Document
... them together in the same constellation. b) The stars all have nearly the same parallax since they are moving together through space. c) None of them has a measurable parallax since they are mostly within our own Solar System. d) They may have significantly different parallaxes. e) We cannot measure ...
... them together in the same constellation. b) The stars all have nearly the same parallax since they are moving together through space. c) None of them has a measurable parallax since they are mostly within our own Solar System. d) They may have significantly different parallaxes. e) We cannot measure ...
The View From Earth
... 1. Earth: (1) rotates on an axis once every 24 hours; (2) revolves about the Sun with period 365.25 days; (3) accompanies the Sun (and other planets) as it moves relative to other stars in its immediate neighborhood; (4) orbits about the center of the Milky Way galaxy, with period 230 million years; ...
... 1. Earth: (1) rotates on an axis once every 24 hours; (2) revolves about the Sun with period 365.25 days; (3) accompanies the Sun (and other planets) as it moves relative to other stars in its immediate neighborhood; (4) orbits about the center of the Milky Way galaxy, with period 230 million years; ...
Astronomy Merit Badge Workshop
... Using a Star Finder (also called a Planisphere), go outside on a clear night, set the correct time and date, and orient yourself so that you and the Star Finder are aligned to true north.* The visible field in your Star Finder should roughly correspond to what you see in the night sky. Pick out 10 c ...
... Using a Star Finder (also called a Planisphere), go outside on a clear night, set the correct time and date, and orient yourself so that you and the Star Finder are aligned to true north.* The visible field in your Star Finder should roughly correspond to what you see in the night sky. Pick out 10 c ...
The Properties of Stars
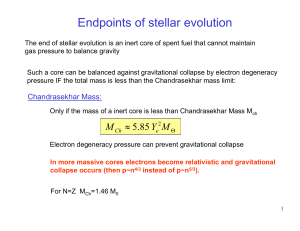
... Mid-mass stars spend their mainsequence lives fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. (50 billion years) When the core runs out of hydrogen, the push outward due to fusion decreases and gravity contracts the star causing fusion to begin in a shell of hydrogen surrounding the core. Shell-hydrogen ...
... Mid-mass stars spend their mainsequence lives fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. (50 billion years) When the core runs out of hydrogen, the push outward due to fusion decreases and gravity contracts the star causing fusion to begin in a shell of hydrogen surrounding the core. Shell-hydrogen ...
The Night Sky September 2016 - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... In the hours before dawn, November gives us a chance to observe meteors from two showers. The first that it is thought might produce some bright events is the Northern Taurids shower which has a broad peak of around 10 days but normally gives relatively few meteors per hour. The peak is around the 1 ...
... In the hours before dawn, November gives us a chance to observe meteors from two showers. The first that it is thought might produce some bright events is the Northern Taurids shower which has a broad peak of around 10 days but normally gives relatively few meteors per hour. The peak is around the 1 ...
It`s Official! Instarmac is one of the UK`s Times TOP 100
... Instarmac Group – the renowned spear head of the Ultracrete, Ultrascape, Ultra Tile and Ultra Floor brands, is pleased to announce that they have officially been named in this year’s TIME TOP 100 companies to work for! The Times’s yearly awards are based on research conducted by Best Companies, wher ...
... Instarmac Group – the renowned spear head of the Ultracrete, Ultrascape, Ultra Tile and Ultra Floor brands, is pleased to announce that they have officially been named in this year’s TIME TOP 100 companies to work for! The Times’s yearly awards are based on research conducted by Best Companies, wher ...
What is a T Tauri star?
... Found in dusty regions- proper motions correlated Off main sequence Sometimes associated with disks and/or outflows ...
... Found in dusty regions- proper motions correlated Off main sequence Sometimes associated with disks and/or outflows ...
Study Guide – Midterm 3
... • Time slows down in strong grav. field…. even GPS systems are affected. ...
... • Time slows down in strong grav. field…. even GPS systems are affected. ...
