Lecture 16
... The following spectra illustrate the visible spectra for O, B, A, F, G, K, and M stars. The broad white band in each spectrum reflects blackbody radiation characteristic of each class of star. Tracking upward the blackbody radiation is peaking at shorter wavelengths, thus, according to Wien’s Law, h ...
... The following spectra illustrate the visible spectra for O, B, A, F, G, K, and M stars. The broad white band in each spectrum reflects blackbody radiation characteristic of each class of star. Tracking upward the blackbody radiation is peaking at shorter wavelengths, thus, according to Wien’s Law, h ...
Spectral Classification and the HR Diagram
... As director of the Harvard College Observatory Edward C. Pickering (1846-1919) undertook the oversight for completion of the Henry Draper Catalogue. Because it was the goal of this project to classify a sufficient number of stars so that it would be years before anyone felt the need to repeat such a ...
... As director of the Harvard College Observatory Edward C. Pickering (1846-1919) undertook the oversight for completion of the Henry Draper Catalogue. Because it was the goal of this project to classify a sufficient number of stars so that it would be years before anyone felt the need to repeat such a ...
Document
... And we know how bright it should be, Result Distance We do this everyday with size. ...
... And we know how bright it should be, Result Distance We do this everyday with size. ...
Lec12
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
Constellations
... 6. What phenomenon is responsible for the fact that some constellations are only visible at certain times during the year? A. The rotation of the earth on its axis B. The revolution of the moon around the earth C. The revolution of the earth around the sun D. The revolution of the sun around the Mil ...
... 6. What phenomenon is responsible for the fact that some constellations are only visible at certain times during the year? A. The rotation of the earth on its axis B. The revolution of the moon around the earth C. The revolution of the earth around the sun D. The revolution of the sun around the Mil ...
science - TCDSB.org
... The Earth rotates once every 24 hours. Each time the Earth rotates we have one day and one night. When we are on the sun side of the earth, we have daylight. When we rotate away from the sun, we have night. ...
... The Earth rotates once every 24 hours. Each time the Earth rotates we have one day and one night. When we are on the sun side of the earth, we have daylight. When we rotate away from the sun, we have night. ...
The Ursa Major Moving Cluster, Collinder 285
... escaped due to mutual encounters, tidal forces of the Milky Way, or encounters with large interstellar clouds and other clusters. Now as they have left the cluster, their orbits around the Milky Way Galaxy's center is still similar to that of the cluster so that they have a common motion. All these ...
... escaped due to mutual encounters, tidal forces of the Milky Way, or encounters with large interstellar clouds and other clusters. Now as they have left the cluster, their orbits around the Milky Way Galaxy's center is still similar to that of the cluster so that they have a common motion. All these ...
Star Maps and Constellations (pdf 3.7 Megs)
... symbolic or geometric grouping (e.g. looks like a "W" or a triangle), the poetic will see epic heroes. These "groupings" of stars are called asterisms. Many are "natural" as evidenced by divergent cultures having many of the same stars grouped together (in some cases, even with similar interpretatio ...
... symbolic or geometric grouping (e.g. looks like a "W" or a triangle), the poetic will see epic heroes. These "groupings" of stars are called asterisms. Many are "natural" as evidenced by divergent cultures having many of the same stars grouped together (in some cases, even with similar interpretatio ...
Slide 1
... processes within the body of the star itself. Stars typically range in mass between 0.08 and 100 solar masses. A Hertzprung-Russell diagram is a very useful illustration of the relationship between various key stellar properties, namely the luminosity and the effective temperature (related to both s ...
... processes within the body of the star itself. Stars typically range in mass between 0.08 and 100 solar masses. A Hertzprung-Russell diagram is a very useful illustration of the relationship between various key stellar properties, namely the luminosity and the effective temperature (related to both s ...
P10263v1.2 Lab 5 Text
... them and chased them for seven years (and continues to “chase” them across the sky as they ride on the back of Taurus the bull). Today there are only six stars in the Pleiades that are easily visible to the naked eye. There are many theories about what happened to the 7th one. Celaeno has often been ...
... them and chased them for seven years (and continues to “chase” them across the sky as they ride on the back of Taurus the bull). Today there are only six stars in the Pleiades that are easily visible to the naked eye. There are many theories about what happened to the 7th one. Celaeno has often been ...
File
... million K, the surface would be liquid form, while if it's cooler than that, it would be solid. Below that is a solid crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
... million K, the surface would be liquid form, while if it's cooler than that, it would be solid. Below that is a solid crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
Ay123 Fall 2011 STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION Problem Set 1
... e. Write down an explicit expression for the total gravitational potential energy of this toy star, and verify that the virial theorem is exactly satisfied. Be sure to discuss matter with a general equation of state, not just an ideal monatomic nonrelativistic gas. 2. The Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale: ...
... e. Write down an explicit expression for the total gravitational potential energy of this toy star, and verify that the virial theorem is exactly satisfied. Be sure to discuss matter with a general equation of state, not just an ideal monatomic nonrelativistic gas. 2. The Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale: ...
