The human race has made great strides in the last few centuries
... usually about 70% the mass of the Sun with a surface temperature comparable to or higher than the Sun. Electron degeneracy pressure can hold up a star of less than 1.44Mo forever but collapses above that Chandrasekhar Limit. White Dwarfs will still be here long all the stars have burned out. If the ...
... usually about 70% the mass of the Sun with a surface temperature comparable to or higher than the Sun. Electron degeneracy pressure can hold up a star of less than 1.44Mo forever but collapses above that Chandrasekhar Limit. White Dwarfs will still be here long all the stars have burned out. If the ...
Name
... 29. The supernova that was recorded in China in 1054 was so bright that it was visible in daylight. It was visible for about ______________months. The spreading gases from the explosion form what is now called the _____________________ ________________. 30. In 1987 a supernova called _______________ ...
... 29. The supernova that was recorded in China in 1054 was so bright that it was visible in daylight. It was visible for about ______________months. The spreading gases from the explosion form what is now called the _____________________ ________________. 30. In 1987 a supernova called _______________ ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
... the shift will be to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) by the same amount. In our ideal case, the measured Doppler velocity would be equal to the earth’s orbital velocity. In an actual application of the method, there are some complications: 1. The star may not be stationary with respect to the sun, ...
... the shift will be to shorter wavelengths (blue shift) by the same amount. In our ideal case, the measured Doppler velocity would be equal to the earth’s orbital velocity. In an actual application of the method, there are some complications: 1. The star may not be stationary with respect to the sun, ...
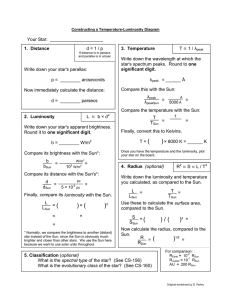
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... Once you have determined the luminosity and temperature of each star, please go to the board and plot that star on the class H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Calculating the radius and spectral type is optional, but strongly encouraged. ...
... Once you have determined the luminosity and temperature of each star, please go to the board and plot that star on the class H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Calculating the radius and spectral type is optional, but strongly encouraged. ...
Document
... the existence of the Big Bang is the observationally well established Hubble law. Edwin Hubble in 1924 found that galaxies move away from us with a speed that increases with distance. Retracing these motions back in time, one nds not only when the universe came into being (Ferreras et al. 2001) but ...
... the existence of the Big Bang is the observationally well established Hubble law. Edwin Hubble in 1924 found that galaxies move away from us with a speed that increases with distance. Retracing these motions back in time, one nds not only when the universe came into being (Ferreras et al. 2001) but ...
Picture: Alnitak is the left-hand star in Orion`s Belt. Image: NASA
... 20 solar masses and a luminosity of 100 to 50,000 times that of the Sun. Often they are found together with O stars in OB associations since, being massive, they are short-lived and therefore do not survive long enough to move far from the place where they were formed. Their brief main sequence care ...
... 20 solar masses and a luminosity of 100 to 50,000 times that of the Sun. Often they are found together with O stars in OB associations since, being massive, they are short-lived and therefore do not survive long enough to move far from the place where they were formed. Their brief main sequence care ...
The Big Dipper Constellation
... The Big Dipper What is a Constellation? From very early times, man has been fascinated by the stars. Early stargazers began naming stars. They also noticed patterns of stars that appeared night after night in the sky. These patterns or groupings of stars are called constellations. They also began to ...
... The Big Dipper What is a Constellation? From very early times, man has been fascinated by the stars. Early stargazers began naming stars. They also noticed patterns of stars that appeared night after night in the sky. These patterns or groupings of stars are called constellations. They also began to ...
G485 5.5.1 Structure of the Universe
... and the tremendous distances from one star to another. Proxima Centauri, the closest star to the Sun, is 4.5 light-years away, so if it has planets in orbit around it, they would not be visible even using the most powerful telescopes. ...
... and the tremendous distances from one star to another. Proxima Centauri, the closest star to the Sun, is 4.5 light-years away, so if it has planets in orbit around it, they would not be visible even using the most powerful telescopes. ...
Sun and Other Stars Notes
... -How is stellar parallax used? -A stars apparent shift relative to some more distant background as the observer’s point of view change -Using the _________________________, astronomers can use two ends of a baseline, or two opposites sides of the Earth, for more distant stars using parallax requires ...
