ASTR 105 Intro Astronomy: The Solar System
... A. The Earth’s orbit around the Sun B. Earth spinning on its axis C. Our solar system moving in the Milky Way ...
... A. The Earth’s orbit around the Sun B. Earth spinning on its axis C. Our solar system moving in the Milky Way ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... wavelength, frequency, and energy? Do you know how light and matter interacts to form an absorption spectrum? Star Properties: Are you familiar with how astronomers use solar units as a way of describing physical qualities of other stars? Do you know the surface temperature, total lifespan, and gene ...
... wavelength, frequency, and energy? Do you know how light and matter interacts to form an absorption spectrum? Star Properties: Are you familiar with how astronomers use solar units as a way of describing physical qualities of other stars? Do you know the surface temperature, total lifespan, and gene ...
neutron star - The University of Chicago
... Earth or White Dwarf to size of Chicago. 100 times more energy than is needed to explode off the outer layers of the massive star. That does not guarantee an explosion! The outer parts of the star, beyond the neutron star, are transparent to the neutrinos, the neutrinos flood out freely and carry of ...
... Earth or White Dwarf to size of Chicago. 100 times more energy than is needed to explode off the outer layers of the massive star. That does not guarantee an explosion! The outer parts of the star, beyond the neutron star, are transparent to the neutrinos, the neutrinos flood out freely and carry of ...
Observing the Sky - University of Northern Iowa
... Above the “Tropic of Cancer”, Latitude = 23.5º N. At the most southerly point – Winter Solstice Above the “Tropic of Capricorn”, Latitude = 23.5º S. ...
... Above the “Tropic of Cancer”, Latitude = 23.5º N. At the most southerly point – Winter Solstice Above the “Tropic of Capricorn”, Latitude = 23.5º S. ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... Sagittarius and this area of the sky is rich in star clusters and nebulae of interest to both astronomers and casual viewers of the sky. Try exploring this area of the sky with a pair of binoculars. The planets: The stage is being set for the late-July appearance of all five visible or naked-eye pla ...
... Sagittarius and this area of the sky is rich in star clusters and nebulae of interest to both astronomers and casual viewers of the sky. Try exploring this area of the sky with a pair of binoculars. The planets: The stage is being set for the late-July appearance of all five visible or naked-eye pla ...
NORTH SOUTH EAST WEST
... opposite the sun in the sky as seen from Earth. Planets at opposition are visible all night. Saturn is in opposition on June 15. In contrast, conjunction means that two objects appear in the same place in the sky as seen from Earth. Mercury is in conjunction with the Sun on June 21. Planets in conju ...
... opposite the sun in the sky as seen from Earth. Planets at opposition are visible all night. Saturn is in opposition on June 15. In contrast, conjunction means that two objects appear in the same place in the sky as seen from Earth. Mercury is in conjunction with the Sun on June 21. Planets in conju ...
Star Types - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... M < 0.08 Msun Brown dwarf (fusion never starts) 0.08 Msun < M < 8 Msun White dwarf Helium White Dwarf: 0.08 Msun < M < 0.4 Msun Carbon White Dwarf: 0.4 Msun < M < 4 Msun Oxygen-Neon White Dwarf: 4 Msun < M < 8 Msun ...
... M < 0.08 Msun Brown dwarf (fusion never starts) 0.08 Msun < M < 8 Msun White dwarf Helium White Dwarf: 0.08 Msun < M < 0.4 Msun Carbon White Dwarf: 0.4 Msun < M < 4 Msun Oxygen-Neon White Dwarf: 4 Msun < M < 8 Msun ...
Problem set 3 solution
... We can measure the period P and estimate Ms by determining its spectral type with our spectrum. Thus, we know vp . If we could measure vs , then Equation 21 would allow us to solve for Mp . However, what we measure is vrs = vs sin i, the radial component of the star’s velocity, and the orbital incli ...
... We can measure the period P and estimate Ms by determining its spectral type with our spectrum. Thus, we know vp . If we could measure vs , then Equation 21 would allow us to solve for Mp . However, what we measure is vrs = vs sin i, the radial component of the star’s velocity, and the orbital incli ...
Homework #3 MHC Astronomy 100/101/110 Prof. Stage For ALL the
... Figure 2 from Schödel et al., Nature, v.417, 2002, p. 694‐696. This figure shows the observed positions and the best‐fit orbit for the star S0‐2 which orbits the galactic center. (Data is a combination of infrared and radio observations using ground‐based telescopes). a. (4pts) Using the best‐fit ...
... Figure 2 from Schödel et al., Nature, v.417, 2002, p. 694‐696. This figure shows the observed positions and the best‐fit orbit for the star S0‐2 which orbits the galactic center. (Data is a combination of infrared and radio observations using ground‐based telescopes). a. (4pts) Using the best‐fit ...
The Properties of Stars
... P is the orbital period of the stars and a is the average distance between them. Because the masses of stars are very large, but a relatively small multiple of the mass of the Sun, it is convenient to use solar mass units. In that case, Kepler’s third law is ...
... P is the orbital period of the stars and a is the average distance between them. Because the masses of stars are very large, but a relatively small multiple of the mass of the Sun, it is convenient to use solar mass units. In that case, Kepler’s third law is ...
Motions of the Sky—2 Sep Hipparchus measures the moon’s distance~200BC
... The sun (and moon and stars) rises & sets. The sun is higher in the sky in summer than winter. • Planets move with respect to the stars. ...
... The sun (and moon and stars) rises & sets. The sun is higher in the sky in summer than winter. • Planets move with respect to the stars. ...
Powerpoint file
... lists this as an A5 V star, but it is a g Dor variable which have spectral types F0-F2. Spectra confirm that it is F-type 1SIMBAD ...
... lists this as an A5 V star, but it is a g Dor variable which have spectral types F0-F2. Spectra confirm that it is F-type 1SIMBAD ...
Day 2
... Finally, the rate of fusion becomes high enough to establish gravitational equilibrium. At this point, fusion becomes self-sustaining and the star settles into its hydrogen burning, main sequence life. The main sequence phase is the longest phase of a star's life, about 10 billion years for a star w ...
... Finally, the rate of fusion becomes high enough to establish gravitational equilibrium. At this point, fusion becomes self-sustaining and the star settles into its hydrogen burning, main sequence life. The main sequence phase is the longest phase of a star's life, about 10 billion years for a star w ...
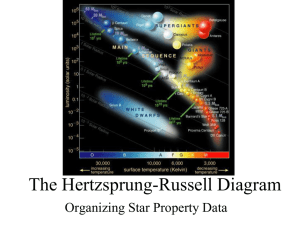
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.