the printable Observing Olympics Object Info Sheet in pdf
... disk. It has a very high surface brightness and some observers report that NGC6572 looks blue while others think it is green. It has an integrated magnitude of 7.0p packed into a tiny 11” disk which is brighter than the famous Ring nebula. NGC 6572 only began to shed its gases a few thousand years a ...
... disk. It has a very high surface brightness and some observers report that NGC6572 looks blue while others think it is green. It has an integrated magnitude of 7.0p packed into a tiny 11” disk which is brighter than the famous Ring nebula. NGC 6572 only began to shed its gases a few thousand years a ...
Stellarium Night Sky Search Key Commands Constellations buttons
... arrows will easily move your view in different directions.] ...
... arrows will easily move your view in different directions.] ...
I CAN SEE THE STARS IN YOUR EYES
... Your space craft begins to travel at the speed of light, taking you towards the sun. Traveling at this speed, the trip from Earth to the sun, a distance of 93 million miles, would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet, to get to the next closest star, Proxima Centauri, would ...
... Your space craft begins to travel at the speed of light, taking you towards the sun. Traveling at this speed, the trip from Earth to the sun, a distance of 93 million miles, would take about 8 minutes, not very long for such a long trip! Yet, to get to the next closest star, Proxima Centauri, would ...
Some Basic Principles from Astronomy
... surface of the Earth, and what we would like to know more about is out there – thataway! [◮ Imagine I am gesturing vaguely at the ceiling as you read this ◭] • In many ways, the story of astronomy began with attempting to measure distances —how big is the Earth? how far away is the Moon? how big is ...
... surface of the Earth, and what we would like to know more about is out there – thataway! [◮ Imagine I am gesturing vaguely at the ceiling as you read this ◭] • In many ways, the story of astronomy began with attempting to measure distances —how big is the Earth? how far away is the Moon? how big is ...
The Southern Fall PDF - Treasures of the Southern Sky
... with the brighter stars and the red emission nebula surrounding part of the cluster, which are both indications of youth. Open clusters such as NGC 3293 are excellent laboratories for studying the late stages of star formation and their early evolution. The young stars have not moved far from their ...
... with the brighter stars and the red emission nebula surrounding part of the cluster, which are both indications of youth. Open clusters such as NGC 3293 are excellent laboratories for studying the late stages of star formation and their early evolution. The young stars have not moved far from their ...
Phys133 SAMPLE questions for MidTerm#1
... 25) How did Eratosthenes estimate the size of the earth in 240 B.C.? A) by measuring the size of the earth's shadow on the Moon in a lunar eclipse B) by observing the duration of a solar eclipse C) by sending fleets of ships around the earth D) by comparing the maximum altitude of the Sun in two cit ...
... 25) How did Eratosthenes estimate the size of the earth in 240 B.C.? A) by measuring the size of the earth's shadow on the Moon in a lunar eclipse B) by observing the duration of a solar eclipse C) by sending fleets of ships around the earth D) by comparing the maximum altitude of the Sun in two cit ...
1705 Star Charts
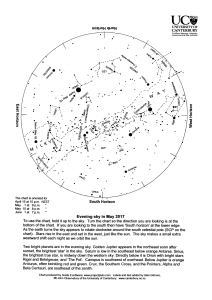
... The Evening Sky in May 2017 Two bright planets and the brightest stars share the evening sky this May. Soon after sunset golden Jupiter appears in the northeast. Beside Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Below Jupiter, near the horizon, is orange Arcturus, the brightest star in the nort ...
... The Evening Sky in May 2017 Two bright planets and the brightest stars share the evening sky this May. Soon after sunset golden Jupiter appears in the northeast. Beside Jupiter is Spica, the brightest star in Virgo. Below Jupiter, near the horizon, is orange Arcturus, the brightest star in the nort ...
Astronomy 103: Midterm 2 Answers Correct answer in bold
... 28. The planets Londinium and Bellerophon orbit a star called the White Sun. Londinium is 1 AU from the star, and Bellerophon is 10 AU away. The brightness of light from the White Sun on Londinium is about 100 watt/meter2. What is the brightness of light from the White Sun on Bellerophon? ...
