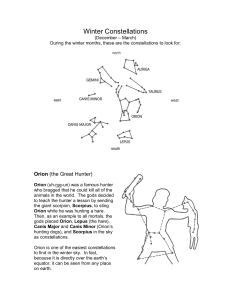
seven winter constellations
... to find because the dog’s collar contains the very brightest star in the night sky. It is called Sirius (see-ree-us), or “the Dog Star.” ...
... to find because the dog’s collar contains the very brightest star in the night sky. It is called Sirius (see-ree-us), or “the Dog Star.” ...
Poetry of the Stars
... Frost refers to Keat’s poem, “Bright Star” (1819); an Eremite is a hermit detached and watching, much like a muse. The star is detached from the Earth as if lofty and watchful. The star cannot tell him about the meaning of life, only what the “heavens declare”. Blackbody radiation was understood tur ...
... Frost refers to Keat’s poem, “Bright Star” (1819); an Eremite is a hermit detached and watching, much like a muse. The star is detached from the Earth as if lofty and watchful. The star cannot tell him about the meaning of life, only what the “heavens declare”. Blackbody radiation was understood tur ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Draw and label the celestial sphere for an observer at any latitude, Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West at any given latitude, Define a constellation and distinguish it from an asterism, Use celestial coordinates of Right Ascension an ...
... Draw and label the celestial sphere for an observer at any latitude, Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West at any given latitude, Define a constellation and distinguish it from an asterism, Use celestial coordinates of Right Ascension an ...
Contents ISP 205 Section 2 Study Guide for Test 3 28 March 2007
... 3. If a giant hand ripped away half the mass of the sun, how would our new sun look different? 4. Will the sun ever be star like Vega (Figure 11.10)? … like Sirius B? 5. Suppose the sun formed in a star cluster 5 Byrs ago. Sketch the HR diagram 4 Byrs ago. You can use Fig 11.10. 6. If a giant hand m ...
... 3. If a giant hand ripped away half the mass of the sun, how would our new sun look different? 4. Will the sun ever be star like Vega (Figure 11.10)? … like Sirius B? 5. Suppose the sun formed in a star cluster 5 Byrs ago. Sketch the HR diagram 4 Byrs ago. You can use Fig 11.10. 6. If a giant hand m ...
PHYS 390 Lectures 1/2 - The Big Picture 1/2
... The Big Picture Distance scales to stars and galaxies are huge by terrestrial standards, requiring larger units of length than km: light-year (ly) = 3.0 x 108 • π x 107 = 9.46 x 1015 m = 9.46 x 1012 km parsec (pc) = 3.26 ly (see below). Distances around the solar system are often quoted in Astronomi ...
... The Big Picture Distance scales to stars and galaxies are huge by terrestrial standards, requiring larger units of length than km: light-year (ly) = 3.0 x 108 • π x 107 = 9.46 x 1015 m = 9.46 x 1012 km parsec (pc) = 3.26 ly (see below). Distances around the solar system are often quoted in Astronomi ...
Cosmic Landscape Introduction Study Notes About how
... represents the mean distance between the Earth and our sun. The AU is approximately 150 million kilometers or 93 million miles. It is approximately 8 light-minutes. Roughly how big across is the Milky Way Galaxy? The Milky Way galaxy is the home of the Sun and our solar system. There are 200 billion ...
... represents the mean distance between the Earth and our sun. The AU is approximately 150 million kilometers or 93 million miles. It is approximately 8 light-minutes. Roughly how big across is the Milky Way Galaxy? The Milky Way galaxy is the home of the Sun and our solar system. There are 200 billion ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (50 pts
... E. the wind speeds are very high and produce a blue shift. 4. The single most important factor influencing a star’s evolution is A. the strength of its magnetic field. B. its rotation rate. C. its surface temperature. D. its mass. E. its diameter. 5. If there are five objects of the same size that h ...
... E. the wind speeds are very high and produce a blue shift. 4. The single most important factor influencing a star’s evolution is A. the strength of its magnetic field. B. its rotation rate. C. its surface temperature. D. its mass. E. its diameter. 5. If there are five objects of the same size that h ...
10 - Keele Astrophysics Group
... Firstly it was necessary to account for the fact that stars have very different radii at different stages in their evolution (i.e. their surface gravity is very different), with larger stars being more luminous. The luminosity together with the temperature completely ...
... Firstly it was necessary to account for the fact that stars have very different radii at different stages in their evolution (i.e. their surface gravity is very different), with larger stars being more luminous. The luminosity together with the temperature completely ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Many ancient cultures saw patterns in the sky and established their own constellations and star lore based on their culture and mythology. Most northern constellations dates back to Babylonians times, 4-5 millennia ago, – Later Greeks adopted them and interpreted according to their mythology ...
... Many ancient cultures saw patterns in the sky and established their own constellations and star lore based on their culture and mythology. Most northern constellations dates back to Babylonians times, 4-5 millennia ago, – Later Greeks adopted them and interpreted according to their mythology ...
GCSE Science Examination Command Words and Examples to
... acting inwards and the forces acting outwards are balanced. Eventually it runs out of hydrogen so the star starts to cool and becomes a red giant. Then it starts to shrink under its own gravity and as the material comes closer together the temperature rises and the star glows much brighter as a whit ...
... acting inwards and the forces acting outwards are balanced. Eventually it runs out of hydrogen so the star starts to cool and becomes a red giant. Then it starts to shrink under its own gravity and as the material comes closer together the temperature rises and the star glows much brighter as a whit ...
