Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect—28 Oct Outline • Announcements
... • Eg, in the visible part of the spectrum, hydrogen emits and absorbs light at 656.2, 486.1, 434.0, 410.1nm. Sodium Hydrogen Calcium Mercury Neon ...
... • Eg, in the visible part of the spectrum, hydrogen emits and absorbs light at 656.2, 486.1, 434.0, 410.1nm. Sodium Hydrogen Calcium Mercury Neon ...
There are 88 constellations in the sky around the Earth. 12 are the
... small telescopes, magnitudes 2.6 and 4.9; Dschubba Delta Scorpii, magnitude 2.3. Zeta Scorpii a naked eye double, magnitudes 3.6 and 4.7. The Myths : the scorpion is associated with the Semitic goddess, Ishara, wife of the corn god Dagan. He is said to have invented the plow. She is later associated ...
... small telescopes, magnitudes 2.6 and 4.9; Dschubba Delta Scorpii, magnitude 2.3. Zeta Scorpii a naked eye double, magnitudes 3.6 and 4.7. The Myths : the scorpion is associated with the Semitic goddess, Ishara, wife of the corn god Dagan. He is said to have invented the plow. She is later associated ...
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... ejected as a planetary nebula similar to the famed Ring Nebula in Lyra. What will be left behind is a white dwarf. Arcturus is the Alpha (meaning brightest) star of the springtime constellation Bootes, The Herdsman. You can find it by using the Big Dipper as your celestial guidepost. Follow the arc ...
... ejected as a planetary nebula similar to the famed Ring Nebula in Lyra. What will be left behind is a white dwarf. Arcturus is the Alpha (meaning brightest) star of the springtime constellation Bootes, The Herdsman. You can find it by using the Big Dipper as your celestial guidepost. Follow the arc ...
HR Diagram of Messier 80 using Hubble Space Telescope Data
... 8. Optional: Download and reduce the data yourself If you want to create the data set below on your own, follow these directions below. Go to http://hla.stsci.edu/ Click “Enter Site.” Search for M80. Then do an “Advanced Search”. Check off only the WFPC2 instrument. Search for Proposal ID 11233. Two ...
... 8. Optional: Download and reduce the data yourself If you want to create the data set below on your own, follow these directions below. Go to http://hla.stsci.edu/ Click “Enter Site.” Search for M80. Then do an “Advanced Search”. Check off only the WFPC2 instrument. Search for Proposal ID 11233. Two ...
Homework #1 Solutions
... 2. a) To answer this question, let’s determine the declination of a star that just barely rises above the horizon for each location. If Alpha Centauri’s declination is greater than this, then we know we can observe it from that location. The declination of a star that just barely rises is δ = −(90◦ ...
... 2. a) To answer this question, let’s determine the declination of a star that just barely rises above the horizon for each location. If Alpha Centauri’s declination is greater than this, then we know we can observe it from that location. The declination of a star that just barely rises is δ = −(90◦ ...
Galactic Star Formation Science with Integral Field
... – BLUE-shifted, collimated [Fe II] jet associated with the brighter lobe of the scattered light nebulosity - no redshifted jet detected – Jet Orientation consistent w/ 63o viewing disk inclination Beck et al. “Laser Fed Adaptive Optics Imaging Spectroscopy of the Candidate Proto-Brown Dwarf IRAS 041 ...
... – BLUE-shifted, collimated [Fe II] jet associated with the brighter lobe of the scattered light nebulosity - no redshifted jet detected – Jet Orientation consistent w/ 63o viewing disk inclination Beck et al. “Laser Fed Adaptive Optics Imaging Spectroscopy of the Candidate Proto-Brown Dwarf IRAS 041 ...
1 - Alice Pevyhouse
... will complete one circle ‘cycle’ and point back at the same point. This is known as? 24.The Earth’s axis of tilt can vary from its current 23.5 degree tilt (T/F) 26. In another 13,000 years, Earth's axial tilt will point in the opposite direction it does now. Assuming the other astronomical influenc ...
... will complete one circle ‘cycle’ and point back at the same point. This is known as? 24.The Earth’s axis of tilt can vary from its current 23.5 degree tilt (T/F) 26. In another 13,000 years, Earth's axial tilt will point in the opposite direction it does now. Assuming the other astronomical influenc ...
without video - Scott Marley
... First Confirmed Discovery On 21 April 1992, radio astronomers Aleksander Wolszczan and Dale Frail announced the discovery of two planets orbiting the pulsar PSR 1257+12. This discovery is generally considered to be the first definitive detection of exoplanets. These pulsar planets are believed to h ...
... First Confirmed Discovery On 21 April 1992, radio astronomers Aleksander Wolszczan and Dale Frail announced the discovery of two planets orbiting the pulsar PSR 1257+12. This discovery is generally considered to be the first definitive detection of exoplanets. These pulsar planets are believed to h ...
