Distances farther out
... Such self absorption also seen in B stars. UV Mg II lines at λ2796 & 2802 (h & k lines, visible only from satellite borne telescopes) - also exhibit self absorption. Wilson Bappu effect: 1956, Wilson & Bappu at Mt Wilson: Width of K2 line correlates very well with visual magnitude of classes G, K, M ...
... Such self absorption also seen in B stars. UV Mg II lines at λ2796 & 2802 (h & k lines, visible only from satellite borne telescopes) - also exhibit self absorption. Wilson Bappu effect: 1956, Wilson & Bappu at Mt Wilson: Width of K2 line correlates very well with visual magnitude of classes G, K, M ...
REGIONAL exam 2013
... 5. Each question is worth one point. Tiebreaker questions are indicated with a (T#) in which the number indicates the order of consultation in the event of a tie. Tiebreaker questions count toward the overall raw score, and are only used as tiebreakers when there is a tie. In such cases, (T1) will b ...
... 5. Each question is worth one point. Tiebreaker questions are indicated with a (T#) in which the number indicates the order of consultation in the event of a tie. Tiebreaker questions count toward the overall raw score, and are only used as tiebreakers when there is a tie. In such cases, (T1) will b ...
Star Classification
... by luminosity and is higher up the yaxis. The temperature is given in degrees Kelvin and is higher on the left side of the x-axis. How does our Sun fare in terms of brightness and color compared with other stars? ...
... by luminosity and is higher up the yaxis. The temperature is given in degrees Kelvin and is higher on the left side of the x-axis. How does our Sun fare in terms of brightness and color compared with other stars? ...
PowerPoint
... balance point (center of mass) for a teeter-totter. Archimedes discovered that the balance point (center of mass) for a board with masses m1 and m2 at each end satisfies m1r1=m2r2 (Law of the Lever). ...
... balance point (center of mass) for a teeter-totter. Archimedes discovered that the balance point (center of mass) for a board with masses m1 and m2 at each end satisfies m1r1=m2r2 (Law of the Lever). ...
TWO DIFFERENT ALTITUDES
... 3. These stars lead directly to Polaris, and are called the ______________. 4. The North Star and the Pole Star are names for ___________. 5. The imaginary line that runs through Earth's north and south poles points to _______. 6. Like the sun and the moon, the stars appear to "rise" and "set.” Howe ...
... 3. These stars lead directly to Polaris, and are called the ______________. 4. The North Star and the Pole Star are names for ___________. 5. The imaginary line that runs through Earth's north and south poles points to _______. 6. Like the sun and the moon, the stars appear to "rise" and "set.” Howe ...
Name Physics 130 Astronomy Exam 2 August 2, 2004 Multiple Choice
... c.) protostars cannot form with masses less than 0.08 solar mass. d.) protostars of less than 0.08 solar masses are not massive enough to contract. 30. _____ An object which is too massive to be a planet but not massive enough to be a star is called a.) a red dwarf b.) a white dwarf c.) a T Tauri st ...
... c.) protostars cannot form with masses less than 0.08 solar mass. d.) protostars of less than 0.08 solar masses are not massive enough to contract. 30. _____ An object which is too massive to be a planet but not massive enough to be a star is called a.) a red dwarf b.) a white dwarf c.) a T Tauri st ...
File
... A collection of gas, stars and dust held together by gravity. About 125 billion galaxies are estimated to exist in the universe What galaxy do we live in? The Milky Way The number of galaxies in the universe According to the textbook, the number of sand grains that would fill a toothpaste cap repres ...
... A collection of gas, stars and dust held together by gravity. About 125 billion galaxies are estimated to exist in the universe What galaxy do we live in? The Milky Way The number of galaxies in the universe According to the textbook, the number of sand grains that would fill a toothpaste cap repres ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... When a cloud starts to collapse, it should fragment. Fragments then collapse on their own, fragmenting further. End product is 100’s or 1000’s of dense clumps each destined to form star, binary star, etc. Hence a cloud gives birth to a cluster of stars. ...
