star
... stars is gone, the stars cast off their gases exposing their cores. • The core eventually becomes a white dwarf, a hot, dense, slowly cooling sphere of carbon. • This is what is expected to happen to the Sun. ...
... stars is gone, the stars cast off their gases exposing their cores. • The core eventually becomes a white dwarf, a hot, dense, slowly cooling sphere of carbon. • This is what is expected to happen to the Sun. ...
Life Cycle of a Star - Intervention Worksheet
... _____ The star begins to run out of fuel and expands into a red giant or red super giant. _____ Stars start out as diffused clouds of gas and dust drifting through space. A single one of these clouds is called a nebula _____ What happens next depends on the mass of the star. _____ Heat and pressure ...
... _____ The star begins to run out of fuel and expands into a red giant or red super giant. _____ Stars start out as diffused clouds of gas and dust drifting through space. A single one of these clouds is called a nebula _____ What happens next depends on the mass of the star. _____ Heat and pressure ...
Physical Science Lecture Notes
... composition of the stars they are looking at. B. Characteristics of Stars 1. Constellation: a group or pattern of stars in the night sky that appeared as symbols or figures to ancient star gazers a. Big Dipper, Orion, Gemini, Little Dipper, etc. 2. Distance units a. AU – astronomical unit – distance ...
... composition of the stars they are looking at. B. Characteristics of Stars 1. Constellation: a group or pattern of stars in the night sky that appeared as symbols or figures to ancient star gazers a. Big Dipper, Orion, Gemini, Little Dipper, etc. 2. Distance units a. AU – astronomical unit – distance ...
PISGAH Text by Dr. Bob Hayward ASTRONOMICAL Astronomer
... the southeast as the sky darkens. On the evening of June 16 the moon will lie just above Mars. Two nights later the moon will have moved on eastward to lie near Saturn. The ringed planet is not as bright as either Jupiter or Mars but should be visible even close to an almost full moon. Saturn is put ...
... the southeast as the sky darkens. On the evening of June 16 the moon will lie just above Mars. Two nights later the moon will have moved on eastward to lie near Saturn. The ringed planet is not as bright as either Jupiter or Mars but should be visible even close to an almost full moon. Saturn is put ...
The Milky Way
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
Spring Constellations
... centaur’s front hooves, Rigil Kentaurus and Hadar, also called ά- and β-Centauri. Our closest neighbor, Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf star 4 LY away, is due south of alpha Centauri. It’s so faint that it can’t be seen with the naked eye. It’s only about 5 times larger than the earth. ...
... centaur’s front hooves, Rigil Kentaurus and Hadar, also called ά- and β-Centauri. Our closest neighbor, Proxima Centauri, a red dwarf star 4 LY away, is due south of alpha Centauri. It’s so faint that it can’t be seen with the naked eye. It’s only about 5 times larger than the earth. ...
9. Lectures on Star Formation.
... -Disks are made up of about 99% gas and 1% dust. Dust is sufficient to make all the planets that we have in our solar system. -Disks appear dark, because are viewed against the bright background of Orion Nebula. Reddish glowing object in the middle is a proto-star: Star hasn’t yet reached the main ...
... -Disks are made up of about 99% gas and 1% dust. Dust is sufficient to make all the planets that we have in our solar system. -Disks appear dark, because are viewed against the bright background of Orion Nebula. Reddish glowing object in the middle is a proto-star: Star hasn’t yet reached the main ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
... Most stars lie in the main sequence because if a star is hotter it is brighter. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line since “hotter means brighter” That Main-Sequence is steeper than a ‘same-size diagonal” shows that larger mass ‘normal’ star ...
Spring 2014 Astronomy Exam Study Guide (Co-Taught)
... 33. Put the following in order of smallest to largest: a. galaxy, planet, solar system, star, universe 34. Put the following in order of first occurring to last occurring: a. black dwarf, fusion, main sequence, nebula, planetary nebula, proto-star, red giant, white dwarf 35. Our star and its planets ...
... 33. Put the following in order of smallest to largest: a. galaxy, planet, solar system, star, universe 34. Put the following in order of first occurring to last occurring: a. black dwarf, fusion, main sequence, nebula, planetary nebula, proto-star, red giant, white dwarf 35. Our star and its planets ...
ASTRONOMY: WHAT DO YOU NEED TO KNOW
... What is the interstellar medium and what is it made of? Low density dust and gas What is a nebula? A visible cloud of dust and gas Be able to identify the three types of nebulae and give their characteristics: (formation, color) Emission nebulae: are produced when a star (temperatures > 25000K) exci ...
... What is the interstellar medium and what is it made of? Low density dust and gas What is a nebula? A visible cloud of dust and gas Be able to identify the three types of nebulae and give their characteristics: (formation, color) Emission nebulae: are produced when a star (temperatures > 25000K) exci ...
