Lecture 19 Brightness Units
... are all due to absorption by atoms starting from the second energy state. – The only way an atom gets into this state is by being hit by a neighbor, and the neighbors at these temperatures are not moving fast enough. Balmer lines are weak. Mar 3, 2006 ...
... are all due to absorption by atoms starting from the second energy state. – The only way an atom gets into this state is by being hit by a neighbor, and the neighbors at these temperatures are not moving fast enough. Balmer lines are weak. Mar 3, 2006 ...
1 Ay 124 Winter 2014 – HOMEWORK #3
... Problem 1 The nearest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, M31, has a very concentrated nucleus. At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc ...
... Problem 1 The nearest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, M31, has a very concentrated nucleus. At a projected radius of 1 arcsec, stars in the nucleus have a line of sight velocity dispersion of 150 km s−1 , and are also rotating about the nucleus at 150 km s−1 . The total luminosity from within 1 arc ...
Deducing Temperatures and Luminosities of Stars
... – L measures star’s “intrinsic” brightness, rather than “apparent” brightness seen from Earth ...
... – L measures star’s “intrinsic” brightness, rather than “apparent” brightness seen from Earth ...
Astronomy 103 Exam 2 Review
... surface and one at rest high above the Earth’s surface. Which statement is correct? A. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running slow with respect to the observer's own clock. B. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running fast with respect to the observer's own clock ...
... surface and one at rest high above the Earth’s surface. Which statement is correct? A. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running slow with respect to the observer's own clock. B. Each observer will see the other's clock to be running fast with respect to the observer's own clock ...
ASTRONOMY 12 Problem Set 4 – Due March 10, 2016 1) After
... are. The total thermal energy in the core (which is all that can be radiated away) is then E ∼ Nion kT where Nion is the number of nuclei in the core. a) Calculate the total number of carbon nuclei (which will be Nion ) in a (pure) carbon core of 0.7 M⊙ . (hint: 1 gram of carbon contains NA /12 carb ...
... are. The total thermal energy in the core (which is all that can be radiated away) is then E ∼ Nion kT where Nion is the number of nuclei in the core. a) Calculate the total number of carbon nuclei (which will be Nion ) in a (pure) carbon core of 0.7 M⊙ . (hint: 1 gram of carbon contains NA /12 carb ...
Chapter 10 Workbook
... Developed 3 laws of ____________________________________________. 1. All ___________________ move in ellipses with the _____________ at one focus. 2. Planets sweep out at ________________ areas of their ____________________ orbit in __________________ times. 3. The time a _________________ takes to ...
... Developed 3 laws of ____________________________________________. 1. All ___________________ move in ellipses with the _____________ at one focus. 2. Planets sweep out at ________________ areas of their ____________________ orbit in __________________ times. 3. The time a _________________ takes to ...
The Swansong of Stars Orbiting Massive Black Holes
... LISA will be able to detect compact objects that spiral into a MBH by GW emission from up to a distance of a Gpc. The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral ...
... LISA will be able to detect compact objects that spiral into a MBH by GW emission from up to a distance of a Gpc. The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral ...
History of the Universe and Solar System
... Bang. (Note: Recent observations suggest this was the case for the first 2/3 of the Universe’s history. The expansion rate now seems to have increased for the last 1/3 of the Universe’s history. This is explained by “dark phantom energy”, which is hypothesized to be forming between galaxies and push ...
... Bang. (Note: Recent observations suggest this was the case for the first 2/3 of the Universe’s history. The expansion rate now seems to have increased for the last 1/3 of the Universe’s history. This is explained by “dark phantom energy”, which is hypothesized to be forming between galaxies and push ...
Red Giants - Uplift North Hills Prep
... RED GIANT PHASE of star’s existance A star experiences an energy crisis and its core collapses when the star's basic, nonrenewable energy source - hydrogen - is used up. A shell of hydrogen on the edge of the collapsed core will be compressed and heated. The nuclear fusion of the hydrogen in the sh ...
... RED GIANT PHASE of star’s existance A star experiences an energy crisis and its core collapses when the star's basic, nonrenewable energy source - hydrogen - is used up. A shell of hydrogen on the edge of the collapsed core will be compressed and heated. The nuclear fusion of the hydrogen in the sh ...
Slide 1
... The Local Group: a galaxy 'poor' cluster of 27 galaxies: three large spirals, 12 dwarf ellipticals, 4 ellipticals, and 8 Irr. Dust in the plane of the Milky Way may obscure more. The Local (Virgo) Supercluster: Pancake-shaped. Composed of the Virgo Cluster (a 'rich' cluster) and about 100 other clus ...
... The Local Group: a galaxy 'poor' cluster of 27 galaxies: three large spirals, 12 dwarf ellipticals, 4 ellipticals, and 8 Irr. Dust in the plane of the Milky Way may obscure more. The Local (Virgo) Supercluster: Pancake-shaped. Composed of the Virgo Cluster (a 'rich' cluster) and about 100 other clus ...
The magnitude scale, parallax, the parsec, and Cepheid distances
... Filters only allow light from a specifice wavelength range through Examples are ugriz or BVRI in the op;cal or YJHK in the near-‐IR Use filter symbols as subscript, i.e., mK = K-‐band magnitude If ...