Star Birth
... Where do new stars form? What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun? When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? Where in the Galaxy does star formation take place? How can the death of on ...
... Where do new stars form? What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun? When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? Where in the Galaxy does star formation take place? How can the death of on ...
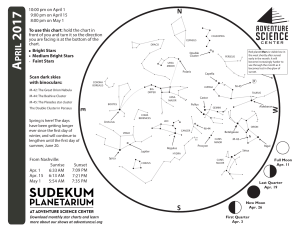
1704 chart front - Adventure Science Center
... the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. Like Orion and Taurus, Mars will be gone by the end of the month. Look high in the north for the Big Dipper. As famous as t ...
... the Bull. Still further beyond Aldebaran, you may find another orange-red dot, the red planet Mars. Mars will be much fainter. If you can’t find it, try scanning with binoculars. Like Orion and Taurus, Mars will be gone by the end of the month. Look high in the north for the Big Dipper. As famous as t ...
April 1st
... • Because nuclear reactions have not yet begun in the protostar’s core, this luminosity is due entirely to the release of gravitational energy as the protostar continues to shrink and material from the surrounding fragment ...
... • Because nuclear reactions have not yet begun in the protostar’s core, this luminosity is due entirely to the release of gravitational energy as the protostar continues to shrink and material from the surrounding fragment ...
Lecture 19 Brightness Units
... are all due to absorption by atoms starting from the second energy state. – The only way an atom gets into this state is by being hit by a neighbor, and the neighbors at these temperatures are not moving fast enough. Balmer lines are weak. Mar 3, 2006 ...
... are all due to absorption by atoms starting from the second energy state. – The only way an atom gets into this state is by being hit by a neighbor, and the neighbors at these temperatures are not moving fast enough. Balmer lines are weak. Mar 3, 2006 ...
main sequence
... that sweep through Earth's line of sight • The "pulses" of high-energy radiation we see from a pulsar are due to a misalignment of the neutron star's rotation axis and its magnetic axis. • Pulsars seem to pulse from our perspective because the rotation of the neutron star causes the beam of radiatio ...
... that sweep through Earth's line of sight • The "pulses" of high-energy radiation we see from a pulsar are due to a misalignment of the neutron star's rotation axis and its magnetic axis. • Pulsars seem to pulse from our perspective because the rotation of the neutron star causes the beam of radiatio ...
Conceptobasico.pdf
... At this time, the object is at its maximum altitude in the sky. The altazimuth coordinates of an object are local coordinates. Stars very far south near the South Celestial Pole do not rise at all, and they remain unseen for observers in the north. As the Earth orbits the Sun, we see the Sun moving ...
... At this time, the object is at its maximum altitude in the sky. The altazimuth coordinates of an object are local coordinates. Stars very far south near the South Celestial Pole do not rise at all, and they remain unseen for observers in the north. As the Earth orbits the Sun, we see the Sun moving ...
Here - Thanet Astronomy Group
... Thanet Astronomy Group Astronomy for Everyone in Plain English What to See, February 2014 ...
... Thanet Astronomy Group Astronomy for Everyone in Plain English What to See, February 2014 ...
Stars in our Galaxy
... while others disappear. Because circumpolar constellations always orbit Polaris they are visible ALL year long while others are not. ...
... while others disappear. Because circumpolar constellations always orbit Polaris they are visible ALL year long while others are not. ...
Reader`s Theater Our Closest Star
... strong enough to hold all of the parts of this system together. Is it any wonder the system is named after me? I am a star, your closest star. I may be millions of times closer to you than other stars, but I am still very far away. It would take a jet plane nineteen years to reach me. But, of course ...
... strong enough to hold all of the parts of this system together. Is it any wonder the system is named after me? I am a star, your closest star. I may be millions of times closer to you than other stars, but I am still very far away. It would take a jet plane nineteen years to reach me. But, of course ...
1 - Quia
... A. Oxygen B. Carbon C. Hydrogen D. Nitrogen 16. What is the first stage in the life cycle of a star? (2 points) ...
... A. Oxygen B. Carbon C. Hydrogen D. Nitrogen 16. What is the first stage in the life cycle of a star? (2 points) ...
AST 112 – Activity #4 The Stellar Magnitude System
... necessary. Hint: Also refer to Table 4-1 above. (a) Is star J further than, closer to, or equal to 10 pc distant? ...
... necessary. Hint: Also refer to Table 4-1 above. (a) Is star J further than, closer to, or equal to 10 pc distant? ...
Document
... isotopes (of any element) having atomic masses 5 or 8 in Nature. At extremely high temperatures, of order 100 million K, a very small equilibrium concentration of Be-8 from the fusion of two helium atoms can be obtained and by reacting with another helium, a stable carbon 12 is formed. The red giant ...
... isotopes (of any element) having atomic masses 5 or 8 in Nature. At extremely high temperatures, of order 100 million K, a very small equilibrium concentration of Be-8 from the fusion of two helium atoms can be obtained and by reacting with another helium, a stable carbon 12 is formed. The red giant ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.