The Death of High Mass Stars
... searchlight is like a lighthouse, which we see as a pulsar if we happen to lie in the searchlight beam. ...
... searchlight is like a lighthouse, which we see as a pulsar if we happen to lie in the searchlight beam. ...
Section 4
... discovered a planet revolving around another ordinary star. They used a method similar to the one used in studying binary stars. The astronomers observed that a star was moving slightly toward and away from us. They knew that the invisible object causing the movement didn’t have enough mass to be a ...
... discovered a planet revolving around another ordinary star. They used a method similar to the one used in studying binary stars. The astronomers observed that a star was moving slightly toward and away from us. They knew that the invisible object causing the movement didn’t have enough mass to be a ...
5th Grade Astronomy Test Study Guide
... 7. The planets and moons orbit the Sun because of the Sun’s gravitational pull. 8. Earth orbiting the Sun is an example of revolution. 9. The shape of planetary orbits is called an ellipse. 10. Earth spinning on its axis is rotation. 11. Earth orbiting the Sun and the Moon orbiting the Earth are all ...
... 7. The planets and moons orbit the Sun because of the Sun’s gravitational pull. 8. Earth orbiting the Sun is an example of revolution. 9. The shape of planetary orbits is called an ellipse. 10. Earth spinning on its axis is rotation. 11. Earth orbiting the Sun and the Moon orbiting the Earth are all ...
How big are stars? How do we know?
... close to the Sun. b) relatively cool giant stars that are relatively close to the Sun. c) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively far from the Sun. d) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively close to the Sun. e) giant stars and relatively hot main sequence stars. ...
... close to the Sun. b) relatively cool giant stars that are relatively close to the Sun. c) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively far from the Sun. d) relatively cool main-sequence stars that are relatively close to the Sun. e) giant stars and relatively hot main sequence stars. ...
PC2491 Examples 2
... the values of Oort’s constants at a radius of 3kpc and hence, or otherwise, the epicyclic frequency in km s-1 kpc-1 If the galaxy has a two armed spiral pattern, and the inner Lindblad resonance is observed to be 3kpc from the galactic centre, estimate the pattern speed and the radius of corotation ...
... the values of Oort’s constants at a radius of 3kpc and hence, or otherwise, the epicyclic frequency in km s-1 kpc-1 If the galaxy has a two armed spiral pattern, and the inner Lindblad resonance is observed to be 3kpc from the galactic centre, estimate the pattern speed and the radius of corotation ...
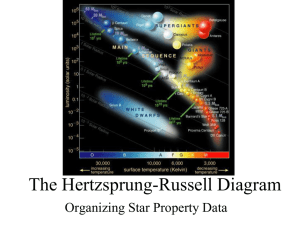
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbits ...
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbits ...
Powers of ten notation
... The Sun on the other hand, takes an average of 24 hours between successive meridian crossings. The difference is due to Earth’s revolution about the Sun. The Sun moves on average 4 minutes eastward each day relative to the stars, staying in the sky longer each day than a star at the same declination ...
... The Sun on the other hand, takes an average of 24 hours between successive meridian crossings. The difference is due to Earth’s revolution about the Sun. The Sun moves on average 4 minutes eastward each day relative to the stars, staying in the sky longer each day than a star at the same declination ...
Astro 3 Spring, 2004 (Prof
... outer layers out into space, creating a type II supernova. -- Type II supernova can be distinguished from type I because they have many hydrogen lines in their spectrum, as stars are mainly composed of hydrogen. They also dim more quickly than type I supernovae. -- The remnant of the explosion will ...
... outer layers out into space, creating a type II supernova. -- Type II supernova can be distinguished from type I because they have many hydrogen lines in their spectrum, as stars are mainly composed of hydrogen. They also dim more quickly than type I supernovae. -- The remnant of the explosion will ...
SW - Calculating Magnitudes
... Here, ‘intensity’, also knowns as ‘counts’, refers to the amount of light that is emitted from the object and received by the CCD (see ‘Photometry in Astronomy’ worksheet). However, it’s a bit of an archaic system in that the brighter an object, the lower its apparent magnitude value. Objects that a ...
... Here, ‘intensity’, also knowns as ‘counts’, refers to the amount of light that is emitted from the object and received by the CCD (see ‘Photometry in Astronomy’ worksheet). However, it’s a bit of an archaic system in that the brighter an object, the lower its apparent magnitude value. Objects that a ...
Star Light, Star Bright
... Point out that many distant stars can be seen in the night sky. Ask, Of all the stars you can see in the night sky, do you think the brightest stars are the closest stars to Earth? ...
... Point out that many distant stars can be seen in the night sky. Ask, Of all the stars you can see in the night sky, do you think the brightest stars are the closest stars to Earth? ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.