... 28. The planets Londinium and Bellerophon orbit a star called the White Sun. Londinium is 1 AU from the star, and Bellerophon is 10 AU away. The brightness of light from the White Sun on Londinium is about 100 watt/meter2. What is the brightness of light from the White Sun on Bellerophon? ...
Lecture 13: The Stars –
... The surface of a planet that close to our sun would be scorching hot. But because the star Gliese 581 is only about 1 percent as bright as the sun, temperatures on the new planet should be much more comfortable. Taking into account the presence of an atmosphere and how much starlight the planet prob ...
... The surface of a planet that close to our sun would be scorching hot. But because the star Gliese 581 is only about 1 percent as bright as the sun, temperatures on the new planet should be much more comfortable. Taking into account the presence of an atmosphere and how much starlight the planet prob ...
Foundations III The Stars
... The surface of a planet that close to our sun would be scorching hot. But because the star Gliese 581 is only about 1 percent as bright as the sun, temperatures on the new planet should be much more comfortable. Taking into account the presence of an atmosphere and how much starlight the planet prob ...
... The surface of a planet that close to our sun would be scorching hot. But because the star Gliese 581 is only about 1 percent as bright as the sun, temperatures on the new planet should be much more comfortable. Taking into account the presence of an atmosphere and how much starlight the planet prob ...
Lecture Ten - The Sun Amongst the Stars Part II
... O-type stars have very few lines because they are so hot that most of their elements have been stripped of electrons – while in cooler, M-type stars, far more atoms retain their electrons. Patterns of absorption lines can reveal the temperatures of the stars to a precision within 50 degrees K – a f ...
... O-type stars have very few lines because they are so hot that most of their elements have been stripped of electrons – while in cooler, M-type stars, far more atoms retain their electrons. Patterns of absorption lines can reveal the temperatures of the stars to a precision within 50 degrees K – a f ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 2
... During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as our Sun could emit over its life span. The explosion expels much or all of the star’s material and causes a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. The interstellar medium is the gas and dust that exists between the s ...
... During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as our Sun could emit over its life span. The explosion expels much or all of the star’s material and causes a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium. The interstellar medium is the gas and dust that exists between the s ...
Lives of stars HR
... of a pulsar, a rapidly rotating stellar remnant which can appear to blink hundreds or thousands of times per second. The most famous pulsar is in the Crab nebula ...
... of a pulsar, a rapidly rotating stellar remnant which can appear to blink hundreds or thousands of times per second. The most famous pulsar is in the Crab nebula ...
Omega Centauri
... Proton captiue processes responsible for these anticorrelations are possible only at temperatures of a few 10 million degrees, in the complete CNO cycle (which implies also an O depletion) not reached in present day globular cluster main sequence and red giant stars. ...
... Proton captiue processes responsible for these anticorrelations are possible only at temperatures of a few 10 million degrees, in the complete CNO cycle (which implies also an O depletion) not reached in present day globular cluster main sequence and red giant stars. ...
Reach for the Stars – Div. B
... Lagoon Nebula(catalogued as Messier 8 or M8, and as NGC 6523) is a giant interstellar cloud in theconstellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula . • The Lagoon Nebula was discovered by Giovanni Hodierna before 1654 and is one of only two star-forming nebulae faintly visible to the ...
... Lagoon Nebula(catalogued as Messier 8 or M8, and as NGC 6523) is a giant interstellar cloud in theconstellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula . • The Lagoon Nebula was discovered by Giovanni Hodierna before 1654 and is one of only two star-forming nebulae faintly visible to the ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... • The expanded gas cools and pressure drops • Gravity then recompresses the gas ...
... • The expanded gas cools and pressure drops • Gravity then recompresses the gas ...
The Milky Way - Houston Community College System
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
White Dwarfs
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
18 are exactly the same ones as for galactic star clusters of early
... in a way which suggests a conventional age similar to that of the Pleiades, but NGC 6067 is 15-20 times richer. The cluster has red supergiants brighter than those in the otherwise similar cluster Mil. A few supergiants straddle across a very well-defined Hertzsprung gap, including the brighest cent ...
... in a way which suggests a conventional age similar to that of the Pleiades, but NGC 6067 is 15-20 times richer. The cluster has red supergiants brighter than those in the otherwise similar cluster Mil. A few supergiants straddle across a very well-defined Hertzsprung gap, including the brighest cent ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.