • (Sun: 1 billion vs. 10 billion ...
Lecture 19: Low
... • Continue with life of a lowlow-mass star (like the Sun) after exhausting H in core -- post MS • Red giant (RG I) phase, with H shell burning • Helium flash goes off in shrinking degenerate core: horizontal branch star with He core burning • Double shell burning (H and He) yields red supergiant (RG ...
... • Continue with life of a lowlow-mass star (like the Sun) after exhausting H in core -- post MS • Red giant (RG I) phase, with H shell burning • Helium flash goes off in shrinking degenerate core: horizontal branch star with He core burning • Double shell burning (H and He) yields red supergiant (RG ...
ppt document
... In the ejection of the planetary nebula and in supernova explosions, some and sometimes most of the mass of the star is ejected back into space. There is a difference, though. The initial mass of the collapsing nebula consisted of mostly hydrogen. The final mass of the expanding nebula is enriched i ...
... In the ejection of the planetary nebula and in supernova explosions, some and sometimes most of the mass of the star is ejected back into space. There is a difference, though. The initial mass of the collapsing nebula consisted of mostly hydrogen. The final mass of the expanding nebula is enriched i ...
Distance measures - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... be made for atmospheric refraction and the effects of "seeing". Also stars actually do appear to move across the sky relative to other stars in a definite direction over time. This is called proper motion and must be accounted for when determining parallaxes. If you study the parallax diagram you wi ...
... be made for atmospheric refraction and the effects of "seeing". Also stars actually do appear to move across the sky relative to other stars in a definite direction over time. This is called proper motion and must be accounted for when determining parallaxes. If you study the parallax diagram you wi ...
Great Astronomers of the 20th Century
... Jill Tarter • Joint appointment at UC Berkeley and SETI ...
... Jill Tarter • Joint appointment at UC Berkeley and SETI ...
Activity: Star Classification - d
... Part 1: Exploring with Classification Each group will receive 1 set of 27 stars. Every star has: a color, name, temperature, size, & luminosity value o The luminosity is compared to the sun's luminosity. If a star has a luminosity value of 5, then it is 5 times brighter than our sun. If a star h ...
... Part 1: Exploring with Classification Each group will receive 1 set of 27 stars. Every star has: a color, name, temperature, size, & luminosity value o The luminosity is compared to the sun's luminosity. If a star has a luminosity value of 5, then it is 5 times brighter than our sun. If a star h ...
Exploring Space
... million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...
... million K, pressure is so great that nuclear fusion occurs- a star is born Heat from fusion of hydrogen is released When balance is maintained from inward pressure (gravity) and outward pressure (heat) the Main-Sequence stage is ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... • Stars at the top above the main sequence are called Supergiants • Stars between the Supergiants and main sequence are called Giants • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
... • Stars at the top above the main sequence are called Supergiants • Stars between the Supergiants and main sequence are called Giants • Stars below the Main Sequence are called White Dwarfs ...
File - Adopt A Constellation
... • Constellations - A pattern or group of stars in the sky that humans observe in a pattern and give a name. • People of ancient time saw the constellations as character or animals in the sky. They made up stories to explain how the object, animal, or character came into the night sky • Earth rotate ...
... • Constellations - A pattern or group of stars in the sky that humans observe in a pattern and give a name. • People of ancient time saw the constellations as character or animals in the sky. They made up stories to explain how the object, animal, or character came into the night sky • Earth rotate ...
Sequencing the Stars
... Open Cluster M44 (Beehive). Image taken by the author. second prominent branch called the horizontal branch. After that, at the last stage, the star rapidly diminishes in brightness and becomes a very faint white dwarf. This last transition takes ...
... Open Cluster M44 (Beehive). Image taken by the author. second prominent branch called the horizontal branch. After that, at the last stage, the star rapidly diminishes in brightness and becomes a very faint white dwarf. This last transition takes ...
Astronomy 1010 final review sample topics
... b.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night, but instead each successive night the stars are slightly displaced relative to where they were the night before c.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night and do not move from one night to the next 3. There are lunar eclipses and th ...
... b.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night, but instead each successive night the stars are slightly displaced relative to where they were the night before c.) stars do not move in the sky during a single night and do not move from one night to the next 3. There are lunar eclipses and th ...
May 2014
... stars, detected other planets through radial velocity (star wobble – and blue/red shift of the star's light), and transiting planets. The Kepler telescope used the dip-in-light transit method for finding planets. This method is very limited, as the planets' orbit have to be in line with our line of ...
... stars, detected other planets through radial velocity (star wobble – and blue/red shift of the star's light), and transiting planets. The Kepler telescope used the dip-in-light transit method for finding planets. This method is very limited, as the planets' orbit have to be in line with our line of ...
Exploring the Universe
... an H-R diagram where most stars spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main sequence ...
... an H-R diagram where most stars spend 90% of their life. i. A diagonal band running from the bright, hot stars on the upper left to the dim, cool stars on the lower right ii. Example: The Sun lies in the main sequence ...
PREVIEW-Reading Quiz 06 - Chapter 12
... Between C and D Between D and E Between B and C Between A and B ...
... Between C and D Between D and E Between B and C Between A and B ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #1
... of sight at b = 0 deg and l = 180 deg. We are interested in observing the most distant solar-type stars (MV ' +5.1) possible, but our apparent magnitude limit for the observations is mV = 24.0. The central stellar density of the halo is expected to be ∼ 1% that of the disk component, but the number ...
... of sight at b = 0 deg and l = 180 deg. We are interested in observing the most distant solar-type stars (MV ' +5.1) possible, but our apparent magnitude limit for the observations is mV = 24.0. The central stellar density of the halo is expected to be ∼ 1% that of the disk component, but the number ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.























