Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
... – So…A smaller star has less fuel, but its rate of fusion is not as fast. Therefore, smaller stars live longer than larger stars because their rate of fuel consumption is not as rapid. ...
... – So…A smaller star has less fuel, but its rate of fusion is not as fast. Therefore, smaller stars live longer than larger stars because their rate of fuel consumption is not as rapid. ...
star
... stars is gone, the stars cast off their gases exposing their cores. • The core eventually becomes a white dwarf, a hot, dense, slowly cooling sphere of carbon. • This is what is expected to happen to the Sun. ...
... stars is gone, the stars cast off their gases exposing their cores. • The core eventually becomes a white dwarf, a hot, dense, slowly cooling sphere of carbon. • This is what is expected to happen to the Sun. ...
Astronomy Power Point
... Radio Telescope • Detects radio waves given off by objects in space • Most have curved reflecting surfaces that are several hundred meters in diameter • The bigger the radio telescope, the more radio waves it can collect ...
... Radio Telescope • Detects radio waves given off by objects in space • Most have curved reflecting surfaces that are several hundred meters in diameter • The bigger the radio telescope, the more radio waves it can collect ...
About the Universe The Universe is everything that exists, including
... the high pressures caused by the high temperatures. Our Sun is at this stable phase in its life. Stars change when they grow older, and eventually they die – but only after billions of years. Stars die when they run out of fuel. When all the hydrogen has been used up in the fusion process, larger nu ...
... the high pressures caused by the high temperatures. Our Sun is at this stable phase in its life. Stars change when they grow older, and eventually they die – but only after billions of years. Stars die when they run out of fuel. When all the hydrogen has been used up in the fusion process, larger nu ...
RS Oph
... Variable Star of the Year RS Ophiuchi RS Oph is the second brightest member of a rare class of cataclysmic variable star known as recurrent novae (Nr). These stars are novae where more than one outburst has been observed and appear to be intermediate in class between the classical novae (single majo ...
... Variable Star of the Year RS Ophiuchi RS Oph is the second brightest member of a rare class of cataclysmic variable star known as recurrent novae (Nr). These stars are novae where more than one outburst has been observed and appear to be intermediate in class between the classical novae (single majo ...
V Example: our SUN (G2V)
... A supernova occurs when the core of the massive star collapses and a shock wave rips the star apart, usually leaving behind a neutron star. Supernovae can also be produced when enough material is deposited on a white dwarf so that is exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit and collapses to a neutron star. B ...
... A supernova occurs when the core of the massive star collapses and a shock wave rips the star apart, usually leaving behind a neutron star. Supernovae can also be produced when enough material is deposited on a white dwarf so that is exceeds the Chandrasekhar limit and collapses to a neutron star. B ...
Luminosity and brightness
... Luminosity and brightness Luminosity Luminosity is a measure of the total energy given output by a star at all wavelengths form gamma radiation to radio waves. For example the Sun gives out about 500 million million million MJ of energy every second so its luminosity is 500 million million million M ...
... Luminosity and brightness Luminosity Luminosity is a measure of the total energy given output by a star at all wavelengths form gamma radiation to radio waves. For example the Sun gives out about 500 million million million MJ of energy every second so its luminosity is 500 million million million M ...
Study Island
... put one group of mice in a cold environment and another group of mice in a hot environment. Everything else about the two environments was the same, including the type and amount of food and water. She allowed the experiment to last for a few generations of mice and tested the activity levels of the ...
... put one group of mice in a cold environment and another group of mice in a hot environment. Everything else about the two environments was the same, including the type and amount of food and water. She allowed the experiment to last for a few generations of mice and tested the activity levels of the ...
Life2
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
The Dramatic Lives of Stars
... B. Grows and cools as it ages C. Shrinks and heats up as it ages D. Shrinks and cools as it ages ...
... B. Grows and cools as it ages C. Shrinks and heats up as it ages D. Shrinks and cools as it ages ...
