spring_2002_final - University of Maryland Astronomy
... A. the strength of its magnetic field. B. its rotation rate. C. its mass. D. its location in the galaxy. E. its surface temperature. 37. Both the largest and the smallest galaxies are classified as A. normal spirals. B. barred spirals. C. quasars. D. pulsars. E. ellipticals. 38. Galileo's telescopic ...
... A. the strength of its magnetic field. B. its rotation rate. C. its mass. D. its location in the galaxy. E. its surface temperature. 37. Both the largest and the smallest galaxies are classified as A. normal spirals. B. barred spirals. C. quasars. D. pulsars. E. ellipticals. 38. Galileo's telescopic ...
Ay123 Fall 2011 STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION Problem Set 5
... 1. Use the Saha equation for hydrogen to plot the ionization fraction y as function of temperature T for a density of ρ = 10−10 g cm−3 . Calculate the adiabatic gradient Γ1 = (d ln P/d ln ρ)ad as function of temperature for the same value of ρ. Make sure the temperature range of your plot covers bot ...
... 1. Use the Saha equation for hydrogen to plot the ionization fraction y as function of temperature T for a density of ρ = 10−10 g cm−3 . Calculate the adiabatic gradient Γ1 = (d ln P/d ln ρ)ad as function of temperature for the same value of ρ. Make sure the temperature range of your plot covers bot ...
Test 1, Feb. 2, 2016 - Brock physics
... 6. The wavelength of a source of light approaching the event horizon of a black hole is (a) blueshifted. (b) redshifted. (c) unchanged. 7. About one quarter of material in a nebula is (a) dust. (b) hydrogen. (c) helium. 8. Which one of these stars spends more time in protostar stage? (a) 1 solar mas ...
... 6. The wavelength of a source of light approaching the event horizon of a black hole is (a) blueshifted. (b) redshifted. (c) unchanged. 7. About one quarter of material in a nebula is (a) dust. (b) hydrogen. (c) helium. 8. Which one of these stars spends more time in protostar stage? (a) 1 solar mas ...
HighRedshiftGalaxies
... A systematic survey is conducted according to some property that is sensitive to the on-going rate of star formation. The volume-average luminosity density is converted into its equivalent star formation rate averaged per unit co-moving volume and the procedure repeated as a function of redshift to ...
... A systematic survey is conducted according to some property that is sensitive to the on-going rate of star formation. The volume-average luminosity density is converted into its equivalent star formation rate averaged per unit co-moving volume and the procedure repeated as a function of redshift to ...
Photosphere
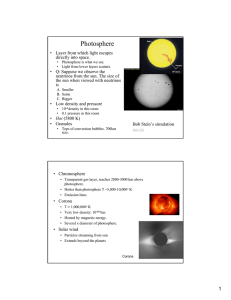
... Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. Luminosity (Lsun) Î ...
... Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. Luminosity (Lsun) Î ...
lecture
... •Produces a two-dimensional map of the gas in the system, but in Velocity Space not the Cartesian Space that we are used to… ...
... •Produces a two-dimensional map of the gas in the system, but in Velocity Space not the Cartesian Space that we are used to… ...
Major Stars of the Orion Constellation
... [Wiscweb] “Astronomers now know that these regular brightness variations are caused by changes in the actual size of the star's atmosphere. According to Robert Burnham, Jr. (1931-93), Betelgeuse is the only marked variable among the first magnitude stars as well as the 11th brightest star in the sky ...
... [Wiscweb] “Astronomers now know that these regular brightness variations are caused by changes in the actual size of the star's atmosphere. According to Robert Burnham, Jr. (1931-93), Betelgeuse is the only marked variable among the first magnitude stars as well as the 11th brightest star in the sky ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
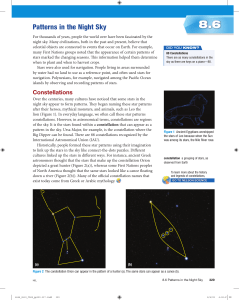
... Familiar winter constellations like Orion begin to set in the west with the onset of darkness, bringing the spring constellations of Leo, Virgo, Coma Bernices and Ursa Major into prominence. It is within these that hosts of galaxies reside. The North Galactic Pole, the point in the sky directly over ...
... Familiar winter constellations like Orion begin to set in the west with the onset of darkness, bringing the spring constellations of Leo, Virgo, Coma Bernices and Ursa Major into prominence. It is within these that hosts of galaxies reside. The North Galactic Pole, the point in the sky directly over ...
11.3.1 Grade 6 Standard 4 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1
... Betelgeuse Polaris (North Star) Sirius (Dog Star) ...
... Betelgeuse Polaris (North Star) Sirius (Dog Star) ...
Great Migrations & other natural history tales
... As seen in the simulation of molecular cloud fragmentation, brown dwarfs (smallest objects simulated as white points) form in large numbers, and are mostly dispersed throughout the Galaxy afterwards. Sometimes, they are found as orbital companions to stars (not frequently, hence the term “brown dwar ...
... As seen in the simulation of molecular cloud fragmentation, brown dwarfs (smallest objects simulated as white points) form in large numbers, and are mostly dispersed throughout the Galaxy afterwards. Sometimes, they are found as orbital companions to stars (not frequently, hence the term “brown dwar ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... context of blackbody radiation and temperature determination. 2: Describe the evidence for the particle nature of light and indicate how the energy per photon is related to the wavelength and frequency in the wave model. 3: State Kirchhoff’s three laws of spectral analysis and indicate what informat ...
... context of blackbody radiation and temperature determination. 2: Describe the evidence for the particle nature of light and indicate how the energy per photon is related to the wavelength and frequency in the wave model. 3: State Kirchhoff’s three laws of spectral analysis and indicate what informat ...
Chapter11
... Previous chapters have used the basic principles of physics as a way to deduce things about stars and the interstellar medium. All of the data we have amassed will now help us understand the life stories of the stars in this chapter and ...
... Previous chapters have used the basic principles of physics as a way to deduce things about stars and the interstellar medium. All of the data we have amassed will now help us understand the life stories of the stars in this chapter and ...
Where do Stars Form ?
... Luminosity-Mass Relation L∗ ∝ M∗4 Main Sequence is also a Mass Sequence Low Mass Stars: cooler & fainter longer MS lifetimes High Mass Stars: hotter & brighter shorter MS lifetimes ...
... Luminosity-Mass Relation L∗ ∝ M∗4 Main Sequence is also a Mass Sequence Low Mass Stars: cooler & fainter longer MS lifetimes High Mass Stars: hotter & brighter shorter MS lifetimes ...
The eleventh annual AST poster session - Home
... map or GPS system. The facts and knowledge we have today concerning the movement of stars in the sky, allow us to use tools such as a sextant to find the true altitude, mathematics, logical thinking and nautical or other almanacs (to know the positions of the heavenly bodies). Therefore, it is possi ...
... map or GPS system. The facts and knowledge we have today concerning the movement of stars in the sky, allow us to use tools such as a sextant to find the true altitude, mathematics, logical thinking and nautical or other almanacs (to know the positions of the heavenly bodies). Therefore, it is possi ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.