Chapter 19 Star Formation
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
ems 6 - LincolnLions.org
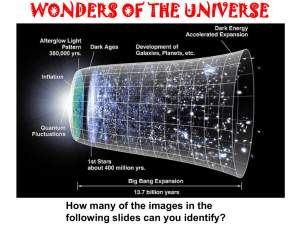
... the matter and energy outward in a cloud Cloud expanded into clumps Clumps evolved into galaxies Universe is still expanding outward ...
... the matter and energy outward in a cloud Cloud expanded into clumps Clumps evolved into galaxies Universe is still expanding outward ...
©JSR 2010 Seeing gravity 1/2 Gravitation – if the Earth could see
... objects themselves have intrinsically different brightnesses (the astronomers’ absolute magnitude) and partly because the light from distant objects fades as the inverse square of the distances they are away. Gravity works in much the same way. The gravitational force experienced by the Earth depend ...
... objects themselves have intrinsically different brightnesses (the astronomers’ absolute magnitude) and partly because the light from distant objects fades as the inverse square of the distances they are away. Gravity works in much the same way. The gravitational force experienced by the Earth depend ...
Grand Tour Worksheet - School District of La Crosse
... 8. How far is the Andromeda galaxy from us? 9. Galaxies may range up to an___________of magnitude larger than our _________ __________ 10. Is the upper limit on the mass of a galaxy knows? 11. Are all galaxy spiral shaped, explain? ...
... 8. How far is the Andromeda galaxy from us? 9. Galaxies may range up to an___________of magnitude larger than our _________ __________ 10. Is the upper limit on the mass of a galaxy knows? 11. Are all galaxy spiral shaped, explain? ...
Chapter 12
... 5. Only stars within about 120 parsecs (400 light-years) have parallax angles great enough to allow accurate calculations of their distances from Earth. 6. The satellite Hipparchos measured positions and parallaxes to an accuracy of 0.001 arcsecond. Its successor, Gaia (to be launched in 2011), will ...
... 5. Only stars within about 120 parsecs (400 light-years) have parallax angles great enough to allow accurate calculations of their distances from Earth. 6. The satellite Hipparchos measured positions and parallaxes to an accuracy of 0.001 arcsecond. Its successor, Gaia (to be launched in 2011), will ...
11.3.1 Grade 6 Standard 4 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1
... 10. Which stars do we always see during the year? Stars... A. B. C. D. ...
... 10. Which stars do we always see during the year? Stars... A. B. C. D. ...
constellations are not real!
... 5th magnitude stars are about the faintest you can see on a good night. There are about 1500 of these stars, but less than 100 of them appear on the charts. f. Some 6th magnitude stars can be seen by the “keen of sight” in constellations such as the Dolphin, Cup, and the Fishes. g. For anything fain ...
... 5th magnitude stars are about the faintest you can see on a good night. There are about 1500 of these stars, but less than 100 of them appear on the charts. f. Some 6th magnitude stars can be seen by the “keen of sight” in constellations such as the Dolphin, Cup, and the Fishes. g. For anything fain ...
Final review - Physics and Astronomy
... Life Elsewhere in the Milky Way: To address question of whether other intelligent life exists in the Milky Way, Frank Drake formulated the Drake Equation. The equation is usually written: ...
... Life Elsewhere in the Milky Way: To address question of whether other intelligent life exists in the Milky Way, Frank Drake formulated the Drake Equation. The equation is usually written: ...
Starlight & Stars - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... The Doppler effect doesn’t affect the overall color of an object, unless it is moving at a significant fraction of the speed of light (VERY fast!) For an object moving toward us, the red colors will be shifted to the orange and the near-infrared will be shifted to the red, etc. All of the colors shi ...
... The Doppler effect doesn’t affect the overall color of an object, unless it is moving at a significant fraction of the speed of light (VERY fast!) For an object moving toward us, the red colors will be shifted to the orange and the near-infrared will be shifted to the red, etc. All of the colors shi ...