Oceanography Chapter 1 – “Origins”
... • Hydrogen atoms: – the most common form of matter in the universe. • Atoms have mass. Clump together under gravity. • Formation of elements: – He through Fe (iron) inside stars (nuclear fusion) – Heavier elements in supernova explosion (Fe & beyond) ...
... • Hydrogen atoms: – the most common form of matter in the universe. • Atoms have mass. Clump together under gravity. • Formation of elements: – He through Fe (iron) inside stars (nuclear fusion) – Heavier elements in supernova explosion (Fe & beyond) ...
Earth
... Heliocentric model explains difference between sidereal day (23 hr, 56 min) and solar day (24 hr). ...
... Heliocentric model explains difference between sidereal day (23 hr, 56 min) and solar day (24 hr). ...
The Sun, at a mean distance of 92.96 million miles, is the closest
... outward and is detected as the sunlight we observe here on Earth about eight minutes after it leaves the Sun. The temperature of the photosphere is about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Above the photosphere lie the tenuous chromosphere and the corona. Visible light from these top regions is usually too ...
... outward and is detected as the sunlight we observe here on Earth about eight minutes after it leaves the Sun. The temperature of the photosphere is about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Above the photosphere lie the tenuous chromosphere and the corona. Visible light from these top regions is usually too ...
Space – Astronomy Review
... Large natural objects that revolve around planets are called satellites. Between Mars and Jupiter, there is a large gap in the solar system where small rocky objects called asteroids exist and form an asteroid belt. A meteoroid is a lump of rock or metal that is trapped by Earth’s gravity and pulled ...
... Large natural objects that revolve around planets are called satellites. Between Mars and Jupiter, there is a large gap in the solar system where small rocky objects called asteroids exist and form an asteroid belt. A meteoroid is a lump of rock or metal that is trapped by Earth’s gravity and pulled ...
Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli) Chapter 33
... B) red giant stars. C) regular stars like our sun. D) white dwarfs. Answer: A Var: 1 7) Black holes A) are gaps in space, containing no matter. B) are predicted by Einstein's special theory of relativity. C) are the collapsed remnant of giant stars. D) cannot be detected in binary star systems. E) a ...
... B) red giant stars. C) regular stars like our sun. D) white dwarfs. Answer: A Var: 1 7) Black holes A) are gaps in space, containing no matter. B) are predicted by Einstein's special theory of relativity. C) are the collapsed remnant of giant stars. D) cannot be detected in binary star systems. E) a ...
High Mass Stars
... The end result of the CNO cycle is the same as for the proton-proton chain - 4 protons produce 1 helium atom and release energy - but the steps are different. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen act as catalysts that speed up the reaction. They aid the reaction without being consumed. Discovering Astronomy ...
... The end result of the CNO cycle is the same as for the proton-proton chain - 4 protons produce 1 helium atom and release energy - but the steps are different. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen act as catalysts that speed up the reaction. They aid the reaction without being consumed. Discovering Astronomy ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 1-4
... stars look close together in the sky, they may actually be hundreds of light years apart because their distance from Earth varies. The ‘shape’ they form is only seen from Earth. The constellation of Orion forms the shape of a hunter and can be seen high in the night sky during summer (in the Souther ...
... stars look close together in the sky, they may actually be hundreds of light years apart because their distance from Earth varies. The ‘shape’ they form is only seen from Earth. The constellation of Orion forms the shape of a hunter and can be seen high in the night sky during summer (in the Souther ...
Star Information ppt.
... We can directly observe the orbital motions of these stars Visual Binary – Orbit around each other ...
... We can directly observe the orbital motions of these stars Visual Binary – Orbit around each other ...
Week 3: Kepler`s Laws, Light and Matter
... emit photons when they come down. Absorption spectrum is produced when we observe a cold gas cloud in front of a hot source of light. In this case, the electrons take away some energy from the light and move up. They may lose this energy by emitting photons in random directions or any other mechanis ...
... emit photons when they come down. Absorption spectrum is produced when we observe a cold gas cloud in front of a hot source of light. In this case, the electrons take away some energy from the light and move up. They may lose this energy by emitting photons in random directions or any other mechanis ...
L19-Review2
... Study the last quiz (questions will be similar) Note that your paper is far more important Don’t panic ...
... Study the last quiz (questions will be similar) Note that your paper is far more important Don’t panic ...
Ch. 1 - University of Tennessee Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Naked eye view of bright stars In Orion ...
... Naked eye view of bright stars In Orion ...
ASTRONOMY 120
... How do astronomers test the theory of stellar evolution? (3 points) Stars change so slowly over time, that we have no hope of observing the changes they go through directly in a human lifetime or even in all of human history. However, we have a galaxy full of many stars at different stages of develo ...
... How do astronomers test the theory of stellar evolution? (3 points) Stars change so slowly over time, that we have no hope of observing the changes they go through directly in a human lifetime or even in all of human history. However, we have a galaxy full of many stars at different stages of develo ...
bbColors
... account the size of and distance to the star. So in truth, we are missing a term of R2 /r2 , where R is the radius of the star, and r is the distance to the star (the 4π’s cancel out, obviously). Since we are only measuring magnitude differences in each filter, this term can be separated (by logarit ...
... account the size of and distance to the star. So in truth, we are missing a term of R2 /r2 , where R is the radius of the star, and r is the distance to the star (the 4π’s cancel out, obviously). Since we are only measuring magnitude differences in each filter, this term can be separated (by logarit ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.