Document
... Our solar system, which lies in the Milky Way Galaxy, is made up of the Sun, eight (named and proven) planets, and the moons. A scientist’s tool for observing the night sky is called a telescope THE MOON: A moon is a sphere that orbits a planet. Earth has one moon. Moon phases are the differ ...
... Our solar system, which lies in the Milky Way Galaxy, is made up of the Sun, eight (named and proven) planets, and the moons. A scientist’s tool for observing the night sky is called a telescope THE MOON: A moon is a sphere that orbits a planet. Earth has one moon. Moon phases are the differ ...
PS#3
... Lsun is 4x1026 W, so this is about 0.001 times the Sun’s luminosity 4. A radio transmitter on a spacecraft emits a signal at a frequency of 10 Hz. At Earth the signal is received and noted to be at 99,970,000Hz. How fast is the spacecraft moving? Is it receding or approaching? ...
... Lsun is 4x1026 W, so this is about 0.001 times the Sun’s luminosity 4. A radio transmitter on a spacecraft emits a signal at a frequency of 10 Hz. At Earth the signal is received and noted to be at 99,970,000Hz. How fast is the spacecraft moving? Is it receding or approaching? ...
Stars and Nebulae
... emission and reflection nebulae, like the famous Orion Nebula shown in the picture on the right. Emission nebulae are clouds of high temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states (neon light ...
... emission and reflection nebulae, like the famous Orion Nebula shown in the picture on the right. Emission nebulae are clouds of high temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states (neon light ...
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
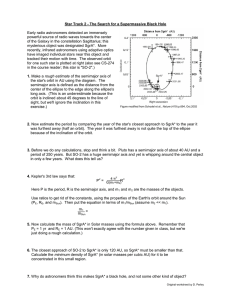
... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tra ...
... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tra ...
Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
... 13. If you plot a very large number of random stars on a HR Diagram measuring their apparent magnitude vs. their B-V magnitude what will you get? a) A nice neat plot with a clear main sequence and clear red giant branch b) A nice neat plot with a clear main sequence but a few red giant branches c) ...
... 13. If you plot a very large number of random stars on a HR Diagram measuring their apparent magnitude vs. their B-V magnitude what will you get? a) A nice neat plot with a clear main sequence and clear red giant branch b) A nice neat plot with a clear main sequence but a few red giant branches c) ...
Star Facts - Dr. Noha MH Elnagdi
... absorbs a color or more of the continuous spectrum, the elements in the atmosphere of a star emits an absorption spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. A absorption spectrum is produced when light from a hot solid or dense gas passes through a cooler gas (which is the atmospheric gases of the ...
... absorbs a color or more of the continuous spectrum, the elements in the atmosphere of a star emits an absorption spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. A absorption spectrum is produced when light from a hot solid or dense gas passes through a cooler gas (which is the atmospheric gases of the ...
Chapter 12: Measuring the Properties of Stars
... 3. It is fairly easy to identify this class of stars, now named Cepheid variables or Cepheids. Each Cepheid has a very constant period of variation, ranging from about 1 day to about 3 months for different Cepheids. 4. In 1908 Henrietta Leavitt discovered that for Cepheids in the Magellanic Clouds, ...
... 3. It is fairly easy to identify this class of stars, now named Cepheid variables or Cepheids. Each Cepheid has a very constant period of variation, ranging from about 1 day to about 3 months for different Cepheids. 4. In 1908 Henrietta Leavitt discovered that for Cepheids in the Magellanic Clouds, ...
January SKY Newsletter 2012
... then reverse direction and wind up back in Leo by early February. This change in position illustrates the retrograde motion of Mars. January is an excellent time to view Mars through a telescope if you want to see the north polar cap and possibly some surface markings. This is also a good time to vi ...
... then reverse direction and wind up back in Leo by early February. This change in position illustrates the retrograde motion of Mars. January is an excellent time to view Mars through a telescope if you want to see the north polar cap and possibly some surface markings. This is also a good time to vi ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.