... Filters only allow light from a specifice wavelength range through Examples are ugriz or BVRI in the op;cal or YJHK in the near-‐IR Use filter symbols as subscript, i.e., mK = K-‐band magnitude If ...
Document
... If a star’s iron core reaches 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, gravity becomes strong enough to combine electrons and protons into neutrons. During this brief period, heavier elements such as gold and uranium are created, as atomic nuclei are smashed together. The core of the star collapses and ...
... If a star’s iron core reaches 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, gravity becomes strong enough to combine electrons and protons into neutrons. During this brief period, heavier elements such as gold and uranium are created, as atomic nuclei are smashed together. The core of the star collapses and ...
Slide 1 - Personal.psu.edu
... outward pressure from the core. The star is now on the Main Sequence • More massive stars follow the same process, but more quickly • Less massive stars form more slowly ...
... outward pressure from the core. The star is now on the Main Sequence • More massive stars follow the same process, but more quickly • Less massive stars form more slowly ...
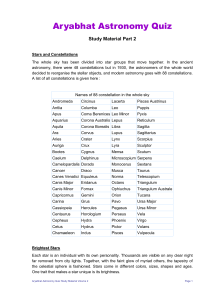
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... Because of its position in the sky, the Alpha Centauri system is not easily visible in much of the Northern Hemisphere. An observer must be at latitudes south of 28 degrees north (or roughly from Naples, Florida and locations further south) to see the closest stellar system to us. The two brighter c ...
... Because of its position in the sky, the Alpha Centauri system is not easily visible in much of the Northern Hemisphere. An observer must be at latitudes south of 28 degrees north (or roughly from Naples, Florida and locations further south) to see the closest stellar system to us. The two brighter c ...
Stellar Distances - Red Hook Central School District
... Ex 5: A study of a star suggests it is a main sequence star. Its apparent brightness is 1 x 10-12 W/m2. The peak is 600 nm. a. Find the surface temperature. b. If the temperature implies a luminosity of 1 x 10 26 W, what is the star’s distance in LY? ...
... Ex 5: A study of a star suggests it is a main sequence star. Its apparent brightness is 1 x 10-12 W/m2. The peak is 600 nm. a. Find the surface temperature. b. If the temperature implies a luminosity of 1 x 10 26 W, what is the star’s distance in LY? ...
November - LVAstronomy.com
... monthly summary. We also accept digital imaging. Visual astronomy depends on what’s seen through the eyepiece. Not only does it satisfy an innate curiosity, but it allows the visual observer to discover the beauty and the wonderment of the night sky. Before photography, all observations depended on ...
... monthly summary. We also accept digital imaging. Visual astronomy depends on what’s seen through the eyepiece. Not only does it satisfy an innate curiosity, but it allows the visual observer to discover the beauty and the wonderment of the night sky. Before photography, all observations depended on ...
The Star
... Journal, my five in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. I would remind them that my order has long been famous for its scientific works. We may be few now, but ever since the eighteenth century we have made contributions to astronomy and geophysics out of all proportion to our num ...
... Journal, my five in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. I would remind them that my order has long been famous for its scientific works. We may be few now, but ever since the eighteenth century we have made contributions to astronomy and geophysics out of all proportion to our num ...
REGIONAL exam 2013
... 5. Each question is worth one point. Tiebreaker questions are indicated with a (T#) in which the number indicates the order of consultation in the event of a tie. Tiebreaker questions count toward the overall raw score, and are only used as tiebreakers when there is a tie. In such cases, (T1) will b ...
... 5. Each question is worth one point. Tiebreaker questions are indicated with a (T#) in which the number indicates the order of consultation in the event of a tie. Tiebreaker questions count toward the overall raw score, and are only used as tiebreakers when there is a tie. In such cases, (T1) will b ...
Chapter 7 Review Answers
... 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have lots of dust and gas, which are the birt ...
... 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have lots of dust and gas, which are the birt ...
Lecture 10 Advanced Variable Star Stuff March 18 2003 8:00 PM
... Cataclysmic variables A white dwarf is the remnant that is left after a star similar to our Sun dies. It blows off all of its outer layers and leaves behind a hot dense core. There is no more fuel for nuclear fusion (the elements left are mainly things like carbon and iron, not easy to fuse). If we ...
... Cataclysmic variables A white dwarf is the remnant that is left after a star similar to our Sun dies. It blows off all of its outer layers and leaves behind a hot dense core. There is no more fuel for nuclear fusion (the elements left are mainly things like carbon and iron, not easy to fuse). If we ...
Astronomy 104: Homework Set 6 Due: Wednesday, April 1, 2015
... Earth. Use the relation between brightness (flux), luminosity and distance (see Destination 7) to determine the ratio of the distance to M 31 and the distance of the LMC? If the LMC is 50 kpc distant, how far is M 31 from Earth? Is your result with 10% of the value for the distance of M31 given in D ...
... Earth. Use the relation between brightness (flux), luminosity and distance (see Destination 7) to determine the ratio of the distance to M 31 and the distance of the LMC? If the LMC is 50 kpc distant, how far is M 31 from Earth? Is your result with 10% of the value for the distance of M31 given in D ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.