Our Solar System
... • Saturn is composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. • Saturn has many rings made of ice. Saturn’s rings are very wide. They extend outward to about 260,000 miles from the surface but are less than 1 mile thick. • Saturn has 18 known moons, some of which orbit inside the rings! • It takes Sa ...
... • Saturn is composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium. • Saturn has many rings made of ice. Saturn’s rings are very wide. They extend outward to about 260,000 miles from the surface but are less than 1 mile thick. • Saturn has 18 known moons, some of which orbit inside the rings! • It takes Sa ...
CHAPTER 2: Gravitation and the Waltz of the Planets
... Do the planets orbit the Sun at constant speeds? Do all the planets orbit the Sun at the same speed? How much force does it take to keep an object moving in a straight line at a constant speed? How does an object’s mass differ when measured on the Earth and on the Moon? ...
... Do the planets orbit the Sun at constant speeds? Do all the planets orbit the Sun at the same speed? How much force does it take to keep an object moving in a straight line at a constant speed? How does an object’s mass differ when measured on the Earth and on the Moon? ...
Option: Astrophysics Objects in the Universe: Asteroid: a small rocky
... o Open Cluster: Up to several hundred stars that are 10 billion years old or less. May still contain gas and dust o Globular Cluster: Cluster of many old stars containing little to no gas or dust ...
... o Open Cluster: Up to several hundred stars that are 10 billion years old or less. May still contain gas and dust o Globular Cluster: Cluster of many old stars containing little to no gas or dust ...
Origin and Nature of Planetary Systems
... planetary systems and compare them with our Solar System. In addition to this, 84 planets orbit a star that is part of a binary star system and 22 planets orbit both stars of a binary system just like Tatooine in Star Wars! There are also two known planets that do not orbit a star—orphan planets. Sc ...
... planetary systems and compare them with our Solar System. In addition to this, 84 planets orbit a star that is part of a binary star system and 22 planets orbit both stars of a binary system just like Tatooine in Star Wars! There are also two known planets that do not orbit a star—orphan planets. Sc ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Reference Point- A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion. International System of Units (SI): A system of measurements based on multiples of ten and on established measures of mass, length, and time. Distance: The length of the path between two points. Motion- th ...
... Reference Point- A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion. International System of Units (SI): A system of measurements based on multiples of ten and on established measures of mass, length, and time. Distance: The length of the path between two points. Motion- th ...
Anw, samenvatting, h15+16
... He found that the brightest star in each galaxy had almost the same intrinsic brightness. When he knew how far away a galaxy was he looked at the red shift. When he knew the red shift he could calculate the velocity of the galaxy. He found a correlation between the distance from Earth and the veloci ...
... He found that the brightest star in each galaxy had almost the same intrinsic brightness. When he knew how far away a galaxy was he looked at the red shift. When he knew the red shift he could calculate the velocity of the galaxy. He found a correlation between the distance from Earth and the veloci ...
star - Bakersfield College
... Close stars will shift at larger angles. Distant stars will shift at smaller angles. ...
... Close stars will shift at larger angles. Distant stars will shift at smaller angles. ...
PHYS 1470 3.0 W16/17 Highlights of Astronomy Assignment #2
... c. What would Venus’ surface temperature, T, be, assuming that Venus radiated into space an amount, Pem , that is equal to the power it absorbed? d. What is the mean temperature on Venus, how much is it different from the temperature you computed in c) and what is the reason for the difference (if t ...
... c. What would Venus’ surface temperature, T, be, assuming that Venus radiated into space an amount, Pem , that is equal to the power it absorbed? d. What is the mean temperature on Venus, how much is it different from the temperature you computed in c) and what is the reason for the difference (if t ...
3observing3s
... Astrology is a pseudoscience, it uses some of the terminology of science, but its basic tenets are not subject to proof ...
... Astrology is a pseudoscience, it uses some of the terminology of science, but its basic tenets are not subject to proof ...
labor - Glencoe
... small mass of tissue that contains lymphocytes and filters pathogens from the lymph; made of a network of connective tissue fibers that contain lymphocytes. ...
... small mass of tissue that contains lymphocytes and filters pathogens from the lymph; made of a network of connective tissue fibers that contain lymphocytes. ...
Stellar parallax-aberration is geocentric
... A2 = the strength of the star’s outward flow of light. a = the angular velocity of the sun about the earth. I.e., the rate at which the earth-sun line rotates about the earth. R = the distance from the earth to the star. ρ = the distance from the earth to the sun. ϕ = the deflection of starlight due ...
... A2 = the strength of the star’s outward flow of light. a = the angular velocity of the sun about the earth. I.e., the rate at which the earth-sun line rotates about the earth. R = the distance from the earth to the star. ρ = the distance from the earth to the sun. ϕ = the deflection of starlight due ...
May 8, 2012 - Plummer Pumas Science
... The Sun’s temperature was much cooler and it was much smaller. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
... The Sun’s temperature was much cooler and it was much smaller. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________ ...
ppt
... • Mars, Jupiter, Saturn: move eastward within the zodiac, but each one makes a westward loop once a year when its farthest from the sun •Uranus, Neptune: need a telescope to see them, bu they each describe westward loops once a year, each smaller than the previous planet. How can this motion be expl ...
... • Mars, Jupiter, Saturn: move eastward within the zodiac, but each one makes a westward loop once a year when its farthest from the sun •Uranus, Neptune: need a telescope to see them, bu they each describe westward loops once a year, each smaller than the previous planet. How can this motion be expl ...
Motions of the Planets: Not the same as Stars!
... • Mars, Jupiter, Saturn: move eastward within the zodiac, but each one makes a westward loop once a year when its farthest from the sun • Uranus, Neptune: need a telescope to see them, bu they each describe westward loops once a year, each smaller than the previous planet. How can this motion be ex ...
... • Mars, Jupiter, Saturn: move eastward within the zodiac, but each one makes a westward loop once a year when its farthest from the sun • Uranus, Neptune: need a telescope to see them, bu they each describe westward loops once a year, each smaller than the previous planet. How can this motion be ex ...
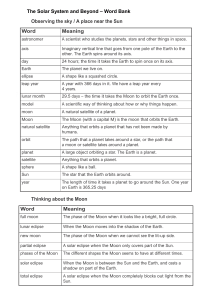
Word Meaning The Solar System and Beyond – Word Bank
... A solar eclipse when the Moon completely blocks out light from the Sun. ...
... A solar eclipse when the Moon completely blocks out light from the Sun. ...
Quiz 1 Review, Astronomy 1144 - astronomy.ohio
... 1. Superior planet - one whose orbit around the Sun is outside that of the Earth’s. 2. Inferior planet - one whose orbit around the Sun is internal to that of the Earth’s. 3. Conjunction - occurs when the Sun is directly between the Earth and a superior planet (superior conjunction), an inferior pla ...
... 1. Superior planet - one whose orbit around the Sun is outside that of the Earth’s. 2. Inferior planet - one whose orbit around the Sun is internal to that of the Earth’s. 3. Conjunction - occurs when the Sun is directly between the Earth and a superior planet (superior conjunction), an inferior pla ...