... When a cloud starts to collapse, it should fragment. Fragments then collapse on their own, fragmenting further. End product is 100’s or 1000’s of dense clumps each destined to form star, binary star, etc. Hence a cloud gives birth to a cluster of stars. ...
Chapter13
... Low luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
... Low luminosity; high temperature => White dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
TAP 702- 6: Binary stars - Teaching Advanced Physics
... In many binary stars, the two stars are not perfectly lined up when seen from Earth. This means that there will not be any dimming or brightening of the light, because the dimmer star will not block out the light from the brighter one. How might an astronomer tell, from the spectrum, that there are ...
... In many binary stars, the two stars are not perfectly lined up when seen from Earth. This means that there will not be any dimming or brightening of the light, because the dimmer star will not block out the light from the brighter one. How might an astronomer tell, from the spectrum, that there are ...
Hinsdale Astro TEST
... 14. Is this a young star or an old star? Image H 15. Give the proper name of this substellar brown dwarf. 16. What type of radiation does this type of object mainly emit? ...
... 14. Is this a young star or an old star? Image H 15. Give the proper name of this substellar brown dwarf. 16. What type of radiation does this type of object mainly emit? ...
Powerpoint for today
... Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius ( ...
... Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius ( ...
Astronomical Toolkit
... When we look at the sky on a clear night we see stars. Some appear bright and others very faint as seen from Earth. Some of the faint stars are intrinsically very bright, but are very distant. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are very faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When ...
... When we look at the sky on a clear night we see stars. Some appear bright and others very faint as seen from Earth. Some of the faint stars are intrinsically very bright, but are very distant. Some of the brightest stars in the sky are very faint stars that just happen to lie very close to us. When ...
Astronomy 10B List of Concepts– by Chapter
... • Which type of galaxy is the Milky Way? • Distances to galaxies • The Hubble Law o The Hubble age of the Universe o Is spacetime expanding or is the matter just flying apart? CHAPTER 18 AGN’S, QUASARS • If a QSO is a AGN, what are TLA's? • Quasars are called “quasi Stellar objects” (QSO) • Luminosi ...
... • Which type of galaxy is the Milky Way? • Distances to galaxies • The Hubble Law o The Hubble age of the Universe o Is spacetime expanding or is the matter just flying apart? CHAPTER 18 AGN’S, QUASARS • If a QSO is a AGN, what are TLA's? • Quasars are called “quasi Stellar objects” (QSO) • Luminosi ...
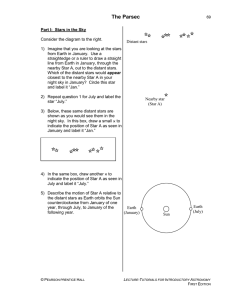
The Parsec
... even the nearest stars are still very far away, parallax angles are extremely small. These parallax angles are measured in “arcseconds” where an arcsecond is 1/3600 of 1 degree. To describe the distances to stars, astronomers use a unit of length called the parsec. 1 parsec is defined as the distanc ...
... even the nearest stars are still very far away, parallax angles are extremely small. These parallax angles are measured in “arcseconds” where an arcsecond is 1/3600 of 1 degree. To describe the distances to stars, astronomers use a unit of length called the parsec. 1 parsec is defined as the distanc ...
Comparing Earth, Sun and Jupiter
... a. If pulsars were binary stars, what would be the size of the semimajor axis? a3 P M ...
... a. If pulsars were binary stars, what would be the size of the semimajor axis? a3 P M ...
Tutorial - TIL BIRNSTIEL
... where S is the solar flux (1360 W m−2 at the Earth’s distance), A is the albedo of the planet, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.67 × 10−8 W m−2 K−4 , in SI units) and f is a constant of order unity (assume f = 4 for the rest of the exercise, why?). • For an Earth albedo of 0.29, derive the habi ...
... where S is the solar flux (1360 W m−2 at the Earth’s distance), A is the albedo of the planet, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.67 × 10−8 W m−2 K−4 , in SI units) and f is a constant of order unity (assume f = 4 for the rest of the exercise, why?). • For an Earth albedo of 0.29, derive the habi ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.