5.1-The process of Science - Homework
... measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time increment defined by the earth's motion; specifically, a complete revolution of the earth about its own ax ...
... measured by successive transits of a reference point on the celestial sphere over the meridian, and each type takes its name from the reference used… www.reson.com/Gloss-d.htm • 1. A basic time increment defined by the earth's motion; specifically, a complete revolution of the earth about its own ax ...
Multiple choice test questions 1, Winter Semester
... B) A model tries to represent only one aspect of nature. C) A model can be used to explain and predict real phenomena. D) All models that explain nature well are correct. E) All current models are correct. 16) From Kepler's third law, an asteroid with an orbital period of 8 years lies at an average ...
... B) A model tries to represent only one aspect of nature. C) A model can be used to explain and predict real phenomena. D) All models that explain nature well are correct. E) All current models are correct. 16) From Kepler's third law, an asteroid with an orbital period of 8 years lies at an average ...
Quiz Maker - Geneva 304
... 77. Features like the Grand Canyon and the Scablands of Washington can be seen on the surface of _____. 78. Do planets that have no atmospheres have extensive wind erosion? Do we see wind erosion on Mars? 79. What causes an earthquake? 80. Atmospheres play a role in determining a planet’s _____. In ...
... 77. Features like the Grand Canyon and the Scablands of Washington can be seen on the surface of _____. 78. Do planets that have no atmospheres have extensive wind erosion? Do we see wind erosion on Mars? 79. What causes an earthquake? 80. Atmospheres play a role in determining a planet’s _____. In ...
Practice Questions: This is a series of practice tests that you should
... a. Solstices b. Equinoxes c. Constellations d. Geocentric models 2. The first footprints on the surface of the moon were made by a. Yuri Gagarin in 1961 b. Copernicus in1534 c. Neil Armstrong in 1969 d. Marc Garneau in 1984 3. Compare the geocentric and heliocentric models. Be sure to address the ...
... a. Solstices b. Equinoxes c. Constellations d. Geocentric models 2. The first footprints on the surface of the moon were made by a. Yuri Gagarin in 1961 b. Copernicus in1534 c. Neil Armstrong in 1969 d. Marc Garneau in 1984 3. Compare the geocentric and heliocentric models. Be sure to address the ...
Formation of the solar system
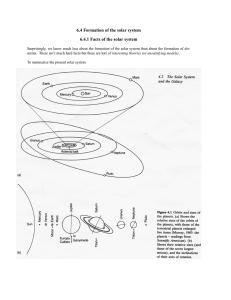
... 6.4.2 Constraints based on the facts of the solar system What constraints does all this put on the formation of the solar system? A. The planet’s obrits are in a common plane, close to the sun’s equatorial plane, so most of the rotational motion is in one plane and has a common axis. B. Planetary or ...
... 6.4.2 Constraints based on the facts of the solar system What constraints does all this put on the formation of the solar system? A. The planet’s obrits are in a common plane, close to the sun’s equatorial plane, so most of the rotational motion is in one plane and has a common axis. B. Planetary or ...
Goal: To understand how we know distances to various
... usually referring to? • A) the apparent difference in position with respect to further objects for 2 positions on the surface of the earth • B) the apparent difference in position of a star over the course of a year • C) the apparent difference in the position of a star over the course of 6 months • ...
... usually referring to? • A) the apparent difference in position with respect to further objects for 2 positions on the surface of the earth • B) the apparent difference in position of a star over the course of a year • C) the apparent difference in the position of a star over the course of 6 months • ...
Science! - Kincaid Elementary Blog
... 20,000 feet. Low clouds are between the ground and 6,000 feet. Which type of cloud would be found at 10,000 feet? ...
... 20,000 feet. Low clouds are between the ground and 6,000 feet. Which type of cloud would be found at 10,000 feet? ...
the universe
... When asteroids collide with one another, bits of broken pieces are scattered in space. These pieces are called meteoroids they could also be bits of comets dust or pieces of a planet or a moon hit by an asteroid or a comet. A meteoroid can sometimes burn up as it passes through Earth’s atmosphere. T ...
... When asteroids collide with one another, bits of broken pieces are scattered in space. These pieces are called meteoroids they could also be bits of comets dust or pieces of a planet or a moon hit by an asteroid or a comet. A meteoroid can sometimes burn up as it passes through Earth’s atmosphere. T ...