File
... Astrophysicists study the physical properties (luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical make-up) of galaxies, stars, and planets. ...
... Astrophysicists study the physical properties (luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical make-up) of galaxies, stars, and planets. ...
The Characteristics of Stars
... Stars are scattered across the Universe at different distances from Earth. The varying distances make it difficult to visually compare stars to determine which are emitting more light and which are emitting less. Although apparent magnitude values help us classify stars according to their observed b ...
... Stars are scattered across the Universe at different distances from Earth. The varying distances make it difficult to visually compare stars to determine which are emitting more light and which are emitting less. Although apparent magnitude values help us classify stars according to their observed b ...
Astronomy Practice Test
... c) black hole _____ an enormous explosion that occurs at the end of a large star’s life d) neutron star _____ after a supernova, the core material of a large star packs e) white dwarf together to form this ...
... c) black hole _____ an enormous explosion that occurs at the end of a large star’s life d) neutron star _____ after a supernova, the core material of a large star packs e) white dwarf together to form this ...
HR Diagram Lab
... Purpose: In this lab we will investigate the relationship between the temperature, brightness and diameter of stars. Introduction The H-R Diagram is a tool that astronomers use to classify stars based on their luminosity, magnitude, temperature, spectral class and evolutionary stage. The H-R Diagram ...
... Purpose: In this lab we will investigate the relationship between the temperature, brightness and diameter of stars. Introduction The H-R Diagram is a tool that astronomers use to classify stars based on their luminosity, magnitude, temperature, spectral class and evolutionary stage. The H-R Diagram ...
The Celestial Sphere - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... on the right. The height of the sun above the horizon determines how much heat and light strike each square meter of ground. During the summer, a shaft of light at noon illuminates a nearly circular patch of ground. During the winter, that same shaft at noon strikes the ground at a steeper angle, sp ...
... on the right. The height of the sun above the horizon determines how much heat and light strike each square meter of ground. During the summer, a shaft of light at noon illuminates a nearly circular patch of ground. During the winter, that same shaft at noon strikes the ground at a steeper angle, sp ...
PC2491 Examples 2
... of the Sun and (r) is the angular velocity at radius r. An H1 cloud in the galactic plane at l=30o is observed to have a velocity relative to the local standard of rest of +80 km s-1. Assume the galactic rotation curve is flat with an amplitude of 220 km s-1 , and that Ro = 8.2 kpc and estimate the ...
... of the Sun and (r) is the angular velocity at radius r. An H1 cloud in the galactic plane at l=30o is observed to have a velocity relative to the local standard of rest of +80 km s-1. Assume the galactic rotation curve is flat with an amplitude of 220 km s-1 , and that Ro = 8.2 kpc and estimate the ...
lect3 — 1 Measuring stars: What can be measured?
... Hence by measuring the apparent magnitude m, and somehow knowing the absolute magnitude M (i.e. the true luminosity), one can infer the distance D (in pc). H-R diagram distance: We discussed the H-R diagram last time as a relation between temperature and luminosity. In observational terms, it is act ...
... Hence by measuring the apparent magnitude m, and somehow knowing the absolute magnitude M (i.e. the true luminosity), one can infer the distance D (in pc). H-R diagram distance: We discussed the H-R diagram last time as a relation between temperature and luminosity. In observational terms, it is act ...
Document
... Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
... Alnitak, which is farthest east on Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex. ...
Chapter 16
... The supernova explosion produces so much light that it can temporarily outshine an entire galaxy. The photons destroy the heavy nuclei through a process of photodisintegration to produce a flood of neutrinos. For all supernovae, the source of light during the decline in brightness after the explosio ...
... The supernova explosion produces so much light that it can temporarily outshine an entire galaxy. The photons destroy the heavy nuclei through a process of photodisintegration to produce a flood of neutrinos. For all supernovae, the source of light during the decline in brightness after the explosio ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.