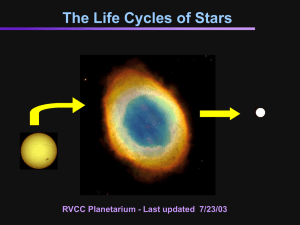
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
The Brightness of Stars
... Stars that are cool, ~3500K, will be reddish; stars that are hot, ~10,000K, will be white White light is a combination of all colors, so a hot star will appear brighter than a red star, all other things being equal, because not all light from a star is visible to the human eye ...
... Stars that are cool, ~3500K, will be reddish; stars that are hot, ~10,000K, will be white White light is a combination of all colors, so a hot star will appear brighter than a red star, all other things being equal, because not all light from a star is visible to the human eye ...
Earth`s Motions
... – Retrograde Motion = backwards (west to east) motion relative to the stars because Earth moves faster than outer planets. This causes the outer planet to temporarily seem to move backward in the sky as we pass it. This variation in motion is how planets were discovered. The retrograde motion of pla ...
... – Retrograde Motion = backwards (west to east) motion relative to the stars because Earth moves faster than outer planets. This causes the outer planet to temporarily seem to move backward in the sky as we pass it. This variation in motion is how planets were discovered. The retrograde motion of pla ...
handout
... position in the sky seemed to tell _________________ that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years ...
... position in the sky seemed to tell _________________ that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years ...
Constellation Information
... site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-power, wide-field telescope, it looks like an old-fashion done-shaped beehive with many extra bees buzzing around it. ...
... site far from light pollution. M44 is also known as the Beehive Cluster, because in binoculars or a low-power, wide-field telescope, it looks like an old-fashion done-shaped beehive with many extra bees buzzing around it. ...
$doc.title
... 2a. Mark and label the Sun (spectral type=G2V, MV = 4.83, B-‐V=+0.66) and the star Vega (spectral type: A0V, MV = 0.5, B-‐V=0.0) in the HR diagram. [Assume the tick marks on the lower horizontal ...
... 2a. Mark and label the Sun (spectral type=G2V, MV = 4.83, B-‐V=+0.66) and the star Vega (spectral type: A0V, MV = 0.5, B-‐V=0.0) in the HR diagram. [Assume the tick marks on the lower horizontal ...
2009 Assessment Schedule (90764)
... Science: Describe the nature and life cycle of stars (90764) Evidence Statement Achievement ...
... Science: Describe the nature and life cycle of stars (90764) Evidence Statement Achievement ...
of a Star
... NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. Launched in February, SDO is the most advanced spacecraft ever designed to study the sun. ...
... NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. Launched in February, SDO is the most advanced spacecraft ever designed to study the sun. ...
here - Lund Observatory
... 1.15. Determine if the star is a supergiant, a giant or a main-sequence star (dwarf). The visual extinction is three times the colour excess B-V. In thr direction of the star the visual extinction, AV, can be assumed to be given by AV = a ⋅ r, where r is the distance to the star and a = 0.003 magnit ...
... 1.15. Determine if the star is a supergiant, a giant or a main-sequence star (dwarf). The visual extinction is three times the colour excess B-V. In thr direction of the star the visual extinction, AV, can be assumed to be given by AV = a ⋅ r, where r is the distance to the star and a = 0.003 magnit ...
A Universe of Dwarfs and Giants
... they are the dying remnants of super giant stars; the outer layer of the star has been blown off into space revealing a hot helium-rich layer beneath. L and T type stars: at the smaller cooler end of things are the tiny red and brown dwarf stars. ...
... they are the dying remnants of super giant stars; the outer layer of the star has been blown off into space revealing a hot helium-rich layer beneath. L and T type stars: at the smaller cooler end of things are the tiny red and brown dwarf stars. ...
Document
... • A computer program that simulates the vision of the sky during day and night Things to observe: • Position on Earth: observe how the view of sky changes as you move E,W, N,S • Note the distribution of sunlight on Earth! • Rotation is around Polaris which is not in zenith ...