The Sun to the Earth - Stanford Solar Center
... The Sun is the only star known to grow vegetables. (Dr.Philip Scherrer, Stanford University) ...
... The Sun is the only star known to grow vegetables. (Dr.Philip Scherrer, Stanford University) ...
MIT
... • Comets - small bodies in the Solar System that (at least occasionally) exhibit a coma (or atmosphere) and/or a tail • Meteorites - small extraterrestrial body that reaches the Earth's surface ...
... • Comets - small bodies in the Solar System that (at least occasionally) exhibit a coma (or atmosphere) and/or a tail • Meteorites - small extraterrestrial body that reaches the Earth's surface ...
Gravity and Motion Motion in astronomy Newton`s Laws of Motion
... An ellipse has polar equation where r, θ are distance and angle as seen from the focus, and a is the semimajor axis -the average distance from the Sun to the planet. The eccentricity e is the ratio of the centre-focus distance CF to the semimajor axis The sum r+r' (see figure) is constant and equal ...
... An ellipse has polar equation where r, θ are distance and angle as seen from the focus, and a is the semimajor axis -the average distance from the Sun to the planet. The eccentricity e is the ratio of the centre-focus distance CF to the semimajor axis The sum r+r' (see figure) is constant and equal ...
PDF file
... - the Sun (helios, in Greek) in the center - Aristarchus, Copernicus - planetary orbits – circles - naturally explains everything we need - not more accurate than Ptolemy's model ...
... - the Sun (helios, in Greek) in the center - Aristarchus, Copernicus - planetary orbits – circles - naturally explains everything we need - not more accurate than Ptolemy's model ...
YOUR NAME 1 Astronomy 18, UCSC Planets and Planetary
... 7) Circle all that apply: Kepler’s third law, p2 = a3, means that a) A planet’s period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit b) All orbits with the same semi-major axis have the same period c) The period of a planet does not depend on its mass d) Planets that are farther from the Sun move ...
... 7) Circle all that apply: Kepler’s third law, p2 = a3, means that a) A planet’s period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit b) All orbits with the same semi-major axis have the same period c) The period of a planet does not depend on its mass d) Planets that are farther from the Sun move ...
The Solar System Inner Planets 14.3
... • Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called the inner planets • The four inner planets are small and dense and have rocky surfaces • They are often called the terrestrial planets ...
... • Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called the inner planets • The four inner planets are small and dense and have rocky surfaces • They are often called the terrestrial planets ...
The Earth in Space
... 1. Year - is the time it takes for the earth to make one complete orbit around the Sun. 2. Month - is the time it takes for the Moon to go through one full period of phases. ...
... 1. Year - is the time it takes for the earth to make one complete orbit around the Sun. 2. Month - is the time it takes for the Moon to go through one full period of phases. ...
Astronomical Terms - Crossroads Academy
... circumpolar stars…stars that never set from where you observe them over an entire year constellation…88 sections of the sky including star arrangements with names mostly derived from ancient astronomy…the study of the celestial objects asterism…group of stars Great Bear (stars — Dubhe, Merak, Mizar, ...
... circumpolar stars…stars that never set from where you observe them over an entire year constellation…88 sections of the sky including star arrangements with names mostly derived from ancient astronomy…the study of the celestial objects asterism…group of stars Great Bear (stars — Dubhe, Merak, Mizar, ...
the solar system
... Over 100 spacecraft launched to explore the moon, including humans Makes a complete orbit of Earth in 27 days ...
... Over 100 spacecraft launched to explore the moon, including humans Makes a complete orbit of Earth in 27 days ...
Grade 11 Cosmology PPT File
... Describes a relationship between the radius of the planets (average distance to the sun) and the time taken for one complete orbit. T2 is proportional to R3 Click for K3 Movie ...
... Describes a relationship between the radius of the planets (average distance to the sun) and the time taken for one complete orbit. T2 is proportional to R3 Click for K3 Movie ...
Ch. 26 The Sun and the Solar System
... counterclockwise orbit at different distances from the Sun and at different speeds ...
... counterclockwise orbit at different distances from the Sun and at different speeds ...
Homework 1
... With light as our only messenger for the explosion of Betelgeuse, we must wait the 600 years for the light of the supernova to reach us. ...
... With light as our only messenger for the explosion of Betelgeuse, we must wait the 600 years for the light of the supernova to reach us. ...