bbColors
... account the size of and distance to the star. So in truth, we are missing a term of R2 /r2 , where R is the radius of the star, and r is the distance to the star (the 4π’s cancel out, obviously). Since we are only measuring magnitude differences in each filter, this term can be separated (by logarit ...
... account the size of and distance to the star. So in truth, we are missing a term of R2 /r2 , where R is the radius of the star, and r is the distance to the star (the 4π’s cancel out, obviously). Since we are only measuring magnitude differences in each filter, this term can be separated (by logarit ...
Star luminosity info and HR diagram
... Have you ever noticed that stars shine in an array of different colors in a dark country sky? If not, try looking at stars with binoculars sometime. Color is a telltale sign of surface temperature. The hottest stars radiate blue or blue-white, whereas the coolest stars exhibit distinctly ruddy hues ...
... Have you ever noticed that stars shine in an array of different colors in a dark country sky? If not, try looking at stars with binoculars sometime. Color is a telltale sign of surface temperature. The hottest stars radiate blue or blue-white, whereas the coolest stars exhibit distinctly ruddy hues ...
Tutorial: Luminosity
... If a sphere of radius d is drawn around the star, it should be clear that the energy/sec through the surface of this sphere is the same as the energy/sec emitted through the surface of the star, since there is no mechanism to create or destroy photons in the space outside the star. The surface of th ...
... If a sphere of radius d is drawn around the star, it should be clear that the energy/sec through the surface of this sphere is the same as the energy/sec emitted through the surface of the star, since there is no mechanism to create or destroy photons in the space outside the star. The surface of th ...
Stars & Galaxies
... Temp just right because of sun Gravity force is just right Single moon provide for gentle tides Atmosphere clear so sun can penetrate Ozone layer protects us from UV Material that accreted had minerals and water to form the Earth’s crust ...
... Temp just right because of sun Gravity force is just right Single moon provide for gentle tides Atmosphere clear so sun can penetrate Ozone layer protects us from UV Material that accreted had minerals and water to form the Earth’s crust ...
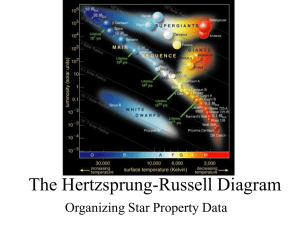
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Physics 1025: Lecture 17 Sun (cont.), Stellar Distances, Parallax
... the wavelength shift from the unshifted line λ. The star’s light will be blue-shifted if the star approaches earth. (Note in the case of an expanding nebula like the Crab Nebula, we assume it expands equally in all directions (i.e. spherically) and set VR= VT and can solve for the distance R to the ...
... the wavelength shift from the unshifted line λ. The star’s light will be blue-shifted if the star approaches earth. (Note in the case of an expanding nebula like the Crab Nebula, we assume it expands equally in all directions (i.e. spherically) and set VR= VT and can solve for the distance R to the ...
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars: Giants, Dwarfs, and the Main
... • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3"/year – Most stars have proper motions less than 1”/year ...
... • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3"/year – Most stars have proper motions less than 1”/year ...
11.3 Measuring Distances in Space
... Determining Distances by Triangulation The distance to a far away object can be determined by measuring two angles and the distance between those two angles. A line (called a baseline) is laid out and angle measurements are taken at the baseline endpoints to the distant object. Geometry and Trigono ...
... Determining Distances by Triangulation The distance to a far away object can be determined by measuring two angles and the distance between those two angles. A line (called a baseline) is laid out and angle measurements are taken at the baseline endpoints to the distant object. Geometry and Trigono ...
Watch - ggg999.org
... The four panels show the power density spectrum of the WIRE 2000 time series along with different simulations. Each simulation is the mean of five simulations with different seed numbers. The hatched regions show the 1-σ variation for selected simulations. ...
... The four panels show the power density spectrum of the WIRE 2000 time series along with different simulations. Each simulation is the mean of five simulations with different seed numbers. The hatched regions show the 1-σ variation for selected simulations. ...
Participant Handout - Math Machines Home
... a very large “red giant,” with a diameter about 600 times that of our Sun. (If our Sun were that large, it would engulf the Earth and extend well beyond the orbit of Mars.) The actual power of a star (the quantity of light it emits per second) is called its “luminosity” and can be measured either in ...
... a very large “red giant,” with a diameter about 600 times that of our Sun. (If our Sun were that large, it would engulf the Earth and extend well beyond the orbit of Mars.) The actual power of a star (the quantity of light it emits per second) is called its “luminosity” and can be measured either in ...
Sun - Blackboard
... • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most ...
... • How does the sky appear to move as Earth rotates? • What causes the seasons? • How can astronomical cycles affect Earth’s climate? As you study the sky and its motions, you will be learning to think of Earth as a planet rotating on its axis. The next chapter will introduce you to some of the most ...
WK8revised
... "One of the most impressive discoveries was the origin of the energy of the stars. One of the men who discovered this was out with his girl friend the night after he realized that nuclear reactions must be going on in the stars in order to make them shine. She said "Look at how pretty the stars shin ...
... "One of the most impressive discoveries was the origin of the energy of the stars. One of the men who discovered this was out with his girl friend the night after he realized that nuclear reactions must be going on in the stars in order to make them shine. She said "Look at how pretty the stars shin ...
Powerpoint for today
... Pulsars are incredibly accurate clocks! Example: period of the first discovered "millisecond pulsar" is: ...
... Pulsars are incredibly accurate clocks! Example: period of the first discovered "millisecond pulsar" is: ...
Click here to the PowerPoint
... 1. The force of gravity acts inwards 2. The pressure of nuclear fusion acts outwards Both forces are equal and balanced – this is why the main sequence star is ...
... 1. The force of gravity acts inwards 2. The pressure of nuclear fusion acts outwards Both forces are equal and balanced – this is why the main sequence star is ...
The Swansong of Stars Orbiting Massive Black Holes
... LISA will be able to detect compact objects that spiral into a MBH by GW emission from up to a distance of a Gpc. The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral ...
... LISA will be able to detect compact objects that spiral into a MBH by GW emission from up to a distance of a Gpc. The signal is expected to be weak. To detect it, it is necessary to know in advance the shape of the wave trains, and to do that, it is necessary to know the eccentricity of the inspiral ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.