Document
... moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
... moving apart so rapidly that their gravitational attraction for one another cannot pull them into orbit about one another ...
Chapter 13: The Death of Stars
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
... luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
temperature - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... Much more analogous to luminosity than apparent magnitude: does not vary with distance to the star. It’s a way of stating a star’s luminosity in terms of a magnitude… the magnitude that star would be on the sky if put at a distance of 10pc. ...
... Much more analogous to luminosity than apparent magnitude: does not vary with distance to the star. It’s a way of stating a star’s luminosity in terms of a magnitude… the magnitude that star would be on the sky if put at a distance of 10pc. ...
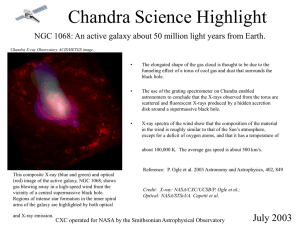
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... X-ray spectra of the wind show that the composition of the material in the wind is roughly similar to that of the Sun’s atmosphere, except for a deficit of oxygen atoms, and that it has a temperature of about 100,000 K. The average gas speed is about 500 km/s. ...
... X-ray spectra of the wind show that the composition of the material in the wind is roughly similar to that of the Sun’s atmosphere, except for a deficit of oxygen atoms, and that it has a temperature of about 100,000 K. The average gas speed is about 500 km/s. ...
1 au d p = 1 au d
... Starting from the observed luminosity function, possible to derive an estimate for the Initial Mass Function (IMF). To define the IMF, imagine that we form a large number of stars. Then: the number of stars that have been x (M)DM = born with initial masses between M and M+DM (careful not to confuse ...
... Starting from the observed luminosity function, possible to derive an estimate for the Initial Mass Function (IMF). To define the IMF, imagine that we form a large number of stars. Then: the number of stars that have been x (M)DM = born with initial masses between M and M+DM (careful not to confuse ...
Notes_ stars and sun
... • Since it only takes sunlight 8 minutes to reach earth, it can be said that the sun is 8 light minutes away. • The closest star to the sun is called Proxima Centauri. This star is 4.24 light years away from earth. This means that when we see the light from Proxima Centauri, it was actually genera ...
... • Since it only takes sunlight 8 minutes to reach earth, it can be said that the sun is 8 light minutes away. • The closest star to the sun is called Proxima Centauri. This star is 4.24 light years away from earth. This means that when we see the light from Proxima Centauri, it was actually genera ...
The Warrumbungle Observer The Warrumbungle Observer
... (18) Alpha Centauri in Centaurus: Bottom and brighter star of the 2 pointers below the Southern Cross. Appears as a bright double star like a pair of headlights. Each star is of a similar size to our Sun but 4.3 light years distant. Only Proxima Centauri is closer to us and appears to orbit this pai ...
... (18) Alpha Centauri in Centaurus: Bottom and brighter star of the 2 pointers below the Southern Cross. Appears as a bright double star like a pair of headlights. Each star is of a similar size to our Sun but 4.3 light years distant. Only Proxima Centauri is closer to us and appears to orbit this pai ...
Spectral analysis for the RV Tau star R Sct: In this section, we will
... have luminosity classes of III, II, or I (where class II has properties in between III and I). Luminosity class V stars, like the sun, are main sequence stars and are generally used for reference as they do not vary and their intrinsic properties are well known. “By eye” we can see that the blue spe ...
... have luminosity classes of III, II, or I (where class II has properties in between III and I). Luminosity class V stars, like the sun, are main sequence stars and are generally used for reference as they do not vary and their intrinsic properties are well known. “By eye” we can see that the blue spe ...
A105 Stars and Galaxies
... Stellar Mass and Fusion • The mass of a main sequence star determines its core pressure and temperature • Stars of higher mass have higher core temperature and more rapid fusion, making those stars both more luminous and shorterlived ...
... Stellar Mass and Fusion • The mass of a main sequence star determines its core pressure and temperature • Stars of higher mass have higher core temperature and more rapid fusion, making those stars both more luminous and shorterlived ...
L = σAT 4
... from the top left to bottom right. This line is known as the MAIN SEQUENCE and stars that are on it are known as the main sequence stars. Our sun is a main sequence star. These stars are ‘normal’ stable starsthe only difference between them is their mass. They are fusing hydrogen to helium. The star ...
... from the top left to bottom right. This line is known as the MAIN SEQUENCE and stars that are on it are known as the main sequence stars. Our sun is a main sequence star. These stars are ‘normal’ stable starsthe only difference between them is their mass. They are fusing hydrogen to helium. The star ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.