Ch. 19 (Starbirth)
... nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to fuse. ...
... nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to fuse. ...
Semester #1 – GeoScience Review Guide – Final Exam Scale
... 1. What is a light-year? How big is it in kilometers? 2. In your scale model of the Solar System, the scale was 1 cm = 10,000,000,000 km. Jupiter is 778,000,000 km from the sun. On your scale model, how many cm was Jupiter from the sun? 3. Is this a true or false statement? 104 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 4 ...
... 1. What is a light-year? How big is it in kilometers? 2. In your scale model of the Solar System, the scale was 1 cm = 10,000,000,000 km. Jupiter is 778,000,000 km from the sun. On your scale model, how many cm was Jupiter from the sun? 3. Is this a true or false statement? 104 = 10 x 10 x 10 x 10 4 ...
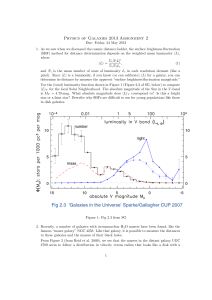
distance to the centre of the Milky Way.
... From measured brightnesses of some of the stars in the globular clusters (in particular, by studying some variable stars of a characteristic luminosity), Shapley was able to derive the distances to many of the clusters. ...
... From measured brightnesses of some of the stars in the globular clusters (in particular, by studying some variable stars of a characteristic luminosity), Shapley was able to derive the distances to many of the clusters. ...
Date_________________ TWINKLE, TWINKLE
... they appear to us, just as car headlights vary in brightness depending on how close they are. To handle this problem, astronomers have defined two properties for stars. The first property is absolute magnitude (M) which is how bright a star would appear if it was at a fixed distance away from the Ea ...
... they appear to us, just as car headlights vary in brightness depending on how close they are. To handle this problem, astronomers have defined two properties for stars. The first property is absolute magnitude (M) which is how bright a star would appear if it was at a fixed distance away from the Ea ...
00
... The effect is seen only when the smaller star eclipses the larger because the higher temperature exists on the inner faces. Since both the effect of ellipticity and the reflection effect result from the closeness of two stars it is difficult to separate one effect from the other. The proximity gives ...
... The effect is seen only when the smaller star eclipses the larger because the higher temperature exists on the inner faces. Since both the effect of ellipticity and the reflection effect result from the closeness of two stars it is difficult to separate one effect from the other. The proximity gives ...
Problem Set 2
... 4. Here we’ll compute the distance and absolute magnitude of SN1987A, the Type IIc supernova that exploded in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The ring around SN1987A measures 1.0062 × 1.0018 on the sky. Assume that the ring is circular; what is its inclination i? Now, the first signal is seen at t0 = 8 ...
... 4. Here we’ll compute the distance and absolute magnitude of SN1987A, the Type IIc supernova that exploded in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The ring around SN1987A measures 1.0062 × 1.0018 on the sky. Assume that the ring is circular; what is its inclination i? Now, the first signal is seen at t0 = 8 ...
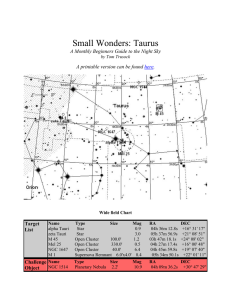
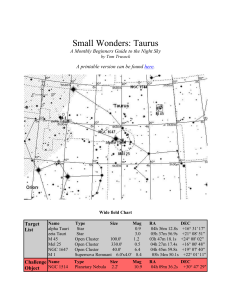
SM_Taurus - Cloudy Nights
... brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance of 1.35 AU. The Hipparcos satellite determined that the center of mass for Mel 2 ...
... brightness, it's relative closeness to Earth translates it into the 13th brightest star in the night sky. Aldebaran is thought to have a large planetary companion which masses around 11 Jupiters and orbits at a distance of 1.35 AU. The Hipparcos satellite determined that the center of mass for Mel 2 ...
CCD PHOTOMETRY OF OPEN STAR CLUSTER M67
... old open star cluster. The distance and age of open star clusters can be determined by comparison of the process of main sequence with a theoretical model. Theoretical isochrones used in this work were published by Bertelli et al. (1994), and include models for different chemical composition and age ...
... old open star cluster. The distance and age of open star clusters can be determined by comparison of the process of main sequence with a theoretical model. Theoretical isochrones used in this work were published by Bertelli et al. (1994), and include models for different chemical composition and age ...
Life_Cycle_of_a_Star_Powerpoint
... • A System of stars, dust, and gases all heald together as a group by gravity. – Our solar system is part of the Milky Way galaxy. – There are more than a billion galaxies in the universe. **3 types of galaxies ...
... • A System of stars, dust, and gases all heald together as a group by gravity. – Our solar system is part of the Milky Way galaxy. – There are more than a billion galaxies in the universe. **3 types of galaxies ...
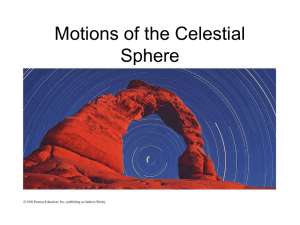
Motions of the Celestial Sphere
... The occupants notice that the stars never rise or set but appear to move in circles parallel to the horizon. Where on the planet did the space ship land? a) At the equator. b) At 45 degrees latitude. c) At one of the celestial poles. ...