... -How is stellar parallax used? -A stars apparent shift relative to some more distant background as the observer’s point of view change -Using the _________________________, astronomers can use two ends of a baseline, or two opposites sides of the Earth, for more distant stars using parallax requires ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... This is still a comfortable time of year to observe in the evening, even so, the nights are becoming longer than the days, so chillier nights can be expected. As the Earth moves from the autumnal equinox the days are closing in rapidly. Throughout this month, the ecliptic is at a very shallow angle ...
... This is still a comfortable time of year to observe in the evening, even so, the nights are becoming longer than the days, so chillier nights can be expected. As the Earth moves from the autumnal equinox the days are closing in rapidly. Throughout this month, the ecliptic is at a very shallow angle ...
Hungry Young Stars: A New Explanation for the FU Ori Outbursts
... • A young star devours embryos that form in the disk, resulting in colossal bursts of luminosity. This process repeats as long as nebular material rains onto the disk. • The new feature in our model is the self-consistent formation and evolution of a gas disk due to matter falling in from the surrou ...
... • A young star devours embryos that form in the disk, resulting in colossal bursts of luminosity. This process repeats as long as nebular material rains onto the disk. • The new feature in our model is the self-consistent formation and evolution of a gas disk due to matter falling in from the surrou ...
Name
... D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What is the energy of this ...
... D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What is the energy of this ...
What The Star of Bethlehem Was Not
... A popular theory for many years was the idea that the Star of Bethlehem might have been a brilliant supernova. Unfortunately, this can be discounted. Many old supernovae are known around the sky – some, like the 1054 supernova, have left a prominent nebula (the Crab Nebula), others, like Tycho’s sup ...
... A popular theory for many years was the idea that the Star of Bethlehem might have been a brilliant supernova. Unfortunately, this can be discounted. Many old supernovae are known around the sky – some, like the 1054 supernova, have left a prominent nebula (the Crab Nebula), others, like Tycho’s sup ...
Magnitudes and Colours of Stars - Lincoln
... Let’s leave brightness for now, and start thinking about stellar size: another important property for classifying stars. It is almost impossible to actually see a star through a telescope and measure its physical diameter. We can do this with objects within the Solar System, but the stars are simply ...
... Let’s leave brightness for now, and start thinking about stellar size: another important property for classifying stars. It is almost impossible to actually see a star through a telescope and measure its physical diameter. We can do this with objects within the Solar System, but the stars are simply ...
Name
... D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What is the energy of this ...
... D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What is the energy of this ...
Planet Earth – Could There be Life?
... Now that we know the Sun star is a good candidate to support life, let’s look at planet Earth’s position relative to the Sun! ...
... Now that we know the Sun star is a good candidate to support life, let’s look at planet Earth’s position relative to the Sun! ...
Planet Earth – Could There be Life?
... Now that we know the Sun star is a good candidate to support life, let’s look at planet Earth’s position relative to the Sun! ...
... Now that we know the Sun star is a good candidate to support life, let’s look at planet Earth’s position relative to the Sun! ...
Name - MIT
... 6) A planet is 4 Astronomical Units from the Sun. What is the planet’s orbital period around the Sun? A) the square of 4, which equals 16 years B) the square root of 4, which equals 2 years C) the square root of 64, which equals 8 years D) the square of 9, which equals 81 years E) the cube of 4, whi ...
... 6) A planet is 4 Astronomical Units from the Sun. What is the planet’s orbital period around the Sun? A) the square of 4, which equals 16 years B) the square root of 4, which equals 2 years C) the square root of 64, which equals 8 years D) the square of 9, which equals 81 years E) the cube of 4, whi ...
Name
... D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What is the energy of this ...
... D) are not electromagnetic waves like visible light is. E) have less energy per photon An infrared photon has a frequency of 1 x 1014 Hz. What is the energy of this ...
Stellar Evolution
... • Mass of Sun • Radius of Earth • Hot as Sun’s core • A million times denser than lead • Slowly cool off ...
... • Mass of Sun • Radius of Earth • Hot as Sun’s core • A million times denser than lead • Slowly cool off ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.