Basic properties of stars
... This is data for NGC 2482. It is about 400 million years old. Stars considerably right of the main sequence are more distant giants. ...
... This is data for NGC 2482. It is about 400 million years old. Stars considerably right of the main sequence are more distant giants. ...
Stellar Evolution - Academic Computer Center
... • The pressures of the surrounding layers are so high that the atoms of the iron core are crushed, smashing the electrons into the protons forming neutrons. • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The ex ...
... • The pressures of the surrounding layers are so high that the atoms of the iron core are crushed, smashing the electrons into the protons forming neutrons. • Once neutrons are formed the collapse stops, the surrounding gas is heated and explodes off the core. This is a supernova explosion. • The ex ...
Search for Student Research Assistant
... (Sco X-1 for short) is a double star system. It’s actually the brightest spot in the sky in X-rays (other than the Sun). Of the two stars, one is a normal star, slightly less massive than our own Sun, but the other is a neutron star (a collapsed star only about 10 km across). Sco X-1 was the first d ...
... (Sco X-1 for short) is a double star system. It’s actually the brightest spot in the sky in X-rays (other than the Sun). Of the two stars, one is a normal star, slightly less massive than our own Sun, but the other is a neutron star (a collapsed star only about 10 km across). Sco X-1 was the first d ...
Peer Instruction/Active Learning
... b) X rays and ultraviolet light c) infrared and gamma rays d) visible light and radio waves e) visible and X rays ...
... b) X rays and ultraviolet light c) infrared and gamma rays d) visible light and radio waves e) visible and X rays ...
S1E4 Extreme Stars
... • The resulting outward pressure which keeps the electrons apart is called electron degeneracy pressure – this is what balances the weight. • Only if more energy drives the electrons into higher energy states, can the density increase. • Adding mass can drive electrons to higher energies so star shr ...
... • The resulting outward pressure which keeps the electrons apart is called electron degeneracy pressure – this is what balances the weight. • Only if more energy drives the electrons into higher energy states, can the density increase. • Adding mass can drive electrons to higher energies so star shr ...
Earth in Space 19-1
... Summer and winter are not affected by changes in Earth's distance from the sun. In fact, when the Northern Hemisphere is having summer, Earth is at ...
... Summer and winter are not affected by changes in Earth's distance from the sun. In fact, when the Northern Hemisphere is having summer, Earth is at ...
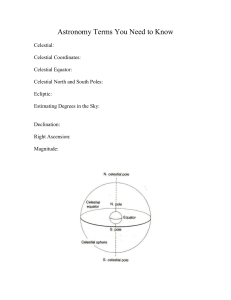
Astronomy Terms You Need to Know
... Suggested Observations for Fall Sky Journal. Fall Sky Journal is due BEFORE winter break in December. ...
... Suggested Observations for Fall Sky Journal. Fall Sky Journal is due BEFORE winter break in December. ...
Indoor lab #1: The Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram and Selection Effects
... a) the average distance of all the stars in your table: b) the number of and average distance of the red giant stars (stars of type 1) c) the number of and average distance of the bluer main sequence stars (stars of type 2) d) the number of and average distance of the redder main sequence stars (sta ...
... a) the average distance of all the stars in your table: b) the number of and average distance of the red giant stars (stars of type 1) c) the number of and average distance of the bluer main sequence stars (stars of type 2) d) the number of and average distance of the redder main sequence stars (sta ...
Unit 1 Test Review Answers - School District of La Crosse
... 4.Diurnal motion is best described by: causes night and day 5. Which of the following would not happen because of precession? 6. It is 3PM in London England(0 degrees). What time would it be in San Francisco(135W) 6 am 7. Nutation is caused by: GRAVITATIONAL TUG OF THE MOON 8. The north celestial po ...
... 4.Diurnal motion is best described by: causes night and day 5. Which of the following would not happen because of precession? 6. It is 3PM in London England(0 degrees). What time would it be in San Francisco(135W) 6 am 7. Nutation is caused by: GRAVITATIONAL TUG OF THE MOON 8. The north celestial po ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.