... • A computer program that simulates the vision of the sky during day and night Things to observe: • Position on Earth: observe how the view of sky changes as you move E,W, N,S • Note the distribution of sunlight on Earth! • Rotation is around Polaris which is not in zenith ...
Which property of a star would not change if we could observe it
... • It works the same with stars! • If we know the total energy output of a star (luminosity), and we can count the number of photons we receive from that star (brightness), we can calculate its distance ...
... • It works the same with stars! • If we know the total energy output of a star (luminosity), and we can count the number of photons we receive from that star (brightness), we can calculate its distance ...
Physical Science Laboratory: Skyglobe
... . to be able to describe the difference in the stars’ apparent movement throughout the night from the equator and from the poles. . to be able to identify Polaris, Vega, Sirius, and other prominent stars. . to be able to describe the Sun’s movement across the sky during the equinoxes and solstices. ...
... . to be able to describe the difference in the stars’ apparent movement throughout the night from the equator and from the poles. . to be able to identify Polaris, Vega, Sirius, and other prominent stars. . to be able to describe the Sun’s movement across the sky during the equinoxes and solstices. ...
File
... as they orbit the Sun, material ________ forming the tail the tail _______ points away from the Sun Halley's comet orbits the Sun every ____ years (1986) Meteors and Meteorites Earth is bombarded everyday by _____ and ______ fragments from space when one of the objects _______ up generatin ...
... as they orbit the Sun, material ________ forming the tail the tail _______ points away from the Sun Halley's comet orbits the Sun every ____ years (1986) Meteors and Meteorites Earth is bombarded everyday by _____ and ______ fragments from space when one of the objects _______ up generatin ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... There is a star system about 45 light years away in the constellation Cygnus. The system we know as HD 187091 (also known as KOI-54 for Kepler Object of Interest 54) is an undistinguished 8th magnitude A star or was before the Kepler telescope took a close look. As it turns out, the system is anythi ...
... There is a star system about 45 light years away in the constellation Cygnus. The system we know as HD 187091 (also known as KOI-54 for Kepler Object of Interest 54) is an undistinguished 8th magnitude A star or was before the Kepler telescope took a close look. As it turns out, the system is anythi ...
Stars and the Sun
... Stars bigger than the Sun • The core is usually left over. – If the core isless than 3 times the mass of the Sun, it will become a neutron star … something so dense that electrons are pushed into the nucleus and cancel out protons and make all neutrons! Some give out regular pulses of radio waves ( ...
... Stars bigger than the Sun • The core is usually left over. – If the core isless than 3 times the mass of the Sun, it will become a neutron star … something so dense that electrons are pushed into the nucleus and cancel out protons and make all neutrons! Some give out regular pulses of radio waves ( ...
Summer Triangle (Winter in the south hemisphere) Lyra
... To ease his pain, the gods placed Cygnus in the sky, where he took the form of a swan. The Chinese also have a myth associated with this constellation. This myth is referred to as the "magpie bridge" 鵲橋. Notable Stars Deneb is a blue-white giant star at the tip of the Northern Cross. It is 1400 ligh ...
... To ease his pain, the gods placed Cygnus in the sky, where he took the form of a swan. The Chinese also have a myth associated with this constellation. This myth is referred to as the "magpie bridge" 鵲橋. Notable Stars Deneb is a blue-white giant star at the tip of the Northern Cross. It is 1400 ligh ...
Astronomy
... 18. What does apparent visual magnitude (mv) measure? What is the highest magnitude of stars that are still visible with the naked eye? How bright stars look from Earth. The dimmest we can see are about a magnitude of 6 ...
... 18. What does apparent visual magnitude (mv) measure? What is the highest magnitude of stars that are still visible with the naked eye? How bright stars look from Earth. The dimmest we can see are about a magnitude of 6 ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.