... The occupants notice that the stars never rise or set but appear to move in circles parallel to the horizon. Where on the planet did the space ship land? a) At the equator. b) At 45 degrees latitude. c) At one of the celestial poles. ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... that they are hot but faint. There are probably very large numbers of these, but they are not easy to detect. ...
... that they are hot but faint. There are probably very large numbers of these, but they are not easy to detect. ...
Chapter 26.4
... they may merge to form an elliptical galaxy. Because stars are so far apart – it may have no affect … then again – we could get ejected out of our “place” on the Orion arm due to collision. ...
... they may merge to form an elliptical galaxy. Because stars are so far apart – it may have no affect … then again – we could get ejected out of our “place” on the Orion arm due to collision. ...
Document
... Stage 4 (low mass) A star like our Sun will contract, becoming a white dwarf, which slowly cools, changing color as it does, until it can no longer be seen a black dwarf. ...
... Stage 4 (low mass) A star like our Sun will contract, becoming a white dwarf, which slowly cools, changing color as it does, until it can no longer be seen a black dwarf. ...
Unit 1
... eddies, which are cooler and darker than the rest of the solar surface • b. solar flares cause the photoshere to expand and cool in the vicinity of the flare • c. magnetic fields breaking through the photosphere inhibit heat conduction where the field is strong • d. masses of heavy elements occlude ...
... eddies, which are cooler and darker than the rest of the solar surface • b. solar flares cause the photoshere to expand and cool in the vicinity of the flare • c. magnetic fields breaking through the photosphere inhibit heat conduction where the field is strong • d. masses of heavy elements occlude ...
Document
... Globular cluster – tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars Open cluster - contain less than a few hundred members, and are often very young - may eventually become disrupted over time and no longer gravitational bound – move in broadly same direction in space – referred to as ste ...
... Globular cluster – tight groups of hundreds of thousands of very old stars Open cluster - contain less than a few hundred members, and are often very young - may eventually become disrupted over time and no longer gravitational bound – move in broadly same direction in space – referred to as ste ...
How Far Can You See?
... next nearest star either. It’s actually a triple system: three stars orbiting each other. The closest of the three, called Proxima Centauri, is a tiny, 4.2-lightyear-distant red ember, visible only through telescopes. But it might not be the record holder either. It’s possible that extremely dim sta ...
... next nearest star either. It’s actually a triple system: three stars orbiting each other. The closest of the three, called Proxima Centauri, is a tiny, 4.2-lightyear-distant red ember, visible only through telescopes. But it might not be the record holder either. It’s possible that extremely dim sta ...
Document
... In 1932, Karl Jansky discovered that the MW produced a broad range of radio emission. Later in 1951, several groups detected the 21-cm hyperfine transition of atomic hydrogen which allowed for precise line-of-sight velocities to be determined without the hindrance of dust absorption. •Gas is confin ...
... In 1932, Karl Jansky discovered that the MW produced a broad range of radio emission. Later in 1951, several groups detected the 21-cm hyperfine transition of atomic hydrogen which allowed for precise line-of-sight velocities to be determined without the hindrance of dust absorption. •Gas is confin ...
Microsoft Word 97
... 1. When did the Milky Way begin? _____________________________________________________ 2. Where does its name come from? ___________________________________________________ 3. What do we see when we look in the sky? _____________________________________________ 4. What does our galaxy look like from ...
... 1. When did the Milky Way begin? _____________________________________________________ 2. Where does its name come from? ___________________________________________________ 3. What do we see when we look in the sky? _____________________________________________ 4. What does our galaxy look like from ...
ppt - Serbian Virtual Observatory - astronomical observatory belgrade
... For all eleven double stars there exist measurements (sufficient number) on the basis of which one can obtain the apparent orbit. Nevertheless, we prefer a combined approach using both apparent orbits and estimation. The first step in the estimation is in fact testing the hypothesis that both stars ...
... For all eleven double stars there exist measurements (sufficient number) on the basis of which one can obtain the apparent orbit. Nevertheless, we prefer a combined approach using both apparent orbits and estimation. The first step in the estimation is in fact testing the hypothesis that both stars ...
1 - Quia
... B. Carbon C. Hydrogen D. Nitrogen 16. What is the first stage in the life cycle of a star? (2 points) ...
... B. Carbon C. Hydrogen D. Nitrogen 16. What is the first stage in the life cycle of a star? (2 points) ...
Properties of Stars - Mr. Carter`s Earth
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightness of ...
Chapter 13 - USD Home Pages
... require a temperature of 600 million K (pg 387). This is a lot hotter than the 10 million K for hydrogen fusion because the carbon nuclei are heavier and have a charge of +6, which gets squared. Oxygen, with a charge of +8, is even more difficult to fuse. The interior of a white dwarf never gets thi ...
... require a temperature of 600 million K (pg 387). This is a lot hotter than the 10 million K for hydrogen fusion because the carbon nuclei are heavier and have a charge of +6, which gets squared. Oxygen, with a charge of +8, is even more difficult to fuse. The interior of a white dwarf never gets thi ...
lecture
... •Produces a two-dimensional map of the gas in the system, but in Velocity Space not the Cartesian Space that we are used to… ...
... •Produces a two-dimensional map of the gas in the system, but in Velocity Space not the Cartesian Space that